Chapter: Medicine and surgery: Haematology and clinical Immunology
Hereditary angioedema - Allergy
Hereditary angioedema
Definition
Inherited complement disorder resulting in episodic angioedema .
Age
Hereditary but may present in adulthood.
Aetiology
Inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. Acute episodes may be triggered by trauma, exercise, menses or emotional stress.
Pathophysiology
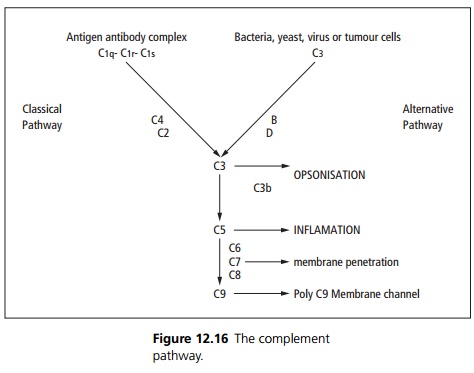
Associated with C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency, which may be quantitative or qualitative. C1 esterase is a non competitive protease inhibitor that inactivates C1. In absence or low levels there is uncontrolled C1 activity with consumption of C4 and C2, C2a fragments cause oedema of the epiglottis and extremities due to release of vasoactive compounds (see Fig. 12.16).
Clinical features
Patients complain of recurrent episodes of swelling in the arms, legs, lips, eyes, tongue or throat. Intestinal swelling can be severe and result in abdominal pain, vomiting, and dehydration. Oedema of the upper airway may result in airway obstruction.
Investigations
C1 esterase levels are low.
Management
Stanozolol and danazol may be used in an attempt to raise serum levels of C1 esterase inhibitor for long term treatment but their use in females leads to menstrual irregularities, fluid retention and androgenicity.
Acute attacks may require treatment with fresh frozen plasma or purified inhibitor.
Related Topics