Chapter: Obstetric and Gynecological Nursing : Normal Pregnancy
Anatomical Varations of the Placenta and the Cord
Anatomical Varations of the
Placenta and the Cord
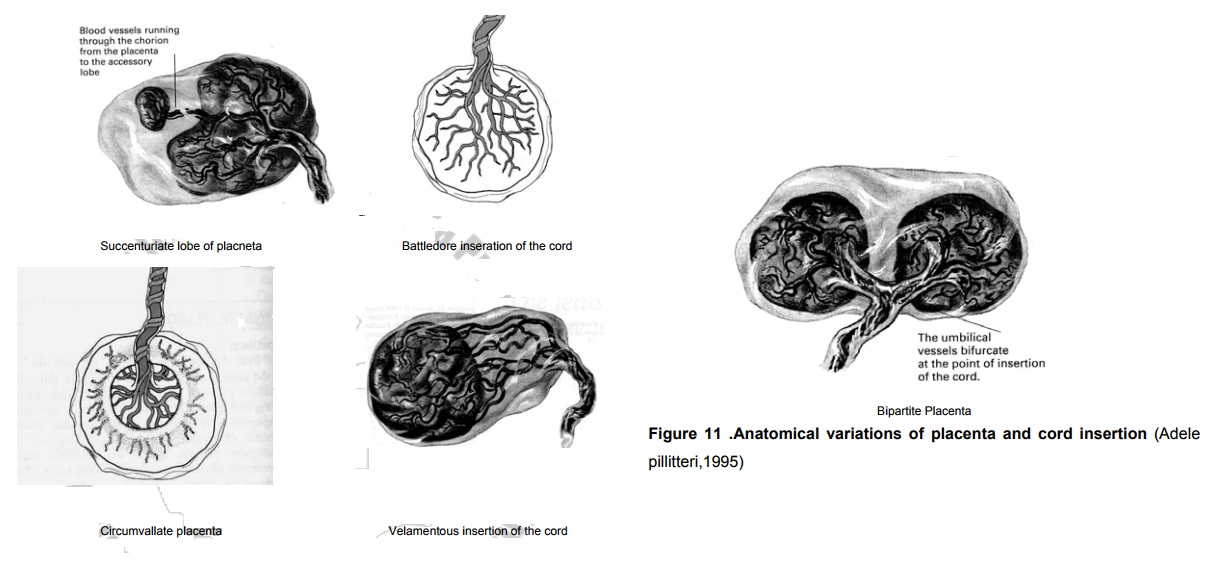
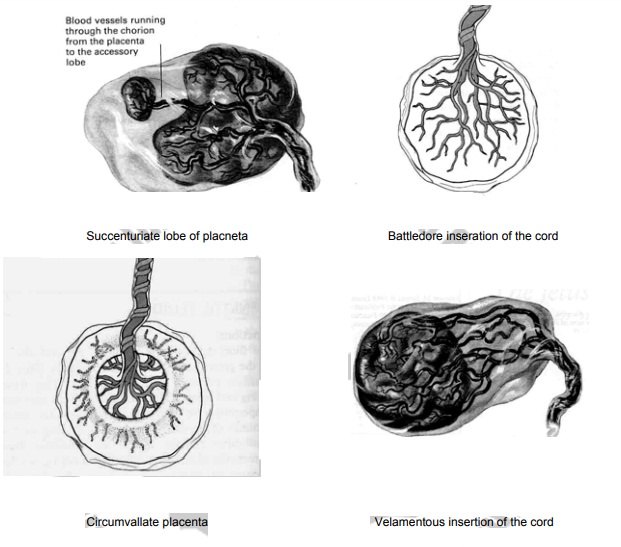
Succenturiate lobe of placneta:
A small extra lobe is present, separate from the main placenta and
joined to it by blood vessles which ran through the memebrane to reach it.
The danger is that this small lobe may be
retained in utroafter delivery, and if it is not removed it may lead to
haemorrhage and infection.
Identification On inspection, the placenta will
appear torn atthe edge, or torn blood vessles may extend beyond the edge of the
placenta.
Circumvallate placenta In this situation an opaque ring
isseen on the fetal surface. It is formed by a doubling back of the chorion and
amnion.
Danger may result in the memberanes
leaving the placentanearer the center instead of at the adge as usually.
Battledore inseration of the
cord The
cord in this case isattached at the very edge of the placenta in the manner of
the table tennis bat.
Danger Likely it is detached up on
applying traction duringactive management of the third stage of labour.
Velamentous insertion of the
cord It
is inserted into thememberans some distance from the edge of the placenta. The
umblical vessles run through the memberanous frorm the cord to the placneta.
Danger The vessles may tear with
cervical dilatation andwould result in sudden blood loss.
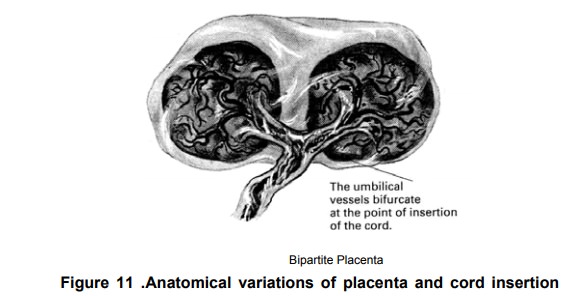
Bipartite Placenta Two complete and separate lobes
arepresent, each with a cord leaving it. The bipartite cord joins a short
distance from the two parts of the placenta.
Danger-The extra lobe may retained
during delivery.
A tripartite Placenta is similar but with three distinct lobes
Placenta infarction
Placental infarction occurs when the blood supply to an area of the
placenta is blocked and tissue necrosis results. It appears most commonly on
the maternal surfaces and most often associated with vascular disease of the
utero- placental unit secondary to maternal hypertension.
As the infarct at area becomes necrotic, fetal circulation is reduced
because blood flow through the placenta will decrease. However, if the
circulation through the rest of the organ is sufficient, a fetus may survive
when as much as 20% to 30% of the placenta is infracted. Placental infractions
can be treated.
Placental tumors (Haemongiomata of the Placenta)
These tumors are relatively common, being found in approximately 1
percent of all placentas. Most tumors are small and without clinical
significance but a few are large and associated with hydraminious, antepartum
hemorrhage and premature labour.
The Umblical Cord
The umblical cord or funis extends from the fetus to the placenta and
transmits the umblical blood vessles, two arteries and one vein. These are
enclosed and protected by Wharton’s jelly, (a gelatious substance formed from
mesoderm). The whole cord is covered in a layer of amnion continuous with that
covering the placenta. The length of the average cord is about 50cm. A cord is
considered to be short when it measures less than 40cm.
Related Topics