Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Political Science History goverment rule laws life Higher secondary school College Notes
Kinds or Types or Classification of Law
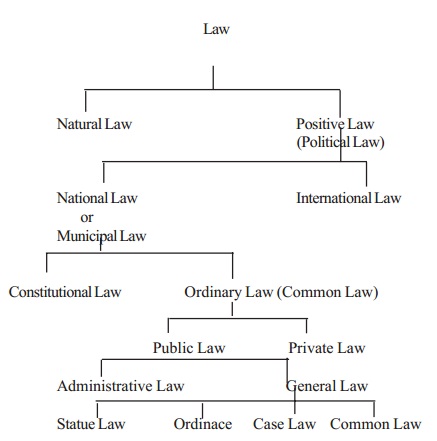
KINDS OF LAW :
Given below is a classification of law by Mac Iver. The Meaning of the above types of law is as follows.
1. Natural law :
Natural Law is often thought to be as divine law. It is not written anywhere; it is found in the minds of men. It is abstract and not created by any human agency or authority. Natural law has its sanction in respect for or fear of some super power.
2. Positive Law :
Positive law is called as political law. It is created by human agency. It is written in nature. It is concrete and can be understood as it is sovereign power of the state. It is determinate and its violation leads to punishment.
3. National Law :
A law formulated by the sovereign authority and applicable to the people living within its territorial jurisdiction is called national law. It determines the private and public relations of the people living in a state.
4. International Law :
International law regulates the conduct and relations of various status in the world. It differs from national law both in the method of creation and enforcement.
The term ' International Law' was coined by Jeremy Bentham in 1780, to designate what had been called as the 'law of nations.'
Wheaton defines international law as 'the body of rules which by custom or treaty civilized states regard as binding upon themselves in their relations with one another, and whose violation gives the injured party a legal right to stress.'
It is generally accepted that, international law is merely a positive morality. Natural law or positive morality is that, the conventional law arising by the voluntary agreement among states.
The only means by which these rules can be enforced are self - help and intervention on the part of other states, which sympathises with the wronged one.
These may not always be effective for the vindication of international law, but it is the task of statesmanship to enlist might on the side of right and thus achieves the triumph of international justice.
5. Constitutional Law :
It is the basic law according to which the activities of the government in a state are conducted. It defines and explains the structure of government and the relationships between the various organs of the government.
6. Ordinary Law :
The law according to which the people in a state, are governed is called ordinary law. It includes all the municipal laws excluding the constitutional law.
It is enacted by the legislature. It is subordinate to the constitutional law.
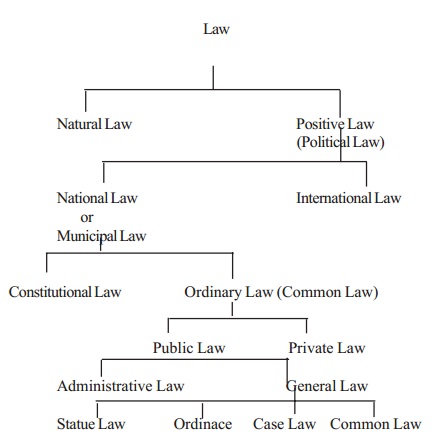
7. Public Law :
Public law deals with relations between the individuals and the state. It covers all forms of crime. In cases involving public law, the state is a party to the case.
8. Private Law :
It deals with the relations between one individual and another. It covers matters such as libel, slander, property, marriage, inheritance etc.
9. Rule of Law :
Englishmen are ruled by the law, and by the law alone; a man with us may be punished for a breach of law, but can be punished for nothing else. - Dicey.
The concept of rule of law is one of the distinguished features of the English constitution, later an accepted creed in almost all democratic countries.
It emerged out of the struggles of centuries of Englishmen for political freedom and individual liberty. It is antithetical to 'Administrative law,' which is prevalent in the continental countries like France.
Rule of law has been studied in detail in this 'introduction to the Law of the Constitution' by A.V.Dicey.
Meaning of Rule of Law :
By rule of law, it is meant that administration is run strictly in accordance with law. There is no room for exercising arbitrary powers by any authority. All are under the same law and none is over and above the law.
No man or institution is empowered to award punishment to any individual arbitrarily. All are subject to the same law irrespective of their rank or status and no discrimination is made for the purpose of administering justice. All are equal before law and all are tried in the same courts.
Basic Features :
The basic features of rules law are :
1. No special rights :
Law does not recognize any special rights or privilege for any individual or group of individuals. Law is supreme not individuals.
2. Equality before law :
Law does not make any distinction between one person and another on the basis of race, religion, sex etc. All are equal before law.
3. Predominance of legal spirit :
This is to mean that no man is punished without a proper trial. No person is deprived of his life, liberty and property except for a breach of law established in a court of law. No person is above law. All persons private citizens and government officials are subject to the same law. There is no separate law for government officials. All are tried by the same courts and the same law is applicable to all. In brief, rule of law implies absence of illegal imprisonment and illegal punishment.
Decline of the Rule of law :
The concept of rule of law as explained by dicey is no longer found in England today. Due to the growth of delegated legislation, advent of administrative tribunals, changed socio - economic circumstances, the emergence of welfare state and the immunities enjoyed by various categories of people, the scope of rule of law is gradually declining.
Administrative Law :
Administrative law is a separate branch of legal discipline dealing with state authority. It directly deals with the conflicts between the state and the individual. It mainly focuses the function of modern state. It evolved from constitutional law and is thus subordinate to it.
Administrative law is defined as the body of rules, which regulate the relations of the administrative or of theadministrative authority towards private citizens.
Basic Features of Administrative Law :
The basic features of administrative law are
1. It deals with the composition and the powers of administrative authorities.
2. It fixes the limits of the powers of those authorities.
3. It prescribes the procedures to be followed by these authorities in exercising such powers.
4. It controls these administrative authorities through judicial and other means.
5. Administrative law has become important in modern times because, the administrative agencies some times fail to act in conformity to the constitutional principles and norms. Administrative law seems to put the bureaucracy within the limits.
Related Topics