Applications of Operational Amplifier - Adder using Operational Amplifier | Linear Integrated Circuits : Applications of Operational Amplifier
Chapter: Linear Integrated Circuits : Applications of Operational Amplifier
Adder using Operational Amplifier
Adder:
Op-amp
may be used to design a circuit whose output is the sum of several input
signals.
Such
a circuit is called a summing amplifier or a summer or adder.
An inverting summer or a non-inverting summer may be discussed now.
Inverting Summing Amplifier:
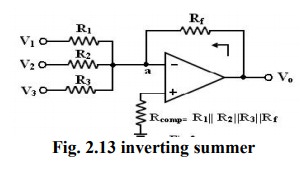
A
typical summing amplifier with three input voltages V1, V2
and V3 three input resistors R1, R2, R3
and a feedback resistor Rf is shown in figure 2.
The
following analysis is carried out assuming that the op-amp is an ideal one,
AOL= ∞.
Since
the input bias current is assumed to be zero, there is no voltage drop across
the resistor Rcomp and hence the non-inverting input terminal is at ground
potential.
I=
V1/R1+V2/R2…..+Vn/Rn;
Vo=
- Rf I=Rf/R( V1+V2+….Vn).
To
find Rcomp, make all inputs V1
= V2 = V3 = 0.
So
the effective input resistance Ri = R1 || R2
|| R3.
Therefore,
Rcomp = Ri || Rf = R1 || R2 || R3
|| R,f.
Non-Inverting Summing Amplifier:
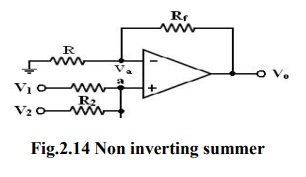
A
summer that gives a non-inverted sum is the non-inverting summing amplifier of
figure Let the voltage at the (-) input terminal be Va. which is a
non-inverting weighted sum of inputs.
Let
R1 = R2 = R3 = R = Rf/2, then Vo
= V1+V2+V3
Related Topics