Chapter: 11th Political Science : Chapter 3 : Basic Concepts of Political Science
Liberty
LIBERTY
Introduction to Liberty
You have liberty to enjoy the freedom sanctioned as
per law. The business of law is to safeguard the liberty of an individual. In
the safety of an individual lies the status of one’s freedom. The law and
liberty are twins and are connected to each other to sanction equal treatment
equally for all. Here we all know that, it is the objective of the state to
safeguard the liberty of its citizens.
Do you know something that the
law of the state propels a reasonable restriction on every individual? That
doesn’t mean the privileges of citizens are compromised. The main objective of
the state is to protect, What is due for him as his right. And in the process
care for the equality of an individual becomes an agenda of state.
Shall we take a journey into the
world of liberty, we intend to enjoy
In a classroom setting, the
liberty of a student varies. In the view of some student, some teachers are
strict and some are liberal, in terms of liberty and freedom he/she enjoys in
the classroom. Teachers have a privilege to sanction reasonable restriction
against student’s undue advantage in a classroom. The sanction of reasonable
restriction by teacher is actually for the smooth conduct of a student and as
well for the effective learning in the classes. Understanding the concept of
liberty begins in the classroom by the conduct and attitude of student towards
his teacher and his classmates. Raising questions to clarify doubts to his
class teacher is his/her right, but the sanction of it becomes liberty. Liberty
is just the sanction of law and the restrictions imposed are also a kind of
liberty. Conducive learning environment of classroom, conditions the student to
understand the meaning and the purpose of liberty.
Learning Objectives
·
The importance of
liberty is introduced by briefing the meaning
and various views of exponents of liberty.
·
While learning the
classification of liberty students, are actually
introduced to different forms of freedom and they way state views liberty.
·
The concept of
liberty is so important that it helps every citizen
realize the value of freedom in a society where state is empowered with
constitutional authority.
·
Students are given
a direction here that some form of restrictions such
as law are also a form of liberty.
·
The safe guards of
liberty especially democracy and independents of
judiciary are few key factors that inculcates the value of liberty.
Liberty remained an essential
element for both man and state for progress. History records very well the
cruelty of absolute monarchy that ignored the claims of liberty in ancient and
medieval ages of England. People could no longer tolerate and rose in revolt
against the absolute monarchy. The struggle continued until Emperor John had to
bow down and ensure freedom for his subjects. Attempt of emperors after Tudor
and Stuart, and the continued absolute monarchy resulted in civil war. King
Charles was beheaded and even during the period of Cromwell people could not
attain freedom.
French Republics
refer to a succession of republics after the proclamation of the French
revolution in 1792. There have been Five republics in the history of France:
French first Republic (1792-1804), French Second( 1848-1852), Third Republic
(1870-1940), Fourth Republic(1946-1958), Fifth Republic was formed on October
5, 1958. The Fifth Republic emerged replacing a weak and factional
parliamentary government with a stronger centralized democracy.
This resulted in the famous
“Glorious revolution” in England in the year 1688, containing the absolute
monarchy for some period and later led to the outbreak of French revolution in
1789.
However it had not given a
desired liberty. The successors of Napoleon behaved like monarchs. The fall of
Napoleon III, resulted in establishing the
Third Republic. After the fall of
Third Republic in 1940 and Fourth Republic in 1958, Fifth republic was
established. Struggle against countries that colonized got liberated after a
long struggle for independence. Italy in nineteenth century and India in
twentieth century made untold sacrifices for attaining national liberty.

Historical Context
v Response
to the rationalism of the Enlightenment
v Response
to the French Revolution (1789)
v The
revolutionaries in France fought for “liberty, equality, and fraternity”
v Ideas of
the French Revolution influenced writers in England — they were inspired by the
fight for democracy and the common man
v Response
to industrialism
v Longing
for nature and simplicity
Meaning Of Liberty
The term ‘liberty’ has been
derived from the Latin word ‘Liber’ which means free from all shackles. The
Latin word ‘Liber’ denotes the absence of all restraints. It means one can do
whatever one likes, regardless of all conditions. Liberty does not permit a person
to do whatever one likes. The basic fact of liberty is that law is the
condition of liberty. According to Professor Barker “Liberty is possible only
in an ordered state, a state where the legal and political aspects of
sovereignty coincide or nearly coincide. Laski believes that ‘Historical
experience has evolved for us rules of convenience which promote right living
and to compel obedience to them is a justifiable limitation of freedom.”
Exponents views on Liberty
v “Liberty
is the positive power of doing and enjoying those things which are worthy of
enjoyment and work”-Gettel
v “Liberty
is the freedom of the individual to express without external hindrances to
personality”-Professor G.D.H. Cole.
v “ Liberty
does not means the absence of restraint but it lies in development of liberty”-
Mahatma Gandhi
v “Without
right then cannot be liberty, because without rights, men are the subjects of
law unrelated to the needs of personality”.-Harold. J. Laski
Two Phases Of Liberty
Positive liberty: Positive liberty mean freedom to do something that the individual should have rights and
opportunities to develop his personality.
Negative Liberty: For J.S. Mill liberty means Negative
liberty He submitted that there should not be any restraint imposed upon man
and his actions. He also asserted that there should not be any hindrance in the
path of man.
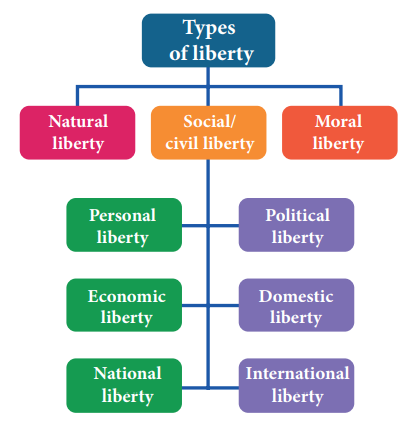
i. Natural Liberty
The concept of Natural liberty
indicates unrestrained freedom to do what ever one likes.
Natural liberty means absence of
all restraint –an unrestrained freedom to do whatever one likes.
“Everyone has a vague notion of
liberty of some kind and a desire for it, but among ten people using the word,
perhaps no two will be able to say exactly what they mean, or if they do so say
it, win agree with each other in their definitions. This general unscientific
use of the word we may call Natural Liberty.”-Professor
R.N. Gilchist.
Arguments On Liberty
JohnLocke: In the state of Nature people enjoyed the rights to
life, liberty and property.
Critic: It is absolutely incorrect because it is only the state
that guarantee the enjoyment of these rights . In the state of nature people
possessed not rights, but the power of animal.
Rousseau: “Man was born free, but every where he is in
chains”
Critic: Rousseau does not appear sound because there is no scope for the growth of human personality.
According to social contractualist, liberty looks like a license than a
liberty. If he is allowed to do whatever he likes, there will be only chaos in
the society.

ii. Civil Liberty
The concept of civil liberty
reflects “Rule of law” civil liberty indicates the liberty man enjoyed in the
society it prevails in the state. It denotes the enjoyment of our rights within
the limits of law. The protection of civil liberty is guaranteed by the laws of
the state.
iii. Political Liberty
The concept of political liberty
means liberty of citizen to participate in the political life and the affairs
of the state. Leacock calls
political liberty as constitutional liberty and Gilchist consider
political liberty as a concept synonymous with democracy. Political liberty
includes minimum rights. These rights are the right to vote, the right to
contest elections, the right to hold public views and criticize the government
and right to petitions.
iv. Personal Liberty
The concept of personal liberty
means the availability of those conditions in which the individual can act as
he pleases without being under any type of arbitrary and illegitimate
restraint. It also means that every individual has the right not to permit any
other individual to interfere in the affairs of his personal life . Every
individual should have the the liberty to dress, food, standard of living,
marriage and education of children etc. The state should not interfere in the
personal matters of the individual such liberty is essential for the free
development of human society .

v. Economic Liberty
The concept of economic liberty
means the liberty to earn one’s daily bread. Beyond the distingtion of caste,
colour, creed and gender every individual should have liberty to earn his daily
bread by fair means.
“By economic liberty I means
security and the opportunity to find reasonable significance in the earning of
one’s daily bread I must be free from the constant fear of unemployment and
insufficiency which perhaps more than other inadequacies’, sap the whole
strength of personality . I must be safeguards against the wants of tomorrow” - Harold.J.
Laski
vi Fiscal Liberty
According to this principle;
there should be no taxation without representation. It was the slogan given by
middle classes who claimed that they should be allowed to decide as to how and
on whom their money was to be spent. Both civil and fiscal liberty were related
to property and the rights of their owners . It was felt by the middle classes
that without fiscal and civil liberty they would not be able to exist and be
exploited by arbitrary rulers.
vii. Domestic Liberty
It covers equal right for women
and children. They need to be protected against maltreatment, cruelty and
exploitation. They were also have the right to education.
viii. National Liberty:
It means the liberty of the
nation or the country. National liberties exist where the nation or the
community is independence and sovereign. National liberty can otherwise also
called as National sovereignty. Every nation wishes to stay independent and
without this independence the progress of the nation or the state is not
possible. Liberation remains an ultimate slogan for all those nations enslaved
by imperialistic forces. Nations colonialized by imperialist force struggled
against foreign empire until freedom is restored.
The struggle of Italy against
Austria, England against Hitler and Napoleon struggle of
African counties against imperialist forces and Indians struggle against
England are few example where struggle was made ultimately for restoring the
liberty of the Nation. When India was attacked by China in 1962, and by
Pakistan in 1965 and 1971 the Government of India made all efforts to safeguard
the freedom of nation.
‘Liberty does not descend upon a
person. People must raise themselves to liberty. Liberty is a blessing that
must be earned in order to be enjoyed’ engraved on the building of central
secretariat New Delhi .
ix. International Liberty
This concept implies peace and
international cooperation and the formation of world federation of states.
Liberals were opposed to the use of force as an instrument of national policy.
capitalism needed peace and international cooperation for the free flow of goods
from one country to another and they needed all political and other barriers to
be removed that stood in the way of the development of world resources.
Perspective of various ideologies on Freedom by Andrew Heywood
Liberals give priority to
freedom as the supreme individualist values. While
classical liberals support negative freedom, understood as the absence of
constraints or freedom of choice, modern liberals advocate positive freedom in
the sense of personal development and human flourishing.
Conservatives have traditionally endorsed a weak view of freedom as the willing
recognition duties and responsibilities, negative freedom posing a threat to
the fabric of society. The new right however, endorses negative freedom in the
economic sphere, freedom of choice in the market place.
Socialists have generally understood freedom in positive terms to refer to self- fulfillment achieved
through either free creative labour or cooperative social interaction. Social
democrats have drawn close to modern liberalism in treating freedom as the
realization of individual potential.
Anarchists regard freedom as an absolute value believing it to be irreconcilable
with any form of political authority. Freedom is understood to mean the
achievement of personal autonomy, not merely being ‘left alone’ but being
rationally self-willed and self-directed.
Fascist rejected any form of liberty as nonsense. ‘True’ freedom, in contrast,
means unquestioning submission to the will of the leader and absorption of the
individual to the national community.
Ecologists particularly deep ecologist, treat freedom as achievement of
oneness, self-realization through the absorption of the personal ego into the
ecosphere or universe. In contrast with the political freedom, this is
sometimes seen as inner freedom, freedom as self-actualization.
Religious fundamentalist see freedom as essentially an inner or spiritual
quality. Freedom means conformity to reveal the will of god, spiritual
fulfillment being associated with submission to religious authority.
Heywood, Andrew.
(2004) Political Ideologies: An Introduction , 4th ed. New York: Macmillan
How are liberty, sovereignty and law are related to each other?
Anarchy doesn’t mean chaos or
disorder, it means freedom from an oppressive centralised authority with a
monopoly on force.
Liberty does not mean the
complete absence of laws. Liberty exist only in a state in order. The state
makes law and the sovereign state operates through these laws. There exist a
close relationship between liberty, sovereignty and law. The anarchist and
syndicalists wanted to abolish the states. They are of the opinion that if
state is more powerful then individual liberty will also be curtailed.
Individualist views
They regarded the control of the
state as harmful to the individual and therefore supported the confinement of
the authority of the state. Though this doctrine resulted in dangerous
consequences in England. It is now universally accepted that laws are the
protectors of liberty. Liberty ceases to exist in the absence of law.
Idealist view
Liberty ceases to exist in the
absence of laws. Obedience to law is obedience to real will according to
Idealist.
How does law protect liberty?
i.
Provides congenial atmosphere for
the smooth running of civilized life in society. Law punish criminal and
defends the rights of the individuals.
ii. Law
guarantee the enjoyment of individual rights and duties and protect them. The
state punishes the individual who causes harm to others and hinders path of
others .
iii. Constitution
is custodian of liberty and it confines the authority of the state and protects
the fundamental right of the people.
How liberty is safeguarded?

i. Democracy
Liberty is safer in democracy
than in any other form of government. Democratic governmentisthegovernmentofthepeople
where as in other forms of government like monarchy and dictatorship all power
are centralized in the hand of one person or a group of person. Opposite
parties are given due respects in democracy and criticism of government is accepted
and tolerated in democracy.
ii. Constitutions
Authority of the state dwells in
the constitution of the respective nation.
Let us read the Preamble of our
Constitution very carefully and understand the meaning of each of its key
words.
The Preamble of Constitution
reads like a poem on democracy. It contains the philosophy on which the entire
Constitution has been built. It provides a standard to examine and evaluate any
law and action of government, to find out whether it is good or bad. It is the
soul of the Indian Constitution.

iii. Fundamental rights
Fundamental rights confines the
authority of the state. Fundamental rights assure us that the state cannot
interfere in the matters of personal life .
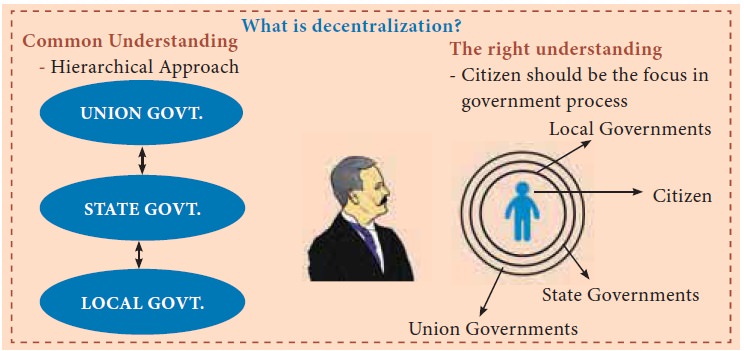
iv. Decentralization of powers
Decentralization of power is
required for the safeguard of liberty. Power should be divided into central,
provincial and local government and such decentralization leads to efficient
administration.
v. Independent judiciary
Safeguard of Liberty depends upon
the independence of judiciary. It should be free from the control of the
executive. In the communist countries or in the countries which have
dictatorship, fundamental rights are given to the people but judiciary is not
free from the influence of the executive. In such countries, the safeguard and
security of fundamental rights, liberty and constitution is not possible.
INDEPENDENT JUDICIARY
The constitution of India makes
provisions for the independence of judiciary because only independent judiciary
can safeguard the rights and liberties of the people, can protect the supremacy
of the constitution
i. An impartial method has been
adopted for the appointment of the
judges
ii. High qualifications have been
fixed for the judges
iii. The judges of
the Supreme Court stay in office till 65 years of age and of High courts till
62 years of age
vi. Economic security
Economic security is a condition
to liberty.“Where
there are rich and poor, educated and uneducated, we always find a relation
of master and servant”. – Laski
Poverty is not an accident. Like
slavery and apartheid, it is man-made and can be removed by the actions of
human beings. - Nelson Mandela
vii. Rule of law
Rule of law is established in
England, USA and India Rule of law mean that there should not be any
distinction of caste and creed colour and race . In the eyes of law all are
equal and all are liable to be punished if they commit crime.
The rule of law was further
popularised in the 19th century by British jurist A. V. Dicey. The concept,
if not the phrase, was familiar to ancient philosophers such as Aristotle,
who wrote “Law should govern”.
viii. Political education and eternal vigilance
Permanent safeguard of liberty is
possible. Educated are acutely aware of their rights and duties. Eternal
vigilance is the prices of liberty and in it absence one can act according to
his will whenever the government crosses the barrier of its authority and
interference in the personal life of the people, may rise in revolt against the
government.
“It is the proud spirit of the
citizens, less than the letter of the law, that is the most real safeguard” - Harold . J. Lask
Related Topics