Chapter: Digital Electronics : Synchronous and Asynchronous Sequential Circuits
Asynchronous Sequential Circuits - Introduction
ASYNCHRONOUS SEQUENTIAL
CIRCUITS – INTRODUCTION
·
Do not
use clock pulses. The change of internal state occurs when there is a change in
the input variable.
·
Their
memory elements are either unclocked flip-flops or time-delay elements.
·
They
often resemble combinational circuits with feedback.
·
Their
synthesis is much more difficult than the synthesis of clocked synchronous
sequential circuits.
·
They are
used when speed of operation is important.
The
communication of two units, with each unit having its own independent clock,
must be done with asynchronous circuits.
The general structure of an asynchronous
sequential circuit is as follows:
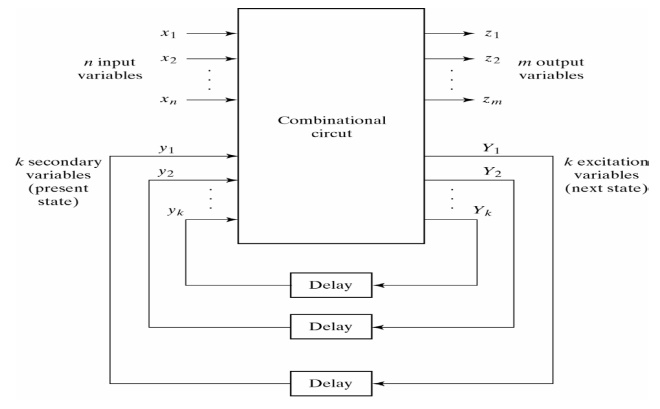
There
are n input variables, m output variables, and k internal states.
Fundamental-mode operation assumes that the input signals change
one at a time and only when the
circuit is in a stable condition.
Related Topics