Chapter: Obstetric and Gynecological Nursing : Normal Pregnancy
Management of 1st Stage of Labour
1. Management of 1st Stage of
Labour
Is the care given through out the 1st stage of labour
A. Adimission procedure
Well coming the mother and her partner
On Arrival
·
Greet the mother
·
Introduce your self
·
Inform relative to wait
B. Admission criteria
·
Check- show
·
rupture of membrane
·
regular uterine contraction with progressive cervical dilatation
History
·
Information from the mother
·
Ask the mother on set of contraction
·
Rupture of membranes / passage of liquor
·
Show or any other bright red bleeding
Physical examination
- The general condition
Exhausted, anemic, pain, dehydrated general edema Vital sign: Blood
Pressure, Temperature, pulse, respiration
Abdominal examination
·
Inspection
·
Palpation lie, presentation, attitude engagement
·
Fundal height
·
Auscultation fetal heart rate & rhythm
Vaginal examination
To cheek if the mother is in labour
. cervical dilatation
. Membrane intact or not
To assess progress of labour
·
Station, Position
·
presenting part; moulding, caput and station
Investigations
Hematology
. Hematocrit
. Hemoglobine
. Blood Group, Rh, cross-
match
Urine analysis
. Protein (Albumin)
. Sugare
. Ketone
Write on patient chart and inform relatives. Use partograph and record on it.
Emotional support
1. A good nurse will give confort, relieve pain,
make strength, prevent exaustion.Maintain cleanliness, asepsis & antisepsis
during labour.
Prevent complications, recognize early & promptly act when
complication occurse unitl the arrival of the docter.
These principles are not confined to labour only, for the management of labour begins during the AnteNatal period, by building woman's heath gaining her confidence, promoting encourage & supervise. Detect abnormalities which may adversely affect labour. The nurse must handle child birth with sensitivity and compassion because the emotions of the woman in labour deeply influence her reaction to discomfort & pain with are a contrn butany factor in determining the amount of physical and mental exhaustion she will experience.
Fear of labour
Child birth and bring occasion - the husband is encouraged to stay with
his wife this gives comfort with happiness to both, she needs the
companionship, love with sympathy of those who are dean to her. Influence of
the mid wife.
The qualities of a good mid wife are sympathetic understanding, patient
& kind because women in labour are sometimes irritable not only must the
midwife desire to give emotional support, she must demonstrate for her
compassion by words & actions.
Companionship is melded - the companionship of the woman in labour needs
the professional presence of the nurse. ExampleCommunication style eg. No loud
talking & noise
Relief of pain & promotion of comfort
Pain exhausts the woman physically & emotionally so it must be
reviled by every obstetrically safe means. The midwife by her kindly confident
bearing & professional proficiency has an assuring beneficent influence.
Back rub and explanation of the labuor process is very much important in pain
relieving.
Fewer drugs are now being prescribed during labour. Eg. pethedine,
analgesia.
Drug choice - if apprehensive a tranqulezer, if tired ahyponotic, for
discomfort & pain an analgesic & sedative.
Diet during labour
During early labour tea & digestive biscuit can scrued.
Avoid dehydration. Prolonged labour can present serious problem. If
dehydration present give I.V infusion 5 or 10 % Dextrose in water and also
Glucose 40%.
Attention to the bladder
A full bladder will prevent the head from engaging, empty bladde revery
2 hours.
Recordings:-
1. Half hourly- maternal pulse, contractions for length, strength and frequency, FHB
2. Every 1 1/2 - 2 hours check bladder
3. Every 4 hours – B/P. Temperature, abdominal
examination for descent,V.E, urine test acetone, albumin
Psychological methods of pain relief
The personality of the mid wife is of paramount impurtancy in handing
women in labour. Many midwives have by their sympathetic understanding manner
unknowingly used psychological mortheds of pain relief.
Cleanliness Antisepsis, Asepsis
The woman must be protected by every available means from infection
which may cause ill-health with loss of life. The woman is venerable to
infection at this time.
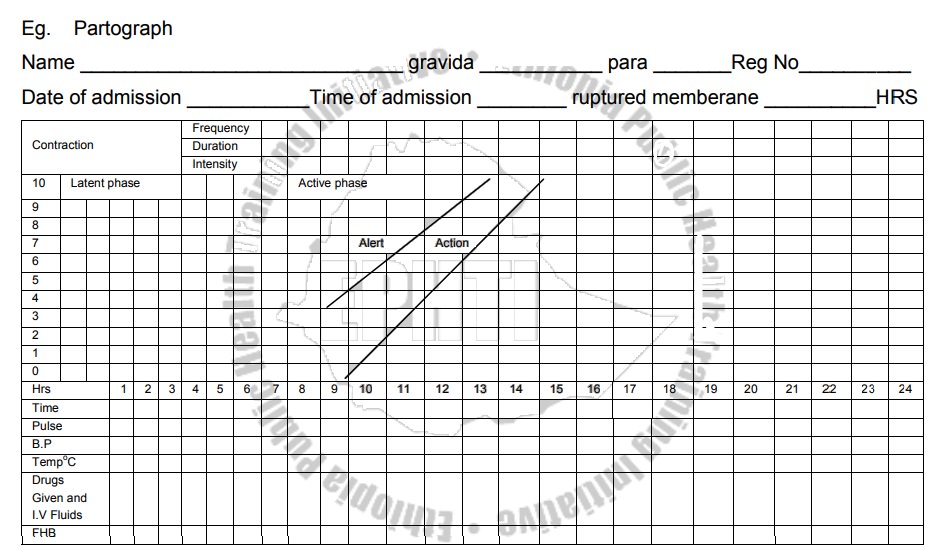
The Partograph
PARTOGRAPH – Managerial tool for the prevention of prolonged labour:-
Measuring progress of labour in relation to time.
Observations charted on partograph
a) The progress of labour with time
- Cervical dilatation
-Descent of fetal head
b) Descent: abdominal palpation of fifths of head felt above the pelvic
brim.
Uterine contraction
·
Frequency per 10 min
·
Duration /shown by different shading/
c) The fetal condition
-
Fetal heart rate
·
-Memberanes & liquor
·
-Moullding of the fetal skull
Grading:
·
normal- space felt between the edged
of parital bone inthe sagital suture.
·
mild- the egde of parital bone comes
very closer at thesagital suture.
·
moderate- the edge of the parital bone
over lap at sagitalsuture but can be easly separated.
·
severe- over lap of the bones and not
separable.
c) The maternal condition
·
Pulse, B/P temperature
·
Drug and IV fluids
·
Urine /volume, protein, acetone/
·
Oxytocin regime
The progress of labour
The 1st stage is divided in to the
latent and active phases
Latent phase- slow period of cervical
dilatation from 0-.2cmsand also it is the period of gradual shortening of the
cervix.
Active phase-faster period of cervical dilatation
from 3-10cmsor full cervical diltation.
Starting the partograph
A partograph chart must only be started when a woman is in labour you
must be sure that she is contracting enough to start a partograph.
In the latent phasec truction must be 2 or more in 10 minute each
lasting 20 second or more.
In the active phase contractions must be 2 or more /10minutes each
lasting 20 second ormore. There difference is in dilatation of cervix.
In the center of the partograph there is a graph. Along the left side
are numbers 0-10 against squares. Each square represents 1cm dilatation. Along
the bottom of the graph are numbers 0-24: each square represents 1 hour.
Dilatation of the cervix is measured in centmeter. The dilatation of the cenvix
is plotted with an "x". The 1st V.E on admission includes a pelvic assessment
& the findings are recorded. The V.E are made ever 4 hrs unless
contraindicated. However in advanced labour women may be assessed more quickly,
particularly the multipara.
Plotting cevical diatation when admission is in the active phase.When a
woman is admitted in the active phase the dilatation of the cervix is plotted
on the alert line and the time written directly under the X in the space for
time. If progress is setisfeutory, the plotting of cervical dilatation will
remain or to the left of the alert line.
The latent phase normally should not take longer than 8hrs. When
admission is in the latent phase, diltation of the cervix is plotted at O time.
Transfer from latent to Active phase
Plotting cervical dilatation when admission is in the latent phase &
goes in to active phase.When labour goes in to the active phase plotting must
be transferred by a broken line to the alert
line.
The recordings of cervical dilatition and time are plotted 4 hrs after
admission then transferred immediately to the alert line using the letters
"TR" leaving the area between the transferred recording blank. The
broken transfer line is not part of the process of labour.
Points to remember
·
The latent phase is from 0-2cm dilatation & is accompanied by
gradual shortening of cencix. It should normally not last longer than 8 hrs.
·
The active phase is from 3-10cms & dilatation should be at the rate
of at least 1cm/hr.
·
When labour progresses well, the dilatation should not move to the rt of
the alert line.
·
When admission to hospital takes place in the active phase the cervical
dilatation is immediately plotted in the alert
line
·
When labour goes from latent to active phase plotting of the dilatation
is immediately transferred from the latent phase to the alert line.
Descent of the Fetal Head
For labor to progress well, dilatation of the cervics should be
accompanied by descent of the head. However, descent may not take place until
the cervics has reached about 7cms dilatation. Descent of the head is measured
by abdominal palpation and expressed interms of fifths above the pelvic brim.
Method – by abdominal palpation identify the anterior shoulaer of the
fetus. Ther distance between this point and the pelvic brim is measured in
fingers and expressed interms of fifth.
E.g 3 figer between the two point indecates
Recording contractions on the partograph
Key points on plotting the partograph
Memberane:
I - Intact
R-Ruptured
A.R.M - Artificial Rupture of memberane
Colour of liquer:
M- Meconium stained
C-clear
A - Absent
Moullding - degree of overlap
Normal separation /can feel sutures/ -
Bones meeting +
Over lapping can be pushed back ++
Over lapping can't be separated +++
Abnormal fetal heart rates
A heart rate greater than 160/minute is tachylardia and a heart rate
less than 120/minute is bradycardia and thse conditions may indicate fetal
distress. If abnormal FHB is heard, listen it every 15 minutes for at least 1
minute immediately after contraction. If the fetal heart remains abnormal over
3 observations action should be taken urless delivery is very close. A heart
beat of 100 or lower indicates very sever distress & action should be taken
at once.
·
Moving to the right of the alert line means warning. Transfer woman from
health center to hospital.
·
Reaching the action line means possible danger. Decision needed on
further management. /usually by obstetrician/.
Vaginal Examination in Labour
When Doing Vaginal Examination Always Remember:-
·
The vaginal is not a sterile cavity, - the Uterus is. Every vaginal
examination increases the danger of intrauterine infection, if carelessly
performed.
·
A vaginal examination is uncomfortable and embarrassing for the patient.
·
Careful abdominal examination gives a lot of information. Do it always
before vaginal examination.
· When doing a vaginal examination, find out all the information you can, this may save it having to be repeated.
Indications
·
When in doubt about the presentation, dilatation, or position and to
assess progress.
·
To assess the shape and size of the pelvis.
·
To know the cause in fetal or maternal distress.
·
When the memberanes rupture and the head is high or there is
Malpresentation, to make sure there is not prolapsed cord.
Information: To be got on Vaginal Examination
1. Presenting Part
- Presentation
- Level of presenting Part
·
Caput
·
Sutures and Fontanelles.
·
Overlapping or moulding
2. Membrens
Intact - Bulging or flat?
Rruptured - Colour of liquar
3. Cervix:
RIPE - firm or soft
EFFACEMENT - long or short - taken up.
OEDEMATOUS- thick or thin
APPLIED to the presenting part- Loose or well applied.
DILATION- Measure in cm.
4. Vagina:
Lax or tight, Warm or hot, Moist or Dray
5. Pelvis:
Cavity, sacral promontory
Curve of the sacrum, iscaheal spine
Lateral pelvic side walls- parallel or convergent
Now Co-relate your findings, after recording them and determine the
stage of labour.
Related Topics