Applications of Operational Amplifier - Differentiator using Operational Amplifier | Linear Integrated Circuits : Applications of Operational Amplifier
Chapter: Linear Integrated Circuits : Applications of Operational Amplifier
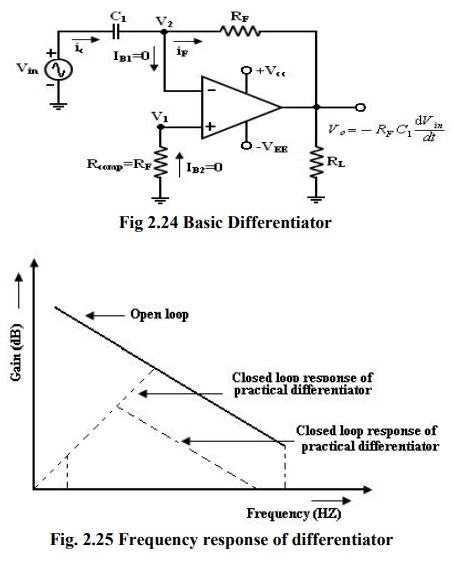
Differentiator using Operational Amplifier
Differentiator:
The
circuit performs the mathematical operation of differentiation (i.e.) the
output waveform is the derivative of the input waveform. The differentiator may
be constructed from a basic inverting amplifier if an input resistor R1
is replaced by a capacitor C1. Since the differentiator performs the
reverse of the integrator function. Thus the output V0 is equal to RF
C1 times the negative rate of change of the input voltage Vin with
time. The –sign indicates a 180º phase shift of the output waveform V0
with respect to the input signal. The below circuit will not do this because it
has some practical problems.
The
gain of the circuit (RF /XC1) R with R in frequency at a rate of 20dB/decade.
This makes the circuit unstable. Also input impedance XC1s with R in frequency
which makes the circuit very susceptible to high frequency noise.
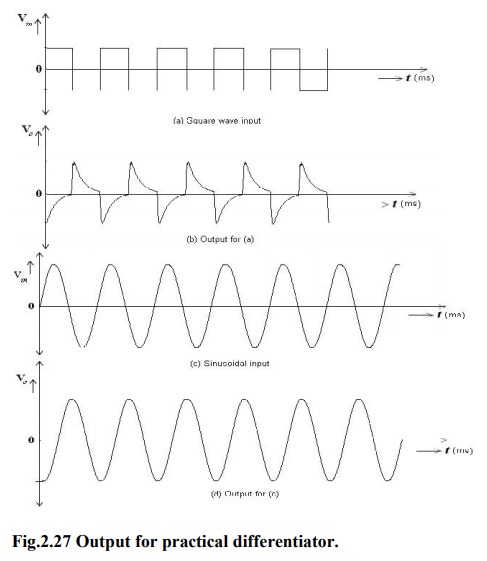
From the above fig. fa = frequency at
which the gain is 0dB and is given by
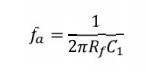
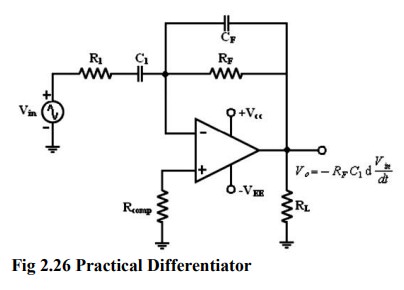
Both stability and high frequency noise
problems can be corrected by the addition of two components. R1 and
CF. This circuit is a practical differentiator.
From Frequency fa to feedback the gain
Rs at 20dB/decade after feedback the gain S at 20dB/
decade. This 40dB/ decade change in gain
is caused by the R1C1 and RFCF
combinations.
The gain limiting frequency fb is given by,
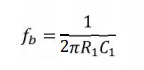
Where
R1C1 = RFCF
R1C1
and RFCF help to reduce the effect of high frequency
input, amplifier noise and offsets.
All
R1C1 and RF CF make the circuit more
stable by preventing the R in gain with frequency.
The
input signal will be differentiated properly, if the time period T of the input
signal is larger than or equal to RFC1 (i.e) T > RFC1
generally, the value of Feedback and in turn R1C1 and RF
CF
values should be selected such that
RF
C1>> R1 C1
A
workable differentiator can be designed by implementing the following steps.
1.
Select
fa equal to the highest frequency of the input signal to be differentiated then
assuming a value of C1 < 1μf. Calculate the value of RF.
2. Choose fb = 20fa and calculate the
values of R1 and CF so that R1 C1 =
RF CF.
Uses:
It
is used in wave shaping circuits to detect high frequency components in an
input signal and also as a rate of change and detector in FM modulators.
Related Topics