Chapter: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology : Pancreatic Hormones & Antidiabetic Drugs
Insulin Secretagogues: Sulfonylureas
INSULIN SECRETAGOGUES: SULFONYLUREAS
Mechanism of Action
The major action of
sulfonylureas is to increase insulin release from the pancreas (Table 41–5).
Two additional mechanisms of action have been proposed—a reduction of serum
glucagon levels and closure of potassium channels in extrapancreatic tissue
(which are of unknown but probably minimal significance).
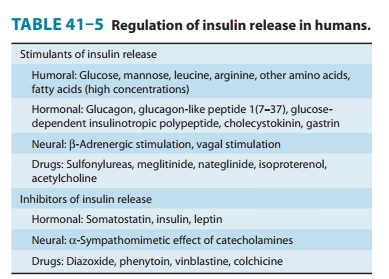
A. Insulin Release from Pancreatic Beta Cells
Sulfonylureas
bind to a 140-kDa high-affinity sulfonylurea recep-tor (Figure 41–2) that is
associated with a beta-cell inward rectifier ATP-sensitive potassium channel.
Binding of a sulfonylurea inhibits the efflux of potassium ions through the
channel and results in depolarization. Depolarization opens a voltage-gated
calcium channel and results in calcium influx and the release of preformed
insulin.
B. Reduction of Serum Glucagon Concentrations
Long-term administration
of sulfonylureas to type 2 diabetics reduces serum glucagon levels, which may
contribute to the hypo-glycemic effect of the drugs. The mechanism for this
suppressive effect of sulfonylureas on glucagon levels is unclear but appears
to involve indirect inhibition due to enhanced release of both insulin and
somatostatin, which inhibit alpha-cell secretion.
Efficacy & Safety of the Sulfonylureas
In 1970, the
University Group Diabetes Program (UGDP) in the USA reported that the number of
deaths due to cardiovascular disease in diabetic patients treated with
tolbutamide was excessive compared with either insulin-treated patients or
those receiving placebos. Owing to design flaws, this study and its
conclusionswere not generally accepted. In the United Kingdom, the UKPDS did
not find an untoward cardiovascular effect of sulfonylurea usage in their
large, long-term study.
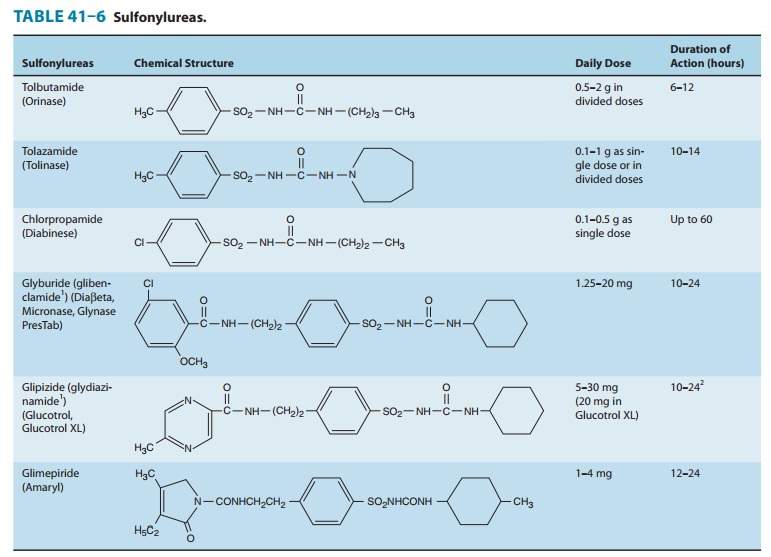
The sulfonylureas
continue to be widely prescribed, and six are available in the USA (Table
41–6). They are conventionally divided into first-generation and
second-generation agents, which differ primarily in their potency and adverse
effects. The first-generation sulfonylureas are increasingly difficult to
procure, and as the second-generation agents become generic and less
expen-sive, the older compounds probably will be discontinued.
Related Topics