Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 15 : Environmental Chemistry
Brief questions and answers: Chemistry: Environmental Chemistry
Environmental Chemistry
Answer the following questions
18. Dissolved oxygen in water is responsible for aquatic life. What processes are responsible for the reduction in dissolved oxygen in water?
●
Micro organisms present in water decompose organic matter like leaves, grass,
trass, phytoplankton and consume dissolved oxygen in water.
●
Algae bloom
19. What would happen, if the greenhouse gases were totally missing in the earth’s atmosphere?
●
If the green house gases are totally missing from earth's atmosphere, then the
earth's average surface temperature would be only about (−18°C) (0°F).
●
Plants cannot carry out photosynthesis if CO2 is not present. Human
beings cannot survive without plants. So, no life on Earth.
20. Define smog.
●
Smog is a combination of smoke and fog which forms droplets that remain suspended
in the air.
●
Smog is a chemical mixture of gases that forms a brownish yellow haze over
urban cities.
●
Smog mainly consists of ground level ozone, oxides of nitrogen, volatile
organic compounds, SO2, acidic aerosols and gases and particulate
matter.
21. Which is considered to be earth’s protective umbrella? Why?
●
Earth's protective umbrella- Ozone
●
At high altitudes to the atmosphere consists of a layer of ozone (O3)
which acts as an umbrella or sheild for harmful UV radiations.
●
It protects us from harmful effect such as skin cancer. UV radiation can
convert molecular oxygen into ozone as shown in the following reaction.
O2(g)
_ uv_→ O(g) + O(g)
O(g)
O2(g) _ uv_→ O3(g)
●
Ozone gas is thermodynamically unstable and readily decomposes too molecular
oxygen.
22. What are degradable and non-degradable pollutants?
i.
Bio-degradable pollutants:
●
The pollutants which can be easily decomposed by the natural biological
processes are called bio-degradable pollutants.
Examples:
Plant wastes, animal wastes etc.
ii.
Non bio-degradable pollutants:
●
The pollutants which cannot be decomposed by the natural biological processes
are called Non bio-degradable pollutants.
Examples:
metal wastes (mainly Hg and Pb), D.D.T, plastics, nuclear wastes etc.,
●
These pollutants are harmful to living organisms even in low concentration.
●
As they are not degraded naturally, it is difficult to eliminate them from our
environment.
23. From where does ozone come in the photo chemical smog?
●
Photochemical smog is the combination of smoke, dust and fog with air
pollutants like oxides of nitrogen and hydrocarbons in the presence of
sunlight.
●
It forms when the sun shines and becomes worse in the afternoon.
●
Chemically it is oxidizing in nature because of high concentration of oxidizing
agents NO2 and O3, so it is also calles as oxidizing
smog. Photochemical smog is formed through sequence of following reactions.
N2
+ O2 → 2NO
2NO
+ O2 → 2NO2
NO2
_sunlight_→ NO + (O)
(O)
+ O2 → O3
24. A person was using water supplied by corporation. Due to shortage of water he started using underground water. He felt laxative effect. What could be the cause?
●
Excessive concentration (>500ppm) of sulphates in underground drinking water
could be the cause for laxative effect. (or)
●
Excessive concentration (>500ppm) of sulphates in underground water could be
the cause for laxative effect.
25. What is green chemistry?
Efforts
to control environmental pollution resulted in development of science for
synthesis of chemicals favorable to environment which is called green
chemistry. Green chemistry means science of environmentally favorable chemical
synthesis.
26. Explain how does greenhouse effect cause global warming

●
The term “ Greenhouse Effect" is used for trapping of heat in the atmosphere
by certain gases.
●
The earth's atmosphere allows most of the visible light from the sun to pass
through and reach Earth's surface.
●
As Earth's surface is heated by sunlight, it radiates part of this energy back
toward space as longer wavelengths (IR).
●
Some of the heat is trapped by CH4, CO2, CFCs and water
vapour present in the atmosphere.
●
They absorb IR radiation and effectively block a large portion of earth's
emitted radiation.
●
The radiation thus absorbed is partly reemitted to earth's surface. Therefore,
the earth's surface gets heated up by a phenomenon called green house effect.
●
Thus green house effect may be defined as the heating up of the earth surface
due to trapping of infrared radiations reflected by earth's surface by CO2
layer in the atmosphere.
●
The heating up of earth through the greenhouse effect is called global warming.
27. Mention the standards prescribed by BIS for quality of drinking water
Standard
characteristics of drinking water
Characteristics
and Desirable limit
I.
Physico-chemical characteristics
i)
PH : 6.5 to 8.5
ii)
Total Dissolved Salts (TDS) : 500 ppm
iii)
Total Hardness as (CaCO3) : 300 ppm
iv)
Nitrate : 45 ppm
v)
Chloride : 250 ppm
vi)
Sulphate : 200 ppm
vii)
Fluoride : 1 ppm
II.
Biological Characteristics
i)
Escherichia Coli (E.Coli) : Not at all
ii)
Coliforms : Not to exceed 10 (In 100 ml water sample)
28. How does classical smog differ from photochemical smog?
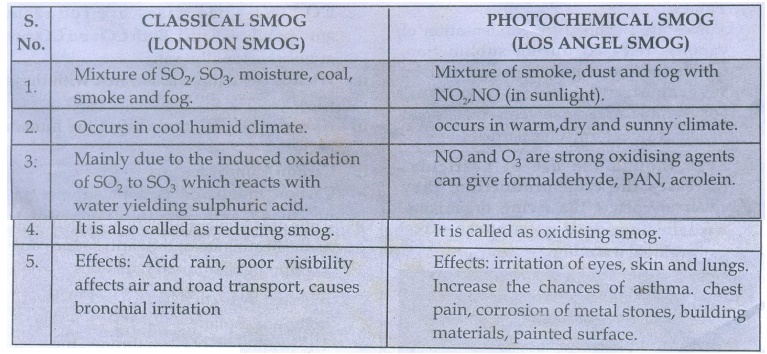
CLASSICAL SMOG (LONDON SMOG)
1. Mixture of SO2, SO3,
moisture, coal, smoke and fog.
2. Occurs in cool humid climate.
3: Mainly due to the induced
oxidation of SO2, to SO3 which reacts with water yielding
sulphuric acid.
4. It is also called as reducing
smog.
5. Effects: Acid rain, poor
visibility affects air and road transport, causes bronchial irritation
PHOTOCHEMICAL SMOG (LOS ANGEL
SMOG)
1. Mixture of smoke, dust
and fog with NO2, NO (in sunlight).
2. occurs in warm,dry and sunny
climate.
3. NO and O3 are
strong oxidising agents can give formaldehyde, PAN, acrolein.
4. It is called as oxidizing
smog.
5. Effects: irritation of eyes,
skin and lungs. Increase the chances of asthma. chest pain, corrosion of metal
stones, building materials, painted surface.
29. What are particulate pollutants? Explain any three.
Particulate
pollutants are small solid particles and liquid droplets suspended in air. Many
of particulate pollutants are hazardous. Examples: dust, pollen, smoke, soot
and liquid droplets (aerosols) etc,.
i)
Smoke:
Smoke
particulate consists of solid particles (or) mixture of solid and liquid
particles formed by combustion of organic matter.
For
example : cigarette smoke, oil smoke, smokes from burning of fossil fuel,
garbage and dry leaves.
ii)
Dust:
Dust
composed of fine solid particles produced during crushing and grinding of solid
materials.
For
example, sand from sand blasting, saw dust from wood works, cement dust from
cement factories and fly ash from powder generating units.
iii)
Mists:
They
are formed by particles of spray liquids and condensation of vapours in air.
For
example, sulphuric acid mist, herbicides and insecticides sprays can form
mists.
iv)
Fumes:
Fumes
are obtained by condensation of vapours released during sublimation,
distillation, boiling, calcination and by several other chemical reactions.
For
example, organic solvents, metals and metallic oxides form fume particles.
30. Even though the use of pesticides increases the crop production, they adversely affect the living organisms. Explain the function and the adverse effects of the pesticides.
Pesticides:
Pesticides
are the chemicals that are used to kill or stop the growth of unwanted
organisms. But these pesticides can affect the health of human beings.
These
are further classified as
a.
Insecticides:
Insecticides
like DDT, BHC, aldrin etc. can stay in soil for long period of time and are
absorbed by soil. They contaminate root crops like carrot, raddish, etc.
b.
Fungicide:
Organo
mercury compounds are used as most common fungicide. They dissociate in soil to
produce mercury which is highly toxic.
c.
Herbicides:
Herbicides
are the chemical compounds used to control unwanted plants. They are otherwise
known as weed killers.
Example:
sodium chlorate(NaClO3) and sodium arsenite (Na3 As O3).
Most of the herbicides are toxic to mammals.
31. Ethane burns completely in air to give CO2, while in a limited supply of air gives CO. The same gases are found in automobile exhaust. Both CO and CO2 are atmospheric pollutants
i. What is the danger associated with these gases
ii. How do the pollutants affect the human body?
i)
Carbon Monoxide:
●
Carbon monoxide is a poisonous gas produced as a result of incomplete
combustion of coal are firewood.
●
It is released into the air mainly by automobile exhaust.
●
It binds with haemoglobin and form carboxy haemoglobin which impairs normal
oxygen transport by blood and hence the oxygen carrying capacity of blood is
reduced.
●
This oxygen deficiency results in headache, dizziness, tension, loss of
consciousness, blurring of eye sight and cardiac arrest.
ii)
Carbon dioxide:
●
Carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere mainly by the process of
respiration, burning of fossil fuels, forest fire, decomposition of limestone
in cement industry etc.
●
Green plants can convert CO2 gas in the atmosphere into carbohydrate
and oxygen through a process called photosynthesis.
●
The increased CO2 level in the atmosphere is responsible for global
warming. It causes headache and nausea.
32. On the basis of chemical reactions involved, explain how do CFC’s cause depletion of ozone layer in stratosphere?
●
The chloro fluoro derivatives of methane and ethane are referred by trade name
Freons. These Chloro Fluoro Carbon compounds are stable, non-toxic,
noncorrosive and non- inflammable, easily liquefiable and are used in
refrigerators, air- conditioners and in the production of plastic foams.
●
CFC's are the exhaust of supersonic air craft's and jumbo jets flying in the
upper atmosphere. They slowly pass from troposphere to stratosphere.
●
They stay for very longer period of 50 −100 years. In the presence of uv
radiation, CFC's break up into chlorine free radical
CF2
Cl2 __hv_→ •CF2 Cl + Cl•
CFCl3
__hv_→
•CF Cl2 + Cl•
Cl•
+ O3 → ClO• + O2
ClO•
+ O → Cl• + O2
●
Chlorine radical is regenerated in the course of reaction. Due to this
continuous attack of Cl thinning of ozone layer takes place which leads
to formation of ozone hole.
●
It is estimated that for every reactive chlorine atom generated in the
stratosphere 1,00,000 molecules of ozone are depleted.
33.How is acid rain formed? Explain its effect
●
Rain water normally has a pH of 5.6 due to dissolution of atmospheric CO2
into it. Oxides of sulphur and nitrogen in the atmosphere may be absorbed by
droplets of water that make up clouds and get chemically converted into
sulphuric acid and nitric acid respectively as a results of pH of rain water
drops to the level 5.6, hence it is called acid rain.
●
Acid rain is a by-product of a variety of sulphur and nitrogen oxides in the
atmosphere. Burning of fossil fuels (coal and oil) in power stations, furnaces,
and petrol, diesel in motor engines produce sulphur dioxide and nitrogen
oxides. The main contributors of acid rain are SO2 and NO2.
They are converted into sulphuric acid and nitric acid respectively by the
reaction with oxygen and water.
2SO2
+ O2 + 2H2O → 2H2SO4
4NO2
+ O2 + 2H2O → 4HNO3
Harmful
effects of acid rain:
Some
harmful effects are discussed below:
i)
Acid rain causes extensive damage to buildings and structural materials of
marbles. This attack on marble is termed as Stone leprosy.
CaCO3
+ H2SO4 → CaSO4 + H2O + CO2
ii)
Acid rain affects plants and animal life in aquatic ecosystem.
iii)
It is harmful for agriculture, trees and plants as it dissolves and removes the
nutrients needed for their growth.
iv)
It corrodes water pipes resulting in the leaching of heavy metals such as iron,
lead and copper into the drinking water which have toxic effects.
v)
It causes respiratory ailment in humans and animals.
34. Differentiate the following
i. BOD and COD
ii. Viable and non-viable particulate pollutants
i)
Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD):
The
total amount of oxygen in milligrams consumed by microorganisms in decomposing
the waste in one liter of water at 20°C for a period of 5 days is called
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) and its value is expressed in ppm.
●
BOD is used as- a measure of degree of water pollution. Clean water would have
BOD value less than 5 ppm whereas highly polluted water has BOD value of 17 ppm
or more.
Chemical
oxygen demand (COD):
●
BOD measurement takes 5 days so another parameter called the Chemical Oxygen
Demand (COD) is measured.
●
Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) is defined as the amount of oxygen required by the
organic matter in a sample of water for its oxidation by a strong oxidising
agent like K2Cr2O7 in acid medium for a period
of 2 hrs.
ii)
a. Viable particulates:
The
viable particulates are the small size living organisms such as bacteria,
fungi, moulds, algae, etc. which are dispersed in air. Some of the fungi cause
allergy in human beings and diseases in plants.
b.
Non-viable particulates:
The
non-viable particulate are small solid particles and liquid droplets suspended
in air. They help in the transportation of viable particles.
Eg:
smoke, dust, mist, fog.
35. Explain how oxygen deficiency is caused by carbon monoxide in our blood? Give its effect
●
Carbon monoxide is a poisonous gas produced as a result of incomplete
combustion of coal are firewood. It is released into the air mainly by
automobile exhaust.
●
It binds with haemoglobin and form carboxy haemoglobin which impairs normal
oxygen transport by blood and hence the oxygen carrying capacity of blood is
reduced.
●
This oxygen deficiency results in headache, dizziness, tension, loss of
consciousness, blurring of eye sight and cardiac arrest.
36. What are the various methods you suggest to protect our environment from pollution?
1)
Waste management: Environmental pollution can be controlled by proper disposal
of wastes.
2)
Recycling: A large amount of disposed waste material can be reused by recycling
the waste, thus it reduces the land fill and converts waste into useful forms.
3)
Substitution of less toxic solvents for highly toxic ones used in certain
industrial processes.
4)
Use of fuels with lower sulphur content (e.g., washed coal).
5)
Growing more trees.
6)
Control measures in vehicle emissions are adequate.
Efforts to control environmental pollution have resulted in development
of science for synthesis of chemical favorable to environment and it is called
green chemistry.
Related Topics