Human Geography of Tamil Nadu - Geographical determinants of Agriculture | 10th Social Science : Geography : Chapter 8 : Human Geography of Tamil Nadu
Chapter: 10th Social Science : Geography : Chapter 8 : Human Geography of Tamil Nadu
Geographical determinants of Agriculture
Geographical determinants of Agriculture
Landform,
climate, soil and irrigation are the factors that determine the growth of
agriculture.
Landform
Tamil
Nadu is a land of diverse landscape comprising of hills, plateaus and plains.
Among them the plains are most suitable for agriculture. The plains with
alluvial soil enhances agricultural productivity. Example: Plains of cauvery.
Agriculture in the plateau is moderate and is poor on the hills.
Climate
Tamil
Nadu is situated in the tropical zone, which is nearer to the equator. The
state experiences a tropical climate. Hence, the temperature in Tamil Nadu is
relatively high almost throughout the year. So, only the tropical crops are
cultivated. Water is another limiting factor of agriculture. Northeast monsoon
is the major source of rainfall for Tamil Nadu. Therefore, the major cropping
season begins with this season. The rainfall in this season and the irrigation
facilities affect agriculture to a large extent.
Soil
Soil is
one of the most essential elements of agriculture. It provides essential
minerals or nutrients for the growth of crops and vegetation. The regions of
river valleys and the coastal plains are the most agriculturally productive
regions of the state as they are covered with fertile alluvial soil.
Irrigation
Monsoon
rainfall in the state is highly irregular. Further it is seasonal. Hence, irrigation
becomes necessary for successful cultivation of crops in the state. In the dry
regions, rain-fed crops are cultivated.
Types and regions of Agriculture Practices in
Tamil Nadu
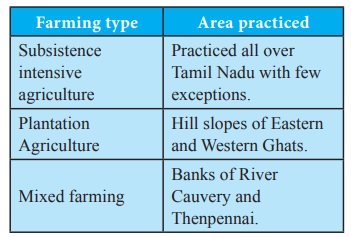
Subsistence intensive agriculture : Practiced all over
Tamil Nadu with few exceptions
Plantation Agriculture : Hill slopes of
Eastern and Western Ghats.
Mixed farming : Banks of River
Cauvery and Thenpennai
Related Topics