Chapter: Biochemistry: Biochemical Techniques
Differential centrifugation technique
Differential centrifugation technique
It is a type of preparative centrifugation.
This method is based on the differences in the sedimentation rate of particles
of different size and density. In differential centrifugation, the material (a
tissue homogenate) to be separated in solution is centrifugally divided in to a
number of fractions by the step wise increase of applied centrifugal field. The
centrifugal field is determined by trial and error method so that the
particular type of material sediments during predetermined time of
centrifugation to sediment the particles in the form of pellet. The supernatant
contains other materials which are unsedimented. At the end of each stage the
pellet and supernatant are separated and the pellet is purified by washing.
Initially, all particles of the homogenate are homogenously distributed through
out the centrifuge tube. During centrifugation, particles move down the
centrifuge tube at their respective sedimentation rates and start to form
pellet at the bottom of the tube. Centrifugation can be continued till all the
components are pelleted one by one by increasing the centrifugal field.
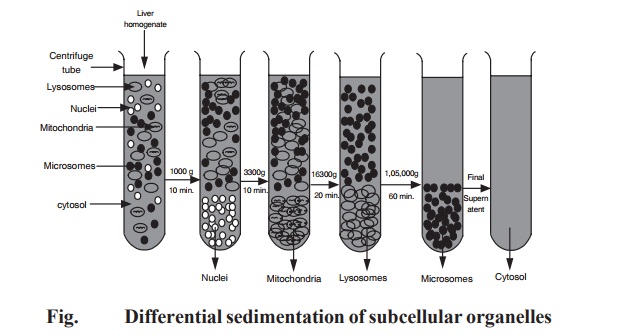
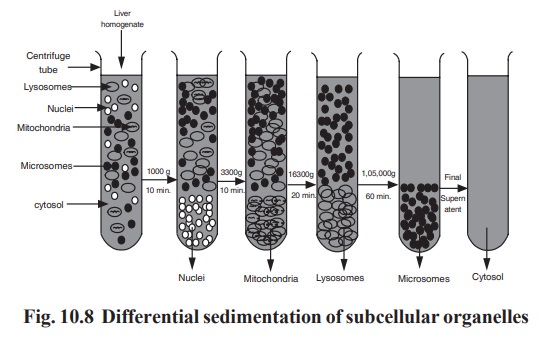
For example, the sub-cellular organelles
(nucleus, mitochondria, lysosomes, microsomes) from a tissue liver homogenate
can be isolated by applying this differential centrifugation techniques. The
technique has the following steps:
a)
Preparation
of liver homogenate – 10% solution in 0.25 molar sucrose.
b) Centrifugation at 1000 g for 10 minutes.
c)
Isolation
of the pellet sedimented which is nucleus.
d) The supernatant decanted from step (c) is
subjected to centrifugation at 3300 g for 10 minutes.
e)
Isolation
of the pellet sedimented which contains mitochondria.
f)
The
supernatant decanted from step (e) is subjected to centrifugation at 16300 g
for 20 minutes.
g)
Isolation
of the pellet sedimented which contains lysosomes.
h) The supernatant decanted from step (g) is
subjected to centrifugation at 105000 g for 60 minutes.
i)
Isolation
of the pellet sedimented which contains microsomes.
j)
The
supernatant obtained in the final step is the cell free cytosol.
The isolation of sub-cellular organelles is an
essential procedure used in many biochemical research laboratories by using
this differential centrifugation techniques. A schematic diagram of step-wise
isolation sub-cellular organelles from a liver homogenate is given in Fig. 10.8.
Applications
of analytical ultra-centrifuge: The analytical ultra-centrifuge
has found many applications in fields of protein and nucleic acid
chemistry. This gives information about (a) determination of molecular weight
of biomolecules, (b) estimation of purity of macromolecules and (c) detection
of conformational changes in macromolecules.
Related Topics