Differential Equations - Introduction | 12th Business Maths and Statistics : Chapter 4 : Differential Equations
Chapter: 12th Business Maths and Statistics : Chapter 4 : Differential Equations
Introduction
Differential Equations
Introduction
Differential equations, began with Gottfried Wilhelm Leibnitz. He was a Germen Philosopher,
mathematicians, and logician.
In lower class, we have studied algebraic equations like 5x
− 3( x − 6) = 4x , x2
− 7x + 12 = 0, | 18x – 5 | = 3 . The goal here was
to solve the equation, which meant to find the value (or values) of the
variable that makes the equation true.
For example, x =
9 is the solution to the first equation because only where 9 is substituted for
x both sides of the equation are identical.
In general each type of algebraic equation had its own particular
method of solution; quadratic equations were solved by one method equations
involving absolute values by another, and so on. In each case, an equation was
presented, and a certain method was employed to arrive at a solution, a method
appropriate or the particular equation at hand.
These same general ideas carry over to differential equations,
which are equations involving derivatives. There are different types of
differential equations, and each type requires its own particular solution
method.
Many problems related to economics, commerce and engineering, when formulated in mathematical forms, lead to differential equations. Many of these problems are complex in nature and very difficult to understand. But when they are described by differential equations, it is easy to analyse them.
A
differential equation is an equation with a function and one or more of its derivatives. (i.e) an equation with the
function y = f(x) and its derivatives dy/dx,
d2y/dx2 ..... is called differential equation.
For
example,
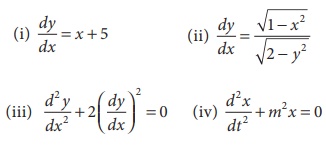
Differential
equations are of two types. One is ordinary differential equations and other
one partial differential equations. Here we study only ordinary differential
equations.
Related Topics