Chapter: Basic Electrical and electronics : Electric Circuits and Measurements
Important Short Questions and Answers: Electric Circuits and Measurements
ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS & MEASUREMENTS
1.
What is
meant by charge?
Charge is
an electrical property of the atomic particles which matter consists. The
charge of an electron is so small. Charge in motion represents current. The
unit of charge is coulomb.
2.
What is
meant by Current?
The flow
of free electrons in a conductor is called current. Unit is ampere (A). I =
Q/t
3. What is
meant by Voltage?
The poterntial difference between two points is
called as voltage. Unit is Volts (V). V=W/Q , W=work done in joules & Q =
charge in coulombs
4. State
Ohm’s Law.
The potential difference across any two ends of a
conductor is directly proportional to the current flowing between the two ends
provided the temperature of the conductor remains constant.
5. State
Krichoff’s Voltage Law
KVL
states that the algebraic sum of voltages in a closed path is zero.
6. State
Krichoff’s current Law.
KCL
states that the algebraic sum of currents in a node is zero.
7.
Give
short notes on resistor.
It is a
property of a substance3 which opposes the flow of electrons. It is denoted by
R and its unit is Ohm
8.
Distinguish
between a Branch and a node of a circuit.
A pair of
network which connects the various points of the network is called branch A
point at which two or more elements are joined together is called node.
9.
Distinguish
between a mesh and a loop of a circuit.
A mesh is
a loop that does not contain other loops. All meshes are loop, but all loops
are
not
meshes. A loop is any closed path of branches
10.
Write
down the formula for a star connected network is converted into a delta
network?
RA=( R1 R2)/( R1 +R2+ R3) RB=( R1 R3)/( R1 +R2+ R3)
RC=( R2 R3)/( R1 +R2+ R3)
11.
Write
down the formula for a delta connected network is converted into a star
network?
R1=(
RARB+RBRC+RCRA)/RC R2=( RARB+RBRC+RCRA)/RB R3=( RARB+RBRC+RCRA)/RA
12.
Define
line currents and phase currents?
The
currents flowing in the lines are called as line currents The currents flowing
through phase are called phase currents
13.
Define
line voltage and phase voltage?
The
voltage across one phase and neutral is called line voltage & the voltage
between two lines is called phase voltage
14. Give the phase value & Line value of a star
connected system.
VL= 3Vph
15. Give the phase value and line valued of a delta
connected system.
IL= 3Iph
16. What is the power equation for a star connected
system?
P= 3I V
cosΦ L L W
17. What is the power equation for a delta
connected system?
P= 3I V
cosΦ L L W
18. What is meant by Real power?
Real
power means the useful power transfer from source to load. Unit is watts.
19. What is meant by apparent power?
Apparent
power is the product of voltage and current and it is not true power. Unit is
VA
20. What is reactive power?
If we consider the circuit as purely inductive the output power is
reactive power. Its unit is VAR
21. Define Instrument.
Instrument
is defined as a device for determining the value or magnitude of a quantity or
variable.
22. Mention the two main differences between an
ammeter and a voltmeter.
Ammeter
Voltmeter
It is a
current measuring device it is a voltage measuring device
Always
connected in series with circuit Always connected in parallel with circuit
The
resistance is very small The resistance is very high
23. What is control system?
A system
consists of a number of components connected together to perform a specific
function . In a system when the output quantity is controlled by varying the
input quantity then the system is called control system.
24. What are the two major types of control system?
The two
major types of control system are open loop and closed loop
25. Define open loop control system.
The
control system in which the output quantity has no effect upon the input
quantity are called open loop control system. This means that the output is not
feedback to the input for correction.
26. .Define closed loop control system.
The
control system in which the output has an effect upon the input quantity so as
to maintain the desired output value are called closed loop control system
27. Mention the errors in Moving iron instruments.
Hysteresis
error
Temperature
error
Stray
magnetic field error
Frequency
error
Eddy
current error
28.
Mention
any two precautions to be taken while using an Ammeter.
It should
never be connected across any source. The polarity must be observed correctly.
First use
the highest range and then decrease the voltage range until the sufficient
deflection is obtained.
29.
Define
Form factor and Crest factor.
Form
factor= RMS value / Average Value
Crest(peak)
factor=Maximum Value / RMS value
30. Which type of instrument is called as universal
instrument?
The
moving iron instrument are known as universal instruments, because these
instruments can be used for AC and DC.
31.
What are
the applications of MI instruments?
i) Used as
multirange ammeters and voltmeters.
ii) Used as
in expensive indicators such as charging and discharging current indicators in
automobiles.
iii)Extensively
used in industries for measurement of AC voltage and current where errors of
the order of 5% to 10% are accepetable.
32. What is meant by eddy current damping?
When the
conductor moves in a magnetic field an emf is induced in it and if a closed
path is provided ,a current flows known as eddy current. This current intersect
with the magnetic field to produce an electromagnetic torque , which opposes
the deflecting torque.
33.
How is
electrical power measured?
i) Using
Voltmeter-ammeter method for DC circuits. ii)Using Watt meters for AC circuits.
34.
What do
you mean by compensation coil in a wattmeter?
By
connecting a compensating coil in series with a pressure coil, The error caused
by the pressure coil flowing in the current coil can be neutralized.
35.What are the three types of power used in a
a.c circuit?
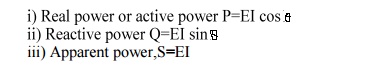
35.
Define
average value.
The
average value of an alternating current is that value of steady direct current
which transfers the same charge as the alternating current flowing for the same
time.
37. Define RMS value.
The
effective value of an alternating current is that value of steady ,direct
current which produces the same heat as that produced by the alternating
current when passed which produces the same heat as that produced by the
alternating current when passed through the same resistance for the same
interval of time.
38. Define reactive power.
The power
consumed by a pure reactance (XL or Xc ) in a a.c circuit is called reactive
power.
Related Topics