Chapter: Digital Electronics : Synchronous and Asynchronous Sequential Circuits
Important Short Questions and Answers: Synchronous and Asynchronous Sequential Circuits
SYNCHRONOUS AND ASYNCHRONOUS
SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS
1. Draw the block diagram for Moore model.
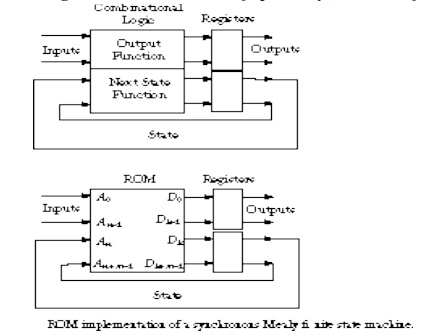
2.
What are hazard free digital circuits?
A
circuit which has no hazard like static-0-hazard and static-1-hazard is called
hazard free digital circuit.
3.
What are the basic building blocks of a
algorithmic state machine chart?
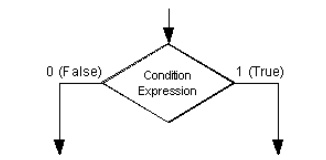
4.
What are the two types of asynchronous
sequential circuits?
·
Fundamental
mode circuit
·
Pulse
mode circuit
5.
What is state table?
The
state table representation of a sequential circuit consists of three sections
labelled present state, next state and output. The present state designates the state of flip-flops before
the occurrence of a clock pulse. The next state shows the states of flip-flops
after the clock pulse, and the output section lists the value of the output
variables during the present state.
6.
What are Hazards?
The
unwanted switching transients (glitches) that may appear at the output of a
circuit are called Hazards.
7.
Distinguish between a flowchart and an ASM
chart.
·
A
conventional flow chart describes the square of procedural steps and decision
paths for an algorithm without concern for their time relationship.
·
The ASM
chart describes the sequence of event as well as timing relationship between
the states of a sequential controller and the events that occur while going
from one state to the next.
8.
What is a state diagram? Give an example.
A state
diagram is a type of diagram used in computer science and related fields to
describe the behaviour of systems. State diagrams require that the system
described is composed of a finite number of states; sometimes, this is indeed
the case, while at other times this is a reasonable abstraction. Many forms of
state diagrams exist, which differ slightly and have different semantics.
9.
Write the VHDL code for a half adder.
HALF
ADDER –
Entity
entity
HALFADD
is port ( A,B : in bit; S,C : out bit );
end
HALFADD; --
Architecture
Architecture
struct of HALFADD is
begin S
<= A xor B;
C <=
A and B;
end
struct;
10.
Write a verilog model of a full subtractor
circuit.
module full_subtractor ( a ,b ,c ,diff ,borrow
);
output
diff ; output borrow ; input a ;
input b
; input c ;
assign
diff = a ^ b ^ c;
assign
borrow = ((~a) & b) | (b & c) | (c & (~a)); end module
11.
Under what circumstances asynchronous circuits
are prepared.
(i)
Fundamental
mode asynchronous circuits
(ii) Pulse mode asynchronous circuits
12.
Differentiate fundamental mode and pulse mode
asynchronous sequential circuits.
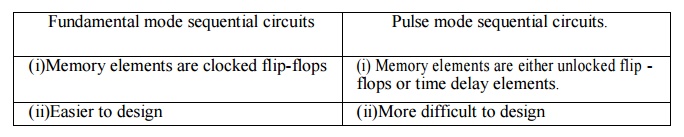
13.
Design a 3 input AND gate using verilog.
module
and ( a ,b ,c ,f);
output
diff ; input a ; input b ; input c ;
assign f
= a &b & c; endmodule
14.
What is synchronous sequential circuit?
·
In
synchronous circuits the input are pulses (or levels and pulses) with certain
restrictions on pulse width and circuit propagation delay. Therefore
synchronous circuits can be divided into clocked sequential circuits and uncklocked
or pulsed sequential circuits.
·
In a clocked
sequential circuit which has flip-flops or, in some instances, gated latches,
for its memory elements there is a (synchronizing) periodic clock connected to
the clock inputs of all the memory elements of the circuit, to synchronize all
internal changes of state
15.
Write short notes on Hazards.
The
unwanted switching transients (glitches) that may appear at the output of a
circuit are called Hazards.
·
Static-0-Hazard
·
Static-1-Hazard
Related Topics