Chapter: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology : Pancreatic Hormones & Antidiabetic Drugs
Insulin Secretagogue: Meglitinide
INSULIN SECRETAGOGUE: MEGLITINIDE
Repaglinide is the first member of the meglitinide group ofinsulin
secretagogues (Table 41–7). These drugs modulate beta-cell insulin release by
regulating potassium efflux through the potassium channels previously
discussed. There is overlap with the sulfonylureas in their molecular sites of
action because the megli-tinides have two binding sites in common with the
sulfonylureas and one unique binding site.
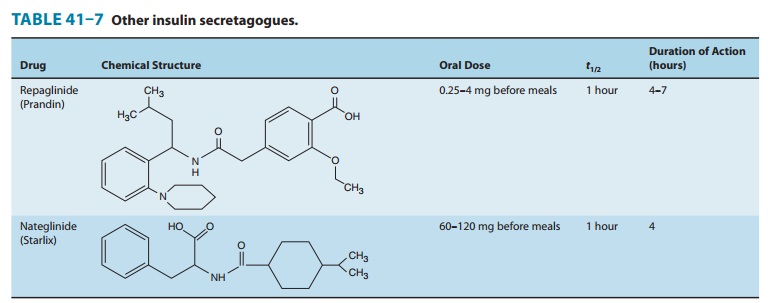
Repaglinide has a very
fast onset of action, with a peak concen-tration and peak effect within
approximately 1 hour after inges-tion, but the duration of action is 4–7 hours.
It is hepatically cleared by CYP3A4 with a plasma half-life of 1 hour. Because
of its rapid onset, repaglinide is indicated for use in controlling
post-prandial glucose excursions. The drug should be taken just before each
meal in doses of 0.25–4 mg (maximum 16 mg/d); hypogly-cemia is a risk if the
meal is delayed or skipped or contains inadequate carbohydrate. This drug
should be used cautiously in individuals with renal and hepatic impairment.
Repaglinide is approved as monotherapy or in combination with biguanides.There
is no sulfur in its structure, so repaglinide may be used in type 2 diabetics
with sulfur or sulfonylurea allergy.
Related Topics