Chapter: Medicine and surgery: Haematology and clinical Immunology
Coagulation screening tests - Investigations and procedures
Coagulation screening tests
The basic coagulation cascade (excluding co factors) is outlined below;
the cascade style of reaction allows a small stimulus of negative charge
contact (such as collagen) or the release of thromboplastin from the tissues to
create a large amount of fibrin product (see Fig. 12.1).
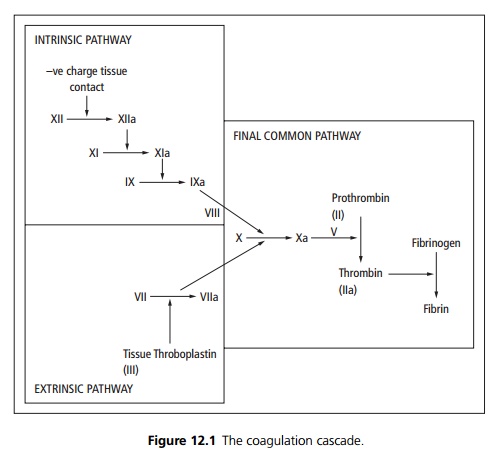
Factors II (prothrombin), VII, IX and X require vitamin K for their
synthesis. The coagulation screen is made up of a combination of tests:
·
The thrombin time (TT) is
initiated by adding thrombin to a sample and thus assesses
deficiencies/dysfunctions in fibrinogen. Fibrinogen levels and fibrin
degradation (D-dimers) products can also be measured as a measure of
intravascular clot break-down, e.g. disseminated intravascular coagulation or
pulmonary embolism.
·
The prothrombin (PT) time is
initiated by the addition of thromboplastin and thus measures the extrinsic and
final common pathway. It is prolonged in deficiencies of factors VII, V, X or
II. It is also prolonged in liver disease and in patients taking warfarin.
·
The activated partial
thromboplastin time (APTT) or partial thromboplastin time with kaolin (PTTK) is
initiated by adding an activator such as kaolin and thus measures the intrinsic
and final common pathway. It is prolonged in deficiencies of factors XII, XI,
IX, VIII, X or V.
·
If the coagulation times are
prolonged, a 50:50 mix of patients and normal plasma is made. If such a mixture
does not correct the time then the result is suggestive of the presence of an
inhibitor of coagulation rather than a factor deficiency. If heparin is
suspected as the cause of a prolonged TT then reptilase or protamine is added
to the sample, which reverses the effects of heparin.
Related Topics