Chapter: Special Electrical Machines : Stepping Motor
Characteristics of Stepper Motor
CHARACTERISTICS OF STEPPER MOTOR
Stepper
motor characteristics are divided into two groups
v Static
characteristics
v Dynamic
characteristics
1. Static characteristics
It is
divided into two charteristics.
(i)Torque
Angle curve
(ii)Torque
current curve
(i)Torque-Angle curve
Torque
angle curve of a step motor is shown in fig.2.32. it is seen that the Torque
increases almost sinusoid ally, with angle Θ from equilibrium.
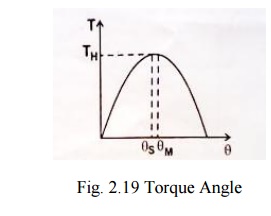
Holding Torque (TH)
It is the
maximum load torque which the energized stepper motor can withstand without
slipping from equilibrium position. If the holding torque is exceeded, the
motor suddenly slips from the present equilibrium position and goes to the
static equilibrium position.
Detent torque (TD):
It is the
maximum load torque which the un-energized stepper motor can withstand
slipping. Detent torque is due to magnetism, and is therefore available only in
permanent magnet and hybrid stepper motor. It is about 5-10 % of holding
torque.
Torque current curve
A typical
torque curve for a stepper motor is shown in fig.2.34. It is seen the curve is
initially linear but later on its slope progressively decreases as the magnetic
circuit of the motor saturates.
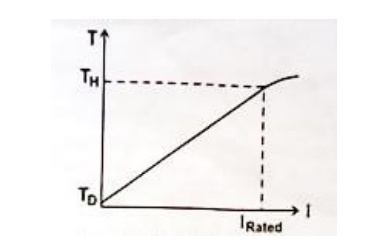
Torque constant (Kt)
Torque
constant of the stepper is defined as the initial slope of the torque-current
(T-I) curve of the stepper motor. It is also known as torque sensitivity. Its
units N-mA, kg-cm/A or OZ-in/A
2. Dynamic characteristics
A stepper
motor is said to be operated in synchronism when there exist strictly one to
one correspondence between number of pulses applied and the number of steps
through which the motor has actually moved. There are two modes of operation.
Start-Stop mode
Also
called as pull in curve or single stepping mode.
Slewing mode
In start
–stop mode the stepper motor always operate in synchronism and the motor can be
started and stopped without using synchronism. In slewing mode the motor will
be in synchronism, but it cannot be started or stopped without losing
synchronism. To operate the motor in slewing mode first the motor is to be
started in start stop mode and then to slewing mode. Similarly to stop the
motor operating in slewing mode, first the motor is to be brought to the start
stop mode and then stop.
Start Stop mode
Start
stop mode of operation of stepper motor is shown in fig.2.35 (a).In this second
pulse is given to the stepper motor only after the rotor attained a steady or
rest position due to first pulse. The region of start-stop mode of operation
depends on the operation depends on the torque developed and the stepping rate
or stepping frequency of stepper motor.
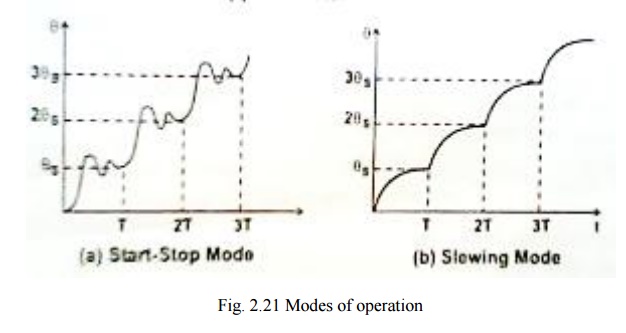
pulse is given to the stepper motor only after the rotor attained a steady or rest position due to first pulse. The region of start-stop mode of operation depends on the operation depends on the torque developed and the stepping rate or stepping frequency of stepper motor.
Related Topics