Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 5 : Taxonomy and Systematic Botany
International Code of Botanical Nomenclature
International Code of Botanical Nomenclature
Assigning name for a plant is known as Nomenclature. This is based on the
rules and recommendations of the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature.
ICBN deals with the names of existing (living) and extinct (fossil) organisms.
The elementary rule of naming of plants was first proposed by Linnaeus in 1737 and 1751 in his Philosophia Botanica. In 1813 a detailed
set of rules regarding plant nomenclature was given by A.P. de Candolle in his
famous work “Theorie elementaire
de la botanique”. Then the present
ICBN was evolved by following the same rules of Linnaeus, A.P. de Candolle and his son Alphonse de Candolle.
ICBN due to specific reasons and in
order to separate plant kingdom from other organisms, is redesignated as ICN.
The International Botanical Congress held in Melbourne in July 2011 brought
this change. The ICN stands for International Code of Nomenclature for Algae,
Fungi and Plants.
ICN Principles
International Code of Nomenclature is based on the
following six principles.
1.
Botanical nomenclature is independent of zoological
and bacteriological nomenclature.
2.
Application of names of taxonomic group is
determined by means of nomenclatural types.
3.
Nomenclature of a taxonomic group is based on priority
of publication.
4.
Each taxonomic group with a particular
circumscription, position and rank can bear only one correct name, the earliest
that is in accordance with the rules except in specified cases.
5. Scientific names of taxonomic
groups are treated as Latin regardless of their derivation.
6.
The rules of nomenclature are retroactive unless
expressly limited.
Codes of Nomenclature
ICN has formulated a set of rules and
recommendations dealing with the botanical name of plants. International
Botanical Congress is held at different places every six years. Proposals for
nomenclatural changes and changes in rules are discussed and implemented.
Changes are published in their website.
18th International Botanical Congress held in
2011at Melbourne, Australia made the following major changes.
1.
The code now permits electronic publication of
names of new taxa.
2.
Latin diagnosis or description is not mandatory and
permits the use of English or Latin for the publication of a new name (Art-39).
3.
“One fungus, one name” and “one fossil one name”
are important changes, the concept of anamorph and telomorph (for fungi) and
morphotaxa (for fossils) have been eliminated. (Previously, sexual and asexual
stages of the fungus/ fossils were provided with different names).
Anamorph – Asexual reproductive stage of fungus.
Telomorph – Sexual reproductive stage of fungus.
4. As an experiment with “registration of names”
new fungal descriptions require the use of an identifier from a “recognized
repository”. There are two recognized repositories Index fungorum and Myco Bank.
![]()
![]()
![]()
19th International Botanical Congress was held in
Shenzhen in China in 2017. Changes accepted by International Botanical Congress
are yet to be published.
Vernacular names (Common names)
Vernacular names are known as common names. They are
very often descriptive and poetic
references to plants. Common name refer to more than one plant or many plants
may have same common name. These names are regional or local and are not
universal. Example: Albizia amara . L
belongs to Mimosaceae is called as Usilai in South Tamilnadu and Thurinji in North Tamilnadu.
Activity
Write common name and scientific name
of 10 different plants around your home.
Scientific Names / Botanical Names
Each and every taxon as per the ICN (species,
genus, family etc) can have only one correct scientific name. Scientific name
of a species is always a binomial. These names are universally applied.
Example: Oryza sativa L. is the
scientific name of paddy.
Polynomial
Polynomial is a descriptive phrase of a plant. Example: Ranunculus calycibus retroflexis pedunculis falcatis caule erecto folius compositis. It means butter cup with reflexed sepals, curved flower stalks, erect stem and compound leaves. Polynomial system did not hold good as it was cumbersome to remember and use. Polynomial system of naming a plant is replaced by a binomial system by Linnaeus.
Binomial
Binomial nomenclature was first introduced by Gaspard Bauhin and it was implemented
by Carolus Linnaeus. Scientific name
of a species consists of two words and according to binomial nomenclature, the
first one is called genus name and
second one is specific epithet. Example: Mangifera
indica. Mangifera is a genus name and
indica is specific epithet. This
system is in vogue even now.
Author citation
This refers to valid name of the taxa accompanied
by the author’s name who published the name validly. Example: Solanum nigrum L. There are two types of author citation.
Single
author: When a single author proposed
a valid name, the name of the author alone is accompanied by his abbreviated
name. Example: Pithecellobium cinereum Benth.
Multiple
authors: When two or more authors
are associated with a valid publication of name, their names should be noted
with the help of Latin word et or
&.
Example: Delphinium
viscosum Hook. f. et Thomson.
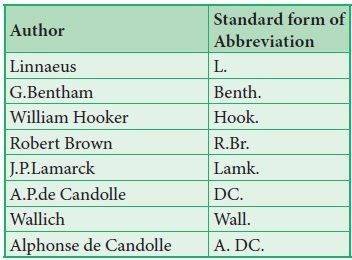
Standard form of author’s abbreviations has to be followed.
Related Topics