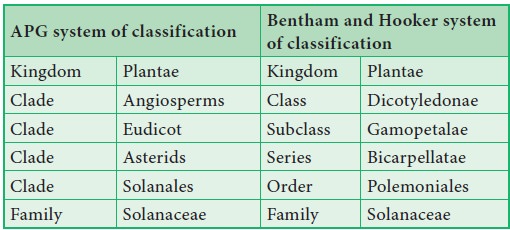
Systematic position, Diagnostic and General characters, Botanical description, Floral Formula, Economic Importance - Family: Solanaceae (Potato Family / Night shade family) | 11th Botany : Chapter 5 : Taxonomy and Systematic Botany
Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 5 : Taxonomy and Systematic Botany
Family: Solanaceae (Potato Family / Night shade family)
Family: Solanaceae (Potato Family / Night shade family)
Systematic Position
Diagnostic Features
·
Leaves alternate, exstipulate.
·
Flowers actinomorphic, pentamerous.
·
Calyx often persistence / accrescent.
·
Stamens 5, epipetalous, poricidal in dehiscence.
·
Carpels 2, ovary superior, 2 chambered, obliquely
placed, falsely four chambered placenta swollen, ovule numerous.
·
Fruits berry or capsule, vascular bundles with both
outer and inner phloem (Bicollateral vascular bundle).

General Characters
Distribution:
Family Solanaceae includes about 88 genera and
about 2650 species, of these Solanum is
the largest genus of the family with
about 1500 species. Plants are worldwide in distribution but more abundant in
South America.
Habit: Mostly
annual herbs, shrubs, small trees (Solanum violaceum) lianas with prickles
( Solanum trilobatum), many with
stellate trichomes; rarely vines (Lycium
sinensis)
Root: Branched tap root system.
Stem: Herbaceous
or woody; erect or twining, or
creeping; sometimes modified into tubers (Solanum
tuberosum) often with bicollateral
vascular bundles.
Leaves: Alternate,
simple, rarely pinnately compound(Solanum tuberosum and (Lycopersicon esculentum ) exstipulate,
opposite or sub-opposite in upper part, unicostate reticulate venation.
Inflorescence:
Generally
axillary or terminal cymose (Solanum) or solitary flowers (Datura stramonium). Extra axillary
scorpiod cyme called rhiphidium (Solanum nigrum) solitary and axillary (Datura and Nicotiana) umbellate cyme (Withania
somnifera).
Flowers: Bracteate
(Petunia), or ebracteate (Withania)
pedicellate, bisexual, heterochlamydeous, actinomorphic or weakly zygomorphic
due to oblique position of ovary pentamerous, hypogynous.
Calyx: Sepals 5,
rarely 4 or 6, Synsepalous, valvale
peristaent, often accrescent (enlarging to envelop the fruit) occasionally
enclosing the fruit ( Physalis, Withania)
Corolla: Petals 5,
sympetalous, rotate, tubular (Solanum) or bell- shaped (Atropa) or infundibuliform ( Petunia) usually alternate with sepals;
rarely bilipped and zygomorphic (Schizanthus)
usually valvate, sometimes convolute (Datura).
Androecium:
Stamens
5, epipetalous, filaments usually
unequal in length, stamens only 2 in Schizanthus(others
3 are reduced to staminode), 4 and
didynamous in (Salpiglossis) Anthers
dithecous, dehisce longitudinally or poricidal.
Gynoecium:
Bicarpellary,
syncarpous obliquely placed, ovary
superior, bilocular but looks tetralocular due to the formation of false septa,
numerous ovules in each locule on axile placentation.
Fruit: A capsule
or berry. In Lycopersicon esculentum, Capsicum, the fruit is a berry and in species of Datura and Petunia, the
fruit is a capsule.
Seed: Endospermous.

Botanical description of Datura
metel
Habit: Large,
erect and stout herb.
Root: Branched
tap root system.
Stem: Stem is
hollow, green and herbaceous with strong odour.
Leaf: Simple,
alternate, petiolate, entire or
deeply lobed, glabrous exstipulate showing unicostate reticulate venation.
Inflorescence:
Solitary
and axillary cyme.
Flower: Flowers
are large, greenish white,
bracteate, ebracteolate, pedicellate,
complete, heterochlamydeous, pentamerous, regular,
actinomorphic, bisexual and hypogynous.
Calyx: Sepals 5,
green synsepalous showing valvate
aestivation. Calyx is mostly persistant, odd sepal is posterior in position.
Corolla: petals 5, greenish white, sympetalous, plicate (folded like a fan) showing twisted aestivation, funnel shaped with wide mouth and 10 lobed.
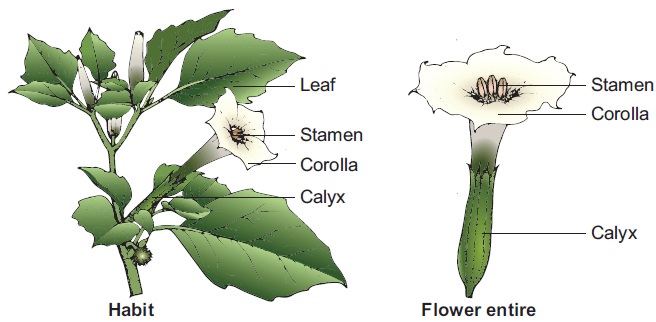
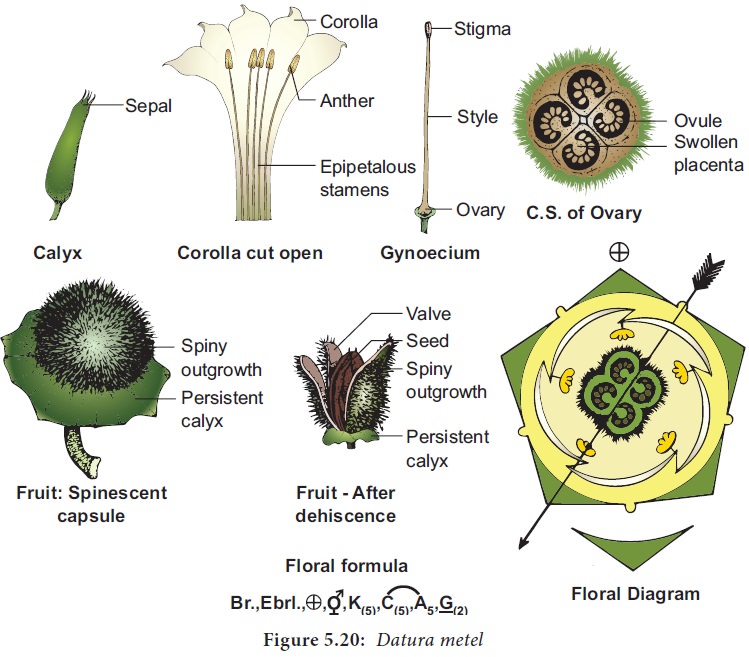
Androecium: Stamens 5, free from one another, epipetalous, alternipetalous and are inserted in the middle of the corolla tube. Anthers are basifixed, dithecous, with long filament, introse and longitudinally dehiscent.
Gynoecium:
Ovary
bicarpellary, syncarpous superior
ovary, basically biloculear but tetralocular due to the formation of false
septum. Carpels are obliquely placed and ovules on swollen axile placentation.
Style simple long and filiform, stigma two lobed.
Fruit: Spinescent
capsule opening by four apical
valves with persistent calyx.
Seed: Endospermous.
Floral Formula:
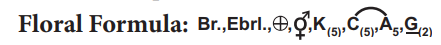
Botanical description of Solanum
americanum
Habit: A small
annual herb
Root: Branched
tap root system.
Stem: Aerial,
erect, green and herbaceous
Leaf: Simple,
alternate but opposite in the floral
region, petiolate, exstipulate ovate, entire or slightly lobed, acute
unicostate reticulate venation.
Inflorescence:
Extra-axillary
(due to fusion of floral axis)
scorpioid cyme called rhiphidium
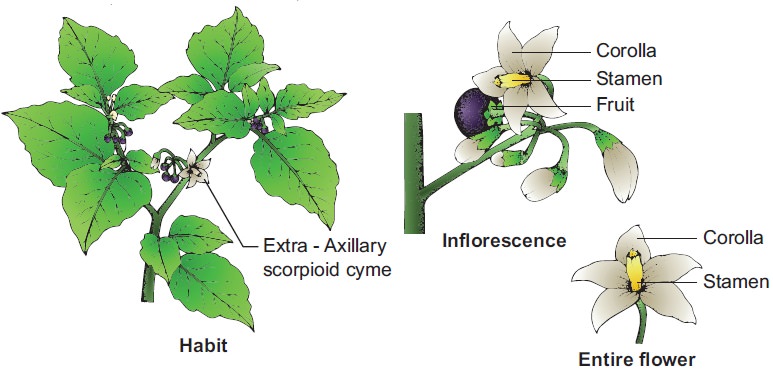
Flower:
Ebracteate, pedicellate, white, bisexual, actinomorphic, heterochlamydeous,
pentamerous, hypogynous white.
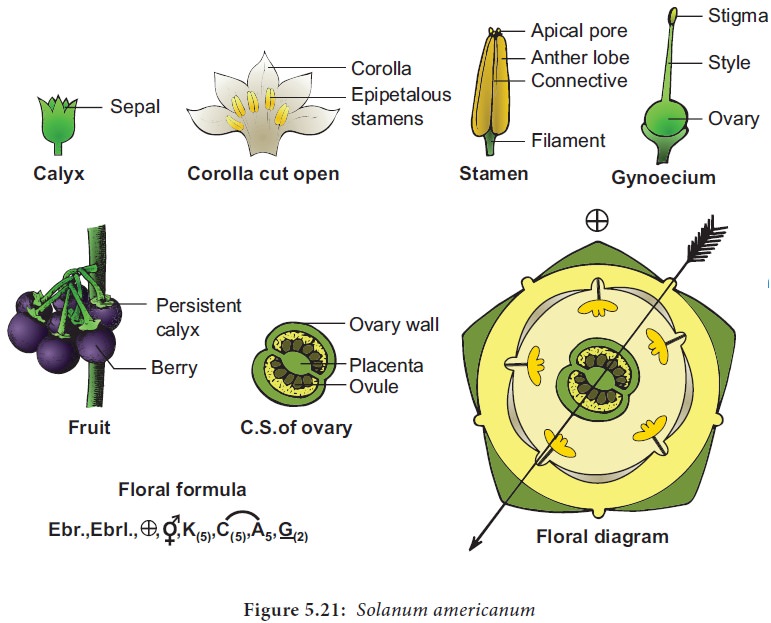
Calyx: Sepals 5,
synsepalous, green, persistent and
showing valvate aestivation.
![]()
![]()
![]()
Corolla: petals 5,
sympetalous, white, showing valvate
aestivation.
Androecium: Stamens 5,
apostamenous, epipetalous, filaments short, anthers conniving and forming an
envelope around the style dithecous, basifixed with apical pores.
Gynoecium:
Bicarpellary,
syncarpous, superior, bilocular,
many ovules in each locule on axile placentation, septum oblique, highly
swollen placenta, style long and hairy at the base, stigma bifid.
Fruit: Berry
Floral Formula:

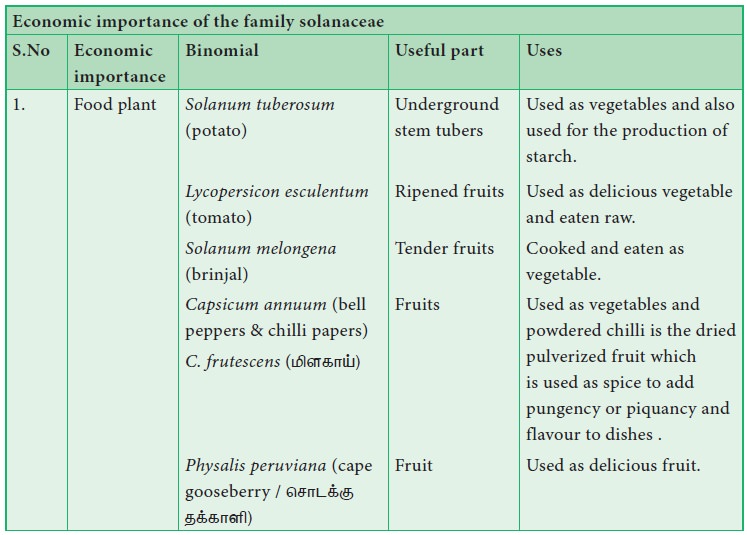
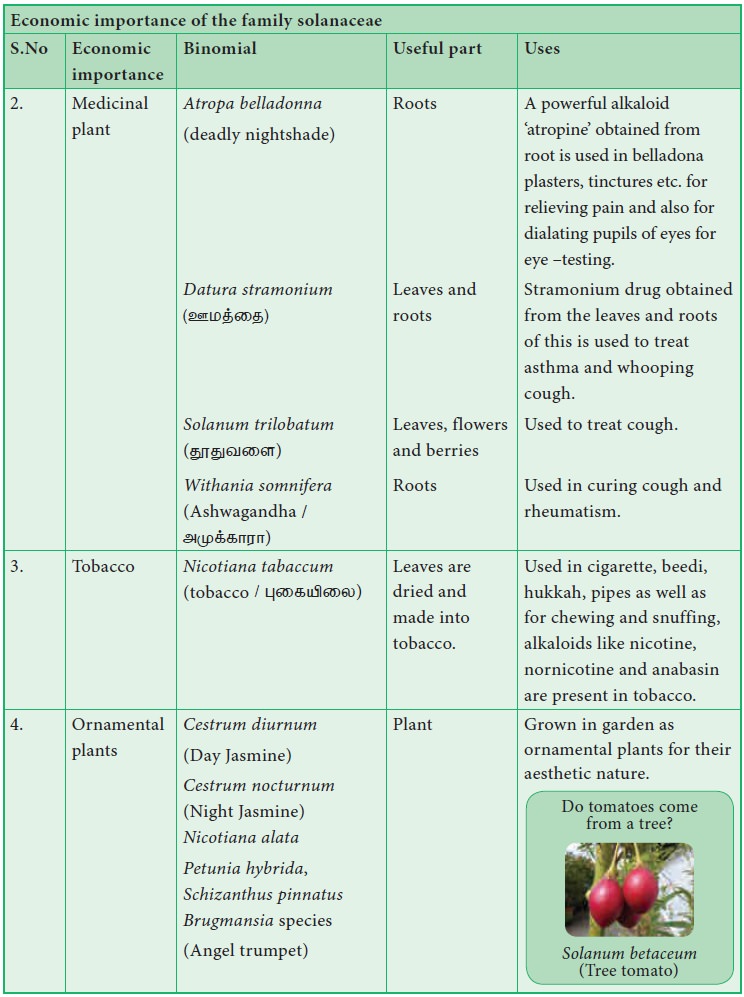
Economic importance
Related Topics