Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Geography earth space Higher secondary school College Notes
Lithosphere : Convergent Boundary
Lithosphere and tectonic plates
Scientists believe the Earth began its life about 4.6 billion years ago. The continents probably began forming about 4.2 billion years ago as the Earth continued to cool. But it was not until the turn of the 20th century that scientists determined that our planet is made up of four main layers: the inner core, outer core, mantle, and crust. The core is composed mostly of iron and is so hot that the outer core is molten, with about 10% sulphur. The inner core is under such extreme pressure that it remains solid.
Most of the Earth's mass is in the mantle, which is composed of iron, magnesium, aluminium, silicon, and oxygen silicatecompounds. At over 1000 degrees C, the mantle is solid but can deform slowly in a plastic manner. The crust is much thinner than any of the other layers, and is composed of the least dense calcium and sodium (Na) aluminum-silicate minerals. Being relatively cold, the crust is rocky and brittle , so it can fracture in earthquakes.
The crust and the upper layer of the mantle together makeup a zone of rigid, brittle rock called the Lithosphere. The layer below the rigid lithosphere is a zone of about 50-100 km down, is especially soft and plastic, and is called the asthenosphere. The asthenosphere is the part of the mantle that flows and moves the plates of the Earth. A heavy load on the crust, like an ice cap, large glacial lake, or mountain range, can bend the lithosphere down into the asthenosphere, which can flow out of the way. The load will sink until it is supported by buoyancy.
The crust is composed of two basic rock types granite and basalt. The continental crust is composed mostly of granite. The oceanic crust consists of a volcanic lava rock called basalt. Basaltic rocks of the ocean crust is much denser and heavier than the granitic rock of the continental crust. Because of this the continents ride on the denser oceanic plates.
The Earth's outermost layer, the lithosphere, is broken into 7 large, rigid pieces called plates: the African, North American, South American, Eurasian, Australian, Antarctic, and Pacific plates. Several minor plates also exist, including the Arabian, Nazca, and Philippines plates. These plates are all moving in different directions and at different speeds from 2 cm to 10 cm per year.
This theory of Plate tectonics explains 'how the earth works' and let us continue and learn more about the plates and their movements. The place where the two plates meet is called a plate boundary. Boundaries have different names depending on how the two plates are moving in relationship to each other.
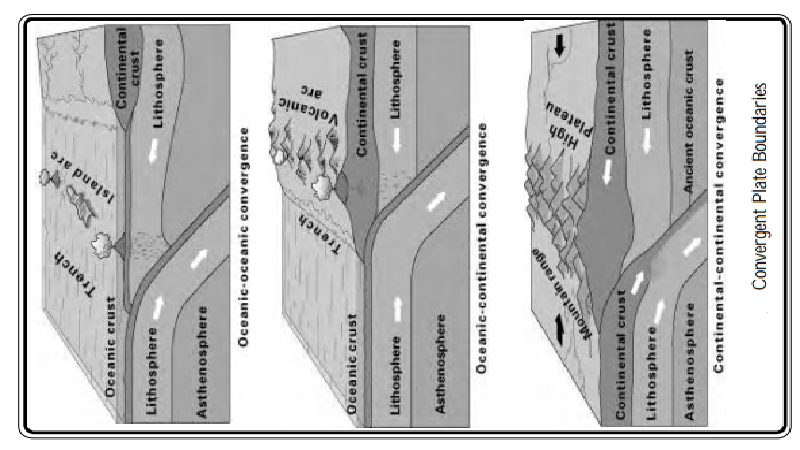
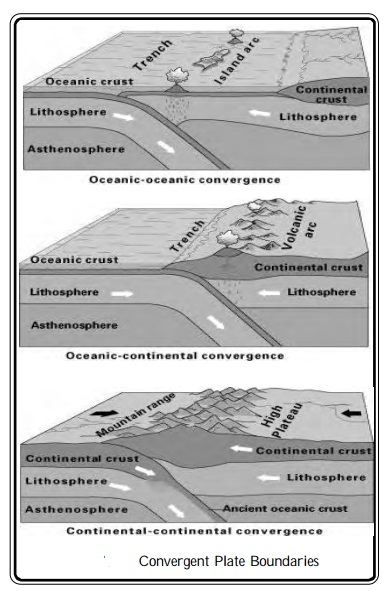
Convergent Boundary : when two plates collide, the edge of one dives beneath the other and ends up being destroyed in the mantle. Places where plates crash or crunch together are called convergent boundaries. Plates only move a few centimeters each year, so collisions are very slow and last millions of years.
Even though plate collisions take a long time, lots of interesting things happen. For example, in the drawing, an oceanic plate has crashed into a continental plate. The continental plate 'front ends' bends and the edge of the continental plate as shown, in has folded into a huge mountain range, while the edge of the oceanic plate has bent downward and dug deep into the Earth. A trench has formed at the bend. The folding and bending makes rock in both plates break and slip, causing earthquakes.
As the edge of the oceanic plate digs into Earth's hot interior, some of the rock in it melts. The melted rock rises up through the continental plate, causing more earthquakes on its way up, and forming volcanic eruptions where in finally reaches the surface. An example of this type of collision is found on the west coast of South America where the oceanic Nazca Plate is crashing into the continent of South America. The crash formed the Andes Mountains, the long string of volcanoes along the mountain crest, and the deep trench off the coast in the Pacific Ocean. Thus when two plates collide with each other mountains, volcanoes and earthquakes are formed.
Mountains, earthquakes, and volcanoes form where plated collide. Millions of people live in and visit the beautiful mountain ranges being built by plate collisions. For example, the Rockies in North America, the Alps in Europe, the Pontic Mountains in Turkey, the Zagors Mountains in Iran, and the Himalayas in central Asia were formed by plate collisions. Each year, thousands of people are killed by earthquakes and volcanic eruptions in those mountains.
Occasionally, big eruptions or earthquakes kill large numbers of people. In 1883 an eruption of Krakatau volcano in Indonesia killed 37,000 people. In 1983 an eruption caused mudslide in Columbia killed 25,000 people. In 1976, an earthquake in Tangshan, China killed an astounding 750,000 people. If we choose to live near convergent plate boundaries, we can build buildings that can resist earthquakes, and we can evacuate areas around volcanoes when they threaten to erupt. Yes, convergent boundaries are dangerous places to live, but with preparation and watchfulness, the danger can be lessened somewhat.
Divergent boundary : Places where plates are coming apart are called divergent boundaries. when Earth's lithosphere is pulled apart, it breaks along parallel faults. The block between the faults crack and drops down into the soft, the asthenosphere. The sinking of the block forms a central valley called a rift. Magma seeps upward to fill the cracks. In this way, new crust is formed along the boundary. Earthquakes occur along the faults, and volcanoes form where the magma reaches the surface.
Divergence can occur on continent and as well as on oceanic floor. Divergence on the continent causes rift valleys and are 30 to 50 kilometers wide. Examples include the East Africa rift in Kenya and Ethiopia, and the Rio Grande rift in New Mexico. Divergerce across the ocean floor causes rift valleys, with only a kilometer or less wide. Divergence along the Mid Atlantic ridge causes the Atlantic Ocean to widen at about 2 centimeters per year.
Most of the world's active volcanoes are located along or near the boundaries between shifting plates. Such volcanoes are called plate-boundary volcanoes. The peripheral areas of the Pacific Ocean Basin, containing the boundaries of several plates, are dotted with many active volcanoes that form the so-called Ring of Fire. The Ring provides excellent examples of plate-boundary volcanoes, including Mount St. Helens.
Related Topics