Numerical Problems with Answers, Solution | Coordinate Geometry | Maths - Exercise 5.6: Multiple Choice Questions | 9th Maths : UNIT 5 : Coordinate Geometry
Chapter: 9th Maths : UNIT 5 : Coordinate Geometry
Exercise 5.6: Multiple Choice Questions
Coordinate Geometry
Exercise 5.6
Multiple Choice Questions
1. If the
y-coordinate of a point is zero, then the point always lies ______
(1) in the
I quadrant
(2) in the
II quadrant
(3) on x-axis
(4) on y-axis
Solution:
Points in x - axis has y - coordinate zero
[Answer: (3) on x-axis]
2. The points
(–5, 2) and (2, –5) lie in the ________
(1) same
quadrant
(2) II and
III quadrant respectively
(3) II and IV quadrant respectively
(4) IV and
II quadrant respectively
Solution:
(–, +) lies IInd
quadrant and (+,–) lies in IVth
quadrant
[Answer: (3) II and IV quadrant respectively]
3. On plotting
the points O(0,0), A(3, – 4), B(3, 4) and C(0, 4) and
joining OA, AB, BC and CO, which of the following figure is obtained?
(1)
Square
(2)
Rectangle
(3) Trapezium
(4)
Rhombus
Solution:
In trapezium one pair of opposite side is parallel.
[Answer: (3) Trapezium]
4. If
P( –1,1), Q( 3,–4), R( 1, –1), S(–2, –3) and T(
–4, 4) are plotted on a graph paper, then the points in the fourth quadrant are
__________
(1) P and T
(2)
Q and R
(3) only S
(4) P and Q
Solution:
Points in IVth quadrant are (+,–)
[Answer: (2) Q and R]
5. The
point whose ordinate is 4 and which lies on the y-axis is _______________
(1)( 4, 0 )
(2) (0, 4)
(3) (1, 4)
(4) (4, 2)
Solution:
Points in y-axis have abscissa a zero
[Answer: (2) (0, 4)]
6. The
distance between the two points ( 2, 3 ) and ( 1, 4 ) is ______
(1)
2
(2)
√56
(3)
√10
(4) √2
Solution:
Distance = √[(x2–x1)2+(y2–y1)2]
[Answer: (4) √2]
7. If
the points A (2,0), B (-6,0), C (3, a–3) lie on the
x-axis then the value of a is _____
(1) 0
(2) 2
(3) 3
(4) –6
Solution:
Points in y-axis have ordinate
zero.
a–3 = 0
⇒ a = 3
[Answer: (3) 3]
8. If ( x+2,
4) = (5, y–2), then the coordinates (x,y) are _____
(1) (7, 12)
(2) (6, 3)
(3) (3, 6)
(4) (2, 1)
Solution:
x + 2 = 5 ⇒ x = 3; y – 2 = 4 ⇒ y = 6
[Answer: (3) (3, 6)]
9. If Q1,
Q2, Q3, Q4 are the quadrants in a Cartesian plane
then Q2 ∩ Q3 is ___________
(1) Q1∩ Q2
(2) Q2∩Q3
(3) Null set
(4) Negative
x-axis.
Solution:
Quadrants do not contain the axis.
[Answer: (3) Null set]
10. The distance
between the point ( 5, –1 ) and the origin is _________
(1) √24
(2) √37
(3) √26
(4) √17
Solution:
Distance = √[(5-0)2 + (–1 – 0)2] = √[52+l2]
= √26
[Answer: (3) √26]
11. The coordinates
of the point C dividing the line segment joining the points P(2,4) and Q(5,7) internally
in the ratio 2:1 is
(1) (7/2,
11/2)
(2) (3,5)
(3) (4,4)
(4) (4,6)
Solution:
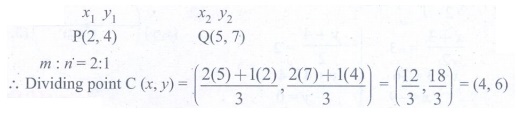
[Answer: (4) (4,6)]
12. If P
(a/3,b/2) is the mid-point of the line segment joining A(−4,3) and B(−2,4)
then (a,b) is
(1) (−9,7)
(2) (−3,
7/2)
(3) (9, −7)
(4) ( 3,
−7/2 )
Solution:
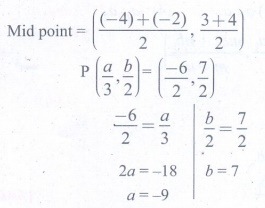
[Answer: (1) (−9,7)]
13.
In what ratio does the point Q(1,6) divide the line segment joining the points
P(2,7) and R(−2,3)
(1) 1:2
(2) 2:1
(3) 1:3
(4) 3:1
Solution:
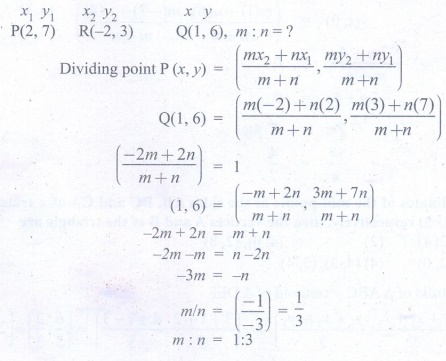
[Answer: (3) 1:3]
14.
If the coordinates of one end of a diameter of a circle is (3,4) and the coordinates
of its centre is (−3,2), then the coordinate of the other end of the diameter is
(1) (0,−3)
(2) (0,9)
(3) (3,0)
(4) (−9,0)
Solution:
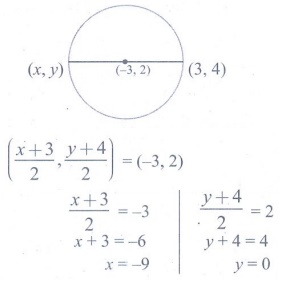
[Answer: (4) (−9,0)]
15.
The ratio in which the x-axis divides the line segment joining the points
A(a1 ,b1 ) and B (a2
,b2 ) is
(1) b1
: b2
(2) −b1 : b2
(3) a1
: a2
(4) −a1 : a2
Solution:
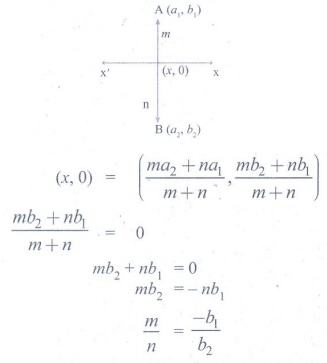
[Answer: (2) −b1 : b2]
16.
The ratio in which the x-axis divides the line segment joining the points
(6,4) and (1, −7) is
(1) 2:3
(2) 3:4
(3) 4:7
(4) 4:3
Solution:
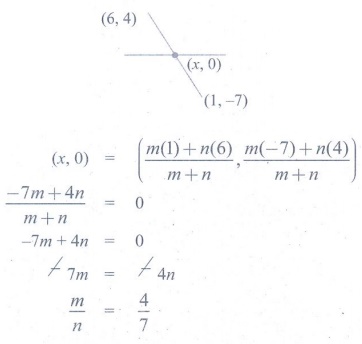
[Answer: (3) 4:7]
17.
If the coordinates of the mid-points of the sides AB, BC and CA
of a triangle are (3,4), (1,1) and (2,−3) respectively, then the vertices A
and B of the triangle are
(1) (3,2), (2,4)
(2) (4,0), (2,8)
(3) (3,4), (2,0)
(4) (4,3), (2,4)
Solution:
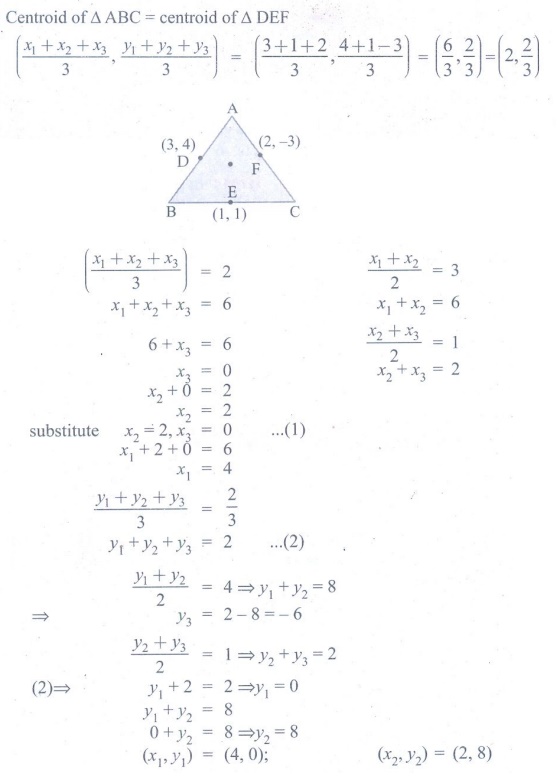
[Answer: (2) (4,0), (2,8)]
18.
The mid-point of the line joining (−a,2b) and (−3a,−4b)
is
(1) (2a,3b)
(2) (−2a, −b)
(3) (2a,b)
(4) (−2a, −3b)
Solution:
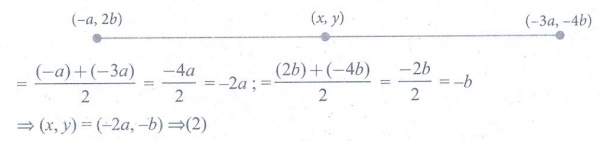
[Answer: (2) (−2a, −b)]
19.
In what ratio does the y-axis divides the line joining the points (−5,1)
and (2,3) internally
(1) 1:3
(2) 2:5
(3) 3:1
(4) 5:2
Solution:
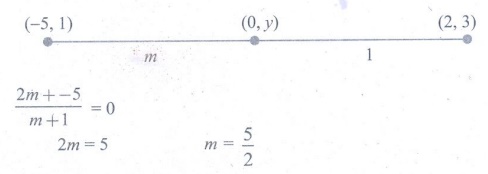
[Answer: (4) 5:2]
20.
If (1,−2), (3,6), (x,10) and (3,2) are the vertices of the parallelogram
taken in order, then the value of x is
(1) 6
(2) 5
(3) 4
(4) 3
Solution:
In parallelogram diagonals
bisect each other.
Mid point of AC = Mid
point of BD
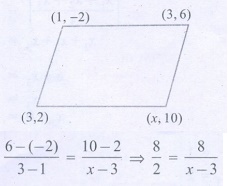
6− (−2) / 3−1 = 10−2 / x−3
8/2 = 8/x−3
x−3 = 2
x = 5
[Answer: (2) 5]
Related Topics