Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Geography earth space Higher secondary school College Notes
Database Management Systems - Databases
Database Management Systems
Databases
Software package is a programme, which is used in a computer to carry out a specific task. For such softwares as the GISs, computer is most basic. In the same vein, statistics is also one of the important basics. In geographical information system, boundaries, places and attribute data are all important. It is on their basis that mapping is done using computers.
Spatial Databases
Let us consider, for example, that we need a population density map. To map it, we should learn to use three basic aspects:
1. Area and boundaries of the map,
2. Data on densities by areas or (by the basic unit of organisation), and
3. Scale of the map.
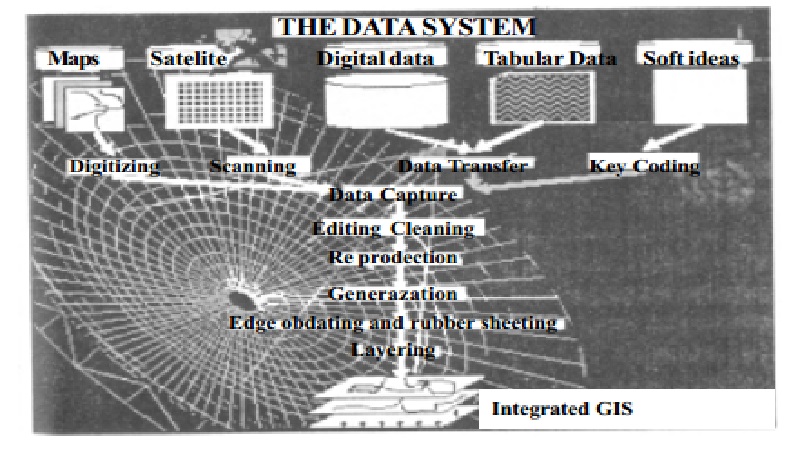
The map to be drawn with the assistance of computer must first be converted into a computer database. In this database, the boundaries are very important. These boundaries have to be filled into the database as lines or arcs and polygons. The digital data (of places and boundaries) must be given their identities known simply as 'labels' and entered into the database. Let us suppose the map we wish to draw relates to a district. The district map will have district boundaries, taluk boundaries and names of the taluks as fundamental data. If we fill these details into the databases, we create a spatially referenced database.
Digitizer
The database so created is known as the spatial database. This may be created in two ways:
1. by generating a database using a computer or
2. by generating a digital database from the boundaries and areas or places using an equipment.
This equipment which can convert points, lines and polygons into a digital database is known as a 'digitizing table'.
Once a computerised spatial database consisting of points, lines and polygons data is created, the next step is to create anattribute database for the same area. The one important activity we must keep in mind is that labels for polygons must be filled in both the databases (digital and attribute) so that the two databases could be linked. Labels help with the relations to be established while mapping. In some cases, the two databases can be created using a relational database management system (RDBMS).
Relational Database Management Systems
To create spatially referenced digital and attribute databases, to manipulate such databases and to operationalise digital methods, there are some software packages known generally as the Database Management Systems (DMS). The specialised among them areknown as Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS).
Relational database management systems are a significant part of the geographical information systems. They are capable of functioning independently as well. With their help, several databases which are required in mapping could be related so that mapping is perfect in all respects. It is exactly by relating various databases and evoking the graphical capabilities of the computers that we draw the maps. It is in this way, the population density map may be drawn as well.
Integrated Geographical Information Systems
Geographical information systems are, in a sense, management systems. Since they are capable of mapping, they are also functioning as the cartographic softwares. With the powers of digital and analytical methods, the geographical information systems are in reality systems of several capabilities. As such, GISs are an integration of:
1. Database management systems,
2. Cartographic systems, and
3. Analytical systems.
These systems are also capable of handling both spatial and aspatial data. Text data are also being used in the GISs. Graphic as well non-graphic characteristics are also handled by these systems.
Thus, it is clear that the geographical information systems are powerful software packages. These have another capability as well. They are capable of processing remotely sensed satellite data (raster) as well. To perform image processing towards mapping, thereare some softwares which are generally called 'integrated softwares'. The GISs which are capable of both image processing and mapping, especially overlaying, are generally called Integrated Geographical Information Systems. Let us see how they are used in applications.
Applications of Geographical Information Systems
Computers occupy a very significant place in GIS applications. GISs are implemented in different platforms of computers, but mostly DOS or UNIX platforms. Digital data as well as text data are used by these systems.
GISs are useful in resources assessment, resources planning, environmental assessments, economic plans and management plans.In the developing countries, land, soil, water, climate, vegetation, animals and population and the interactions among them are all related to planning, food production and food security. Several international organisations are concerned with growth, development, welfare and integration and they are engaged in developmental activities at the global, regional and local levels. All of these international organisations are now engaged in GIS applications which could help world development .integration and they are engaged in developmental activities at the global, regional and local levels. All of these international organisations are now engaged in GIS applications which could help world development .
In fact, the uses of the GISs are innumerable. For example, an agricultural scientist, by using the GIS, may determine exactly where a particular crop may be grown and (s)he may also assess the nature of soils in the areas suitable for such a crop. In this assessment, (s)he will use soil types, landforms, precipitation and a host of other data towards analysing possibilities for cropping the specific crop with mapping. (S)he may also determine suitable locations for cropping through overlaying maps of different aspects.
(S)he may overlay maps such as transport map, map of distribution of labour, map of distance to markets and the like and thus determine ' suitable areas'. Similarly, taking the effects of activities on environment, their impacts and the intensity of such impacts, the areas subjected to deterioration can be identified on maps (stresses on environment) and measures to prevent the deterioration may be suggested.
More important than all of these applications is the fact that the GISs are being used not only in geography but also in other sciences and technological departments. That the GISs are capable of assisting a wide range of scientific studies is a matter of pride for all of us, who are students and practitioners of geography today.
Related Topics