Solutions | Science - Book Back Questions with Answers | 10th Science : Chapter 9 : Solutions
Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 9 : Solutions
Book Back Questions with Answers
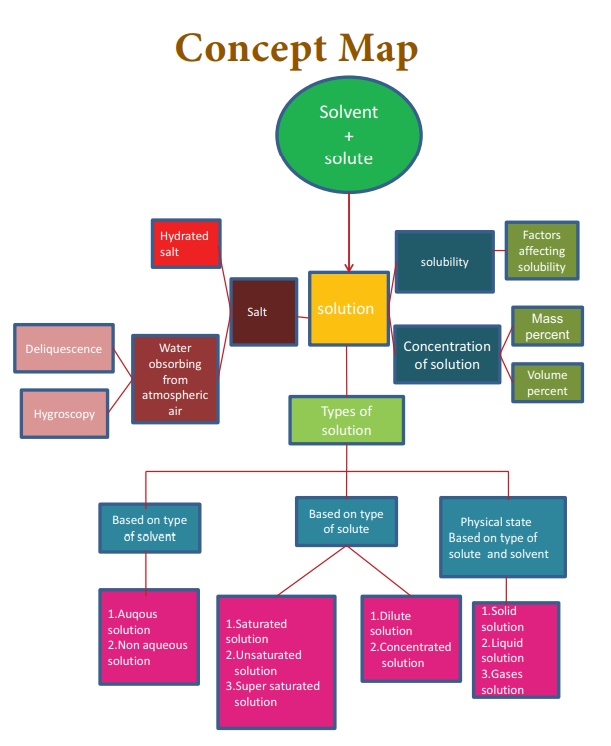
Solutions (Science)
I. Choose the correct answer.
1. A solution is a __________ mixture.
a. homogeneous
b. heterogeneous
c. homogeneous and heterogeneous
d. non homogeneous
2. The number of components in a binary solution is __________
a. 2
b. 3
c. 4
d. 5
3. Which of the following is the universal solvent?
a. Acetone
b. Benzene
c. Water
d. Alcohol
4. A solution in which no more solute can be dissolved in a definite amount of solvent at a given temperature is called _______
a. Saturated solution
b. Un saturated solution
c. Super saturated solution
d. Dilute solution
5. Identify the non aqueous solution.
a. sodium chloride in water
b. glucose in water
c. copper sulphate in water
d. sulphur in carbon-di-sulphide
6. When pressure is increased at constant temperature the solubility of gases in liquid ___________.
a. No change
b. increases
c. decreases
d. no reaction
7. Solubility of NaCl in 100 ml water is 36 g. If 25 g of salt is dissolved in 100 ml of water how much more salt is required for saturation _____________.
a. 12g
b. 11g
c. 16g
d. 20g
8. A 25% alcohol solution means
a. 25 ml alcohol in 100 ml of water
b. 25 ml alcohol in 25 ml of water
c. 25 ml alcohol in 75 ml of water
d. 75 ml alcohol in 25 ml of water
9. Deliquescence is due to __________
a. Strong affinity to water
b. Less affinity to water
c. Strong hatred to water
d. Inertness to water
10. Which of the following is hygroscopic in nature?
a. ferric chloride
b. copper sulphate penta hydrate
c. silica gel
d. none of the above
II. Fill in the blanks
1. The component present in lesser amount, in a solution is called Solute
2. Example for liquid in solid type solution is
3. Solubility is the amount of solute dissolved in 100 g of solvent.
4. Polar compounds are soluble in polar solvents
5. Volume persentage decreases with increases in temperature because
III. Match the following
1. Blue vitriol – CaSO4 .2H2O
2. Gypsum – CaO
3. Deliquescence – CuSO4 .5H2O
4. Hygroscopic – NaOH
Answer:
1. Blue vitriol –
2. Gypsum – CaSO4 .2H2O
3. Deliquescence – NaOH
4. Hygroscopic – CaO
IV. True or False: (If false give the correct statement)
1. Solutions which contain three components are called binary solution. - False
Solutions which contain three components are called Trinary solution.
2. In a solution the component which is present in lesser amount is called solvent. - True
3. Sodium chloride dissolved in water forms a non-aqueous solution.
4. The molecular formula of green vitriol is MgSO4.7H2O
The molecular formula of green vitriol is Mg SO4.7H2O.
5. When Silica gel is kept open, it absorbs moisture from the air, because it is hygroscopic in nature
V. Short answer
1. Define the term: Solution
Solution is a homogeneous mixture of one or more substances.
2. What is mean by binary solution
Solutions which are made of one solute and one solvent (two components) are called binary solutions.
3. Give an example each i) gas in liquid ii) solid in liquid iii) solid in solid iv) gas in gas
(i) Gas - Liquid - carbon-di-oxide dissolved in water (Soda water)
(ii) Solid - Liquid - Sodium chloride dissolved in water
(iii) Solid - Solid - Copper dissolved in gold (Alloys)
(iv) Gas - Gas - Mixture of Helium-Oxygen gases,
4. What is aqueous and non-aqueous solution? Give an example.
(i) Aqueous solution: The solution in which water acts as a solvent is called aqueous solution.
E.g. Common salt in water, Sugar in water, Copper sulphate in water etc.
(ii) Non - Aqueous solution: The solution in which any liquid other than water acts as a solvent is called non - aqueous solution.
E.g: Sulphur dissolved in carbon disulphide.
5. Define Volume percentage
Volume percentage is defined as the percentage by volume of solute (in ml) present in the given volume of the solution.
Volume Percentage = [ Volume of the sloute / Volume of the solution ] * 100
6. The aquatic animals live more in cold region Why?
Aquatic animals live more in cold regions because, more amount of dissolved oxygen is present in the water of cold regions. This shows that the solubility of oxygen is more in water at low temperature.
7. Define Hydrated salt.
When ionic substances are dissolved in water to make their saturated aqueous solution, their ions attract water molecules which then attached chemically in certain ratio. This process is called hydration.
8. A hot saturated solution of copper sulphate forms crystals as it cools. Why?
As the solution cools, the water molecules move closer together again and there's less room for the solution to hold onto as much of the dissolved solid. So copper sulphate crystallises as the solid is cooled.
9. Classify the following substances into deliquescent, hygroscopic.
Conc. Sulphuric acid, Copper sulphate penta hydrate, Silica gel, Calcium chloride, and Gypsum salt.
Deliquescent: Calcium chloride, Copper sulphate, pentahydrate and gypsum salts
Hygroscopic: Silica gel, Cone. Sulphic acid
VI. Long answer:
1. Write notes on i) saturated solution ii) unsaturated solution
Answer:
(i) Saturated solution
: A solution in which no more solute can be dissolved in a definite
amount of the solvent at a given temperature is called saturated solution.
E.g. 36 g of sodium chloride in 100g of water at 25° C
forms saturated solution.
(ii) Unsaturated solution : Unsaturated solution is
one that contains less solute than that of the saturated solution at a given
temperature.
E.g. 10 g or 20 g or 30 g of Sodium chloride in 100 g
of water at 25° C
2. Write notes on various factors affecting solubility.
Answer:
There
are three main factors which govern the solubility of a solute. They are:
Nature of the solute and solvent, Temperature, Pressure
Nature of the solute and solvent:
(i) The nature of the solute and solvent plays an
important role in solubility.
(ii) Solubility is based on the phrase “like dissolves
like”. The expression means that dissolving occurs when similarities exist between
the solvent and the solute. For example: Common salt is a polar compound and
dissolves readily in polar solvent like water.
(iii) Non-polar compounds are soluble in non-polar
solvents. For example: Sulphur dissolves in carbon disulphide.
Effect of Temperature :
Solubility of Solids in Liquid:
(i) Generally, solubility of a solid solute in a
liquid solvent increases with increase in temperature.
(ii) In endothermic process, solubility increases with
increase in temperature.
(iii) In exothermic process, solubility decreases with
increase in temperature.
Solubility of Gases in liquid :
Solubility of gases in liquid decrease with increase in temperature.
Effect of Pressure : When the pressure is increased,
the solubility of a gas in liquid increases. When pressure is increased, more
gas molecules strike the surface of the liquid and mix into the solution.
3. a) What happens when MgSO4.7H2O is heated? Write the appropriate equation
b) Define solubility
Answer:
a) When magnesium sulphate heptahydrate crystals are
gently heated, it loses seven water molecules, and becomes anhydrous magnesium
sulphate.
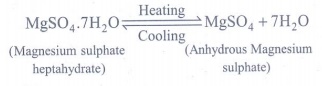
(Magnesium sulphate heptahydrate)
(Anhydrous Magnesium sulphate)
b)
Solubility is defined as the number of grams of a solute that can be dissolved
in l00g of a solvent to form its saturated solution at a given temperature and
pressure.
Solubility
= [ Mass of the solute / Mass of the solvent ] × 100
4. In what way hygroscopic substances differ from deliquescent substances.
Answer:
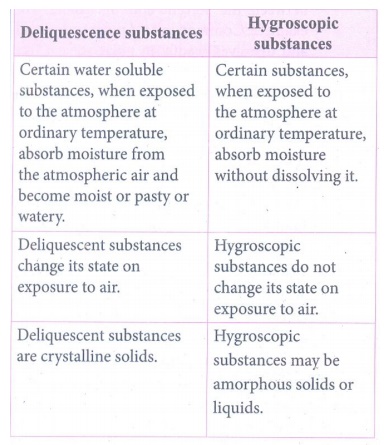
Deliquescence
substances
•
Certain water soluble substances, when exposed to the atmosphere at ordinary
temperature, absorb moisture from the atmospheric air and become moist or pasty
or watery.
•
Deliquescent substances change its state on exposure to air.
•
Deliquescent substances are crystalline solids.
Hygroscopic
Substances
•
Certain substances, when exposed to the atmosphere at ordinary temperature,
absorb moisture without dissolving it.
•
Hygroscopic substances do not change its state on exposure to air.
•
Hygroscopic substances may be amorphous solids or liquids.
5. A solution is prepared by dissolving 45 g of sugar in 180 g of water. Calculate the mass percentage of solute.
Answer:
Mass
percentage = ( Mass of the solute / Mass of the solution ) × 100
=
[ Mass of the solute / (Mass of the solute + Mass of the solvent)] × 100
=
[ 45 / (45+180)] × 100 = 45 / 225 × 100
Mass
percentage = 20%
6. 3.5 litres of ethanol is present in 15 litres of aqueous solution of ethanol. Calculate volume percent of ethanol solution.
Answer:
Volume
percentage = [Volume of the solute / Volume of the solution] × 100
=
[3.5 / 15] × 100
= 23.33%
VII. HOT
1. Vinu dissolves 50 g of sugar in 250 ml of hot water, Sarath dissolves 50 g of same sugar in 250 ml of cold water. Who will get faster dissolution of sugar? and Why?
50 g of sugar in 250 ml of hot water will dissolve faster as solubility of solid solute in liquid solvent increases with increase in temperature.
2. 'A' is a blue coloured crystaline salt. On heating it loses blue colour and to give 'B'. When water is added, 'B' gives back to 'A'. Identify A and B, write the equation.
CuSO4.5H2O → Heating → CuSO4 + 5H2O
CuSO4.5H2O ← Cooling ← CuSO4 + 5H2O
CuSO4.5H2O ↔ CuSO4 + 5H2O
(A) : CuSO4.5H2O : Copper sulphate Pentahydrate - Blue
(B) : CuSO4 : Anhydrous Copper sulphate - White
3. Will the cool drinks give more fizz at top of the hills or at the foot? Explain
Cool drinks will fizz more at the top of the hill since when pressure decrease solubility of a gas in liquid decreases so CO2 bubbles out as a gas in a soda can.
Related Topics