Taxonomy and Systematic Botany - Cladistics | 11th Botany : Chapter 5 : Taxonomy and Systematic Botany
Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 5 : Taxonomy and Systematic Botany
Cladistics
Cladistics
Analysis of the taxonomic data, and the types of
characters that are used in classification have changed from time to time.
Plants have been classified based on the morphology before the advancement of
microscopes, which help in the inclusions of sub microscopic and microscopic
features. A closer study is necessary while classifying closely related plants.
Discovery of new finer molecular analytical techniques coupled with advanced
software and computers has ushered in a new era of modern or phylogenetic
classification.
The method of classifying organisms into
monophyletic group of a common ancestor based on shared apomorphic characters is called cladistics
(from Greek, klados-branch).
The outcome of a cladistic analysis is a cladogram, a tree-shaped diagram that
represent the best hypothesis of phylogenetic relationships. Earlier generated
cladograms were largely on the basis of morphological characters, but now
genetic sequencing data and computational softwares are commonly used in
phylogenetic analysis.
Cladistic analysis
Cladistics is one of the primary methods of
constructing phylogenies, or evolutionary histories. Cladistics uses shared,
derived characters to group organisms into clades. These clades have atleast
one shared, derived character found in their most recent common ancestor that
is not found in other groups hence they are considered more closely related to
each other. These shared characters can be morphological such as, leaf, flower,
fruit, seed and so on; behavioural, like opening of flowers nocturnal/diurnal;
molecular like, DNA or protein sequence and more.
Cladistics accept only monophyletic groups. Paraphyletic and polyphyletic taxa are occasionally considered when such taxa
conveniently treated as one group for practical purposes. Example: dicots,
sterculiaceae. Polyphyletic groups are rejected by cladistics.
i. Monophyletic
group; Taxa comprising all the
descendants of a common ancestor.
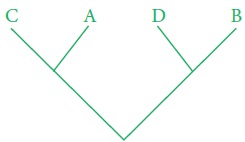
ii.
Paraphyletic group; Taxon that includes
an ancestor but not all of the descendants of that ancestor.
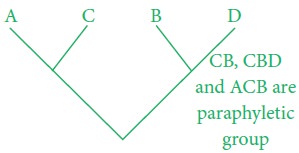
iii.
Polyphyletic group; Taxa that includes
members from two different lineages.
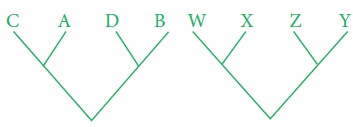
Need for cladistics
1.
Cladistics is now the most commonly used and
accepted method for creating phylogenetic system of classifications.
2.
Cladistics produces a hypothesis about the
relationship of organisms to predict the morphological characteristics of
organism.
3.
Cladistics helps to elucidate mechanism of
evolution.
Related Topics