Environmental Chemistry - Types of air pollutants | 11th Chemistry : UNIT 15 : Environmental Chemistry
Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 15 : Environmental Chemistry
Types of air pollutants
Types of air pollutants
Air pollutants may exist in two major forms namely, gases and particulates.
1. Gaseous air pollutants
Oxides of sulphur, oxides of nitrogen, oxides of carbon, and hydrocarbons are the gaseous air pollutants.
a. Oxides of Sulphur
Sulphur dioxide and sulphur trioxide are produced by burning sulphur containing fossil fuels and roasting sulphide ores. Sulphur dioxide is a poisonous gas to both animals and plants. Sulphur dioxide causes eye irritation, coughing and respiratory diseases like asthma, bronchitis,etc.
Sulphur dioxide is oxidised into more harmful sulphur trioxide in the presence of particulate matter present in polluted air .
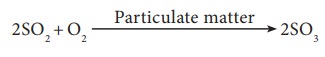
SO3 combines with atmospheric water vapour to form H2SO4 , which comes down in the form of acid rain.
SO3 + H2O → H2SO4
![]()
![]() Some harmful effects of acid rain will be discussed in section 15.3
Some harmful effects of acid rain will be discussed in section 15.3
b. Oxides of nitrogen
Oxides of nitrogen are produced during high temperature combustion processes, oxidation of nitrogen in air and from the combustion of fuels (coal, diesel, petrol etc.).
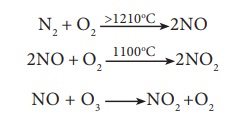
The oxides of nitrogen are converted into nitric acid which comes down in the form of acid rain. They also form reddish brown haze in heavy traffic. Nitrogen dioxide potentially damages plant leaves and retards photosynthesis. NO 2 is a respiratory irritant and it can cause asthma and lung injury. Nitrogen dioxide is also harmful to various textile fibres and metals.
c. Oxides of carbon
The major pollutants of oxides of carbon are carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide.
(i) Carbon Monoxide
Carbon monoxide is a poisonous gas produced as a result of incomplete combustion of coal are firewood. It is released into the air mainly by automobile exhaust. It binds with haemoglobin and form carboxy haemoglobin which impairs normal oxygen transport by blood and hence the oxygen carrying capacity of blood is reduced. This oxygen deficiency results in headache, dizziness, tension, Loss of consciousness, blurring of eye sight and cardiac arrest.
(ii) Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere mainly by the process of respiration, burning of fossil fuels, forest fire, decomposition of limestone in cement industry etc.
Green plants can convert CO2 gas in the atmosphere into carbohydrate and oxygen through a process called photosynthesis. The increased CO 2 level in the atmosphere is responsible for global warming. It causes headache and nausea.
(d) Hydrocarbon
The compounds composed of carbon and hydrogen only are called hydrocarbons. They are mainly produced naturally (marsh gas) and also by incomplete combustion of automobile fuel.
They are potential cancer causing (carcinogenic) agents. For example, polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) are carcinogenic, they cause irritation in eyes and mucous membranes.
2. Greenhouse effect and Global warming:
In 1987, Jean Baptiste Fourier a French mathematician and scientist coined the term“Greenhouse Effect” for trapping of heat in the atmosphere by certain gases.

The earth’s atmosphere allows most of the visible light from the Sun to pass through and reach Earth’s surface. As Earth’s surface is heated by sunlight, it radiates part of this energy back toward space as longer wavelengths (IR).
Some of the heat is trapped by CH4, CO2, CFCs and water vapour present in the atmosphere. They absorb IR radiation and effectively block a large portion of earth’s emitted radiation. The radiation thus absorbed is partly reemitted to earth’s surface. Therefore, the earth’s surface gets heated up by a phenomenon called greenhouse effect.
Thus Greenhouse effect may be defined as the heating up of the earth surface due to trapping of infrared radiations reflected by earth’s surface by CO2 layer in the atmosphere”. The heating up of earth through the greenhouse effect is called global warming.
Without the heating caused by the greenhouse effect, Earth’s average surface temperature would be only about −18 °C (0 °F). Although the greenhouse effect is a naturally occurring phenomenon, it is intensified by the continuous emission of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
During the past 100 years, the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere increased by roughly 30 percent and the amount of methane more than doubled.If these trends continue, the average global temperature will increase which can lead to melting of polar ice caps and flooding of low lying areas. This will increase incidence of infectious diseases like dengue, malaria etc.
3. Acid Rain
Rain water normally has a pH of 5.6 due to dissolution of atmospheric CO2 into it. Oxides of sulphur and nitrogen in the atmosphere may be absorbed by droplets of water that make up clouds and get chemically converted into sulphuric acid and nitric acid respectively as a results of pH of rain water drops to the level 5.6, hence it is called acid rain.
Acid rain is a by-product of a variety of sulphur and nitrogen oxides in the atmosphere. Burning of fossil fuels (coal and oil) in power stations, furnaces and petrol, diesel in motor engines produce sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides. The main contributors of acid rain are SO2 and NO2 .They are converted into sulphuric acid and nitric acid respectively by the reaction with oxygen and water.
2SO2 + O2 + 2H2O → 2H2SO4
4NO2 + O2 + 2H2O→ 4HNO3
Harmful effects of acid rain:
Some harmful effects are discussed below.
i. Acid rain causes extensive damage to buildings and structural materials of marbles. This attack on marble is termed as Stone leprosy.
CaCO3 + H2SO4→ CaSO4 + H2O +CO2↑
ii. Acid rain affects plants and animal life in aquatic ecosystem.
iii. It is harmful for agriculture, trees and plants as it dissolves and removes the nutrients needed for their growth.
iv. It corrodes water pipes resulting in the leaching of heavy metals such as iron, lead and copper into the drinking water which have toxic effects.
v. It causes respiratory ailment in humans and animals.

Related Topics