Chapter: Basic Electrical and electronics : Electric Circuits and Measurements
Steady State Solution of DC Circuits and Problems based on ohm’s law
Steady State Solution of DC Circuits:
Resistance in series connection:
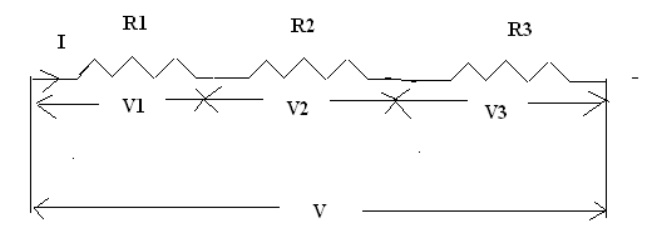
The
resistors R1, R2, R3 are connected in series
across the supply voltage “V”. The total current flowing through the circuit is
denoted as “I”. The voltage across the resistor R1, R2
and R3 is V1, V2, and V3
respectively.
V1
= I*R1 (as per ohms law)
V2=
I*R2
V3
= I*R3
V = V1+V2+V3
= IR1+IR2+IR3
= (R1+R2+R3)
I IR = (R1+R2+R3) I
R = R1+R2+R3
Resistance in parallel connection:
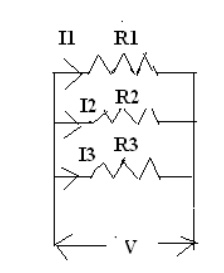
The
resistors R1, R2, R3 are connected in parallel
across the supply voltage “V”. The total current flowing through the circuit is
denoted as “I”. The current flowing through the resistor
R1,
R2 and R3 is I1, I2, and I3
respectively.
I = V / R
(as per ohms law)
I 1
= V1 / R1
I2
= V2 / R2
I3
= V3 / R3
V1
= V2 = V3 = V
From the
above diagram
I = I1+I2+I3
= V1
/ R1 + V2 / R2 + V3 / R3
= V / R1+
V/R2 +V/R3
I = V (1/R1 +1/R2 +1/R3)
V / R = V
(1/R1 +1/R2 +1/R3)
1/R = 1/R1 +1/R2
+1/R3
Problems based on ohm’s law
Problem 1:
A current of 0.5 A is flowing through the resistance of 10Ω.Find the
potential difference between its ends.
Given data:
Current I= 0.5A.
Resistance
R=1Ω
T o f i n d
Potential
difference V = ?
Formula used:
V = IR
Solution:
V = 0.5 Ă—
10 = 5V.
Result :
The
potential difference between its ends = 5 V
Problem :2
A supply voltage of 220V is applied to a 100 Ω resistor. Find the
current flowing through
it.
Given data
Voltage V
= 220V
Resistance R = 100Ω
To find:
Current I
= ?
Formula used:
Current I
= V / R
Solution:
Current I
= 220/100
= 2.2 A
Result:
The
current flowing through the resistor = 2.2 A
Problem : 3
Calculate the resistance of the conductor if a current of 2A flows
through it when the potential difference across its ends is 6V.
Given data
Current I
= 2A
Voltage V
= 6V
To find:
Resistance
R = ?
Formula used:
Resistance
R = V / I
Solution:
Resistance
R = 6 / 2
= 3 Ω
Result:
The value
of resistance R = 3Ω
Problem: 4
Calculate the current and resistance of a 100 W, 200V electric bulb.
Given data:
Power P =
100W
Voltage V
= 200V
To find:
Current I
=?
Resistance
R =?
Formula used:
Power P =
V *I
Current I
= P / V
Resistance
R = V / I
Solution:
Current I
= P / V
= 100 / 200
= 0.5 A
Resistance R = V / I
= 200 / 0.2
= 400 Ω
Result:
The value
of the current I = 0.5 A
The value
of the Resistance R = 400 Ω
Problem: 5
A circuit is made of 0.4 Ω wire, a 150Ω bulb and a 120Ω rheostat
connected in series. Determine the total resistance of the circuit.
Given data:
Resistance
of the wire = 0.4Ω
Resistance of bulb =
1 5 0 Ω
Resistance of rheostat = 120Ω
To find:
The total
resistance of the circuit R T =?
Formula used:
The total
resistance of the circuit R T = R1+R2+R3
Solution:
Total
resistance ,R = 0.4 + 150 +120
= 270.4Ω
Result:
The total
resistance of the circuit R T = 270.4 Ω
Problem 6:
Three resistances of values 2Ω, 3Ω and 5Ω are connected in series
across 20 V, D.C supply
.Calculate (a) equivalent resistance of the circuit (b) the total
current of the circuit (c) the voltage drop across each resistor and (d) the
power dissipated in each resistor.
Given data:
R1
= 2Ω
R2
= 3Ω
R3
= 5Ω
V = 20V
To find:
R T
=?
I T
=?
V1,
V2, V3 =?
P1,
P2, P3 =?
Formula used:
RT
= R1+R2+R3 (series connection)
IT
= VT / RT
V1
= R1*I1
V2=
R2*I2
V3
= R3*I3
P1=V1*I1
P2=V2*I2
P3=V3*I3
Solution:
RT = R1+R2+R3
= 2+3+5
RT = 10Ω
IT = VT / RT = 20
/ 10
IT = 2 A
In series
connection I1 = I2 = I3 = IT = 2A
V1 = I1*R1 = 2*2
V1 = 4 V
V2 = I2*R2 = 2*3
V2 = 6 V
V3 = I3*R3 = 5*2
V3 = 10V
P1
= V1*I1
= 4*2
P1 = 8W
P2
= V2*I2
= 6*2
P2 = 12W
P3 = V3*I3 = 10*2
P3 = 20W
Result:
(a).
Equivalent resistance of the circuit RT = 10Ω
(b). The
total current of the circuit IT
= 2A
(c).
Voltage drop across each resistor V1 = 4 V, V2 = 6 V, V3
= 10V
(d). The
power dissipated in each resistor P1 = 8W, P2 = 12W, P3
= 20W
Related Topics