Chapter: Medicine and surgery: Genitourinary system
Bladder outflow obstruction - Disorders of the bladder and prostate
Disorders of the bladder and prostate
Bladder outflow obstruction
Definition
Obstruction to urinary flow from the bladder to the urethral meatus.
Incidence/prevalence
Common in men.
Age
Increases with age
Sex
M > F
Aetiology
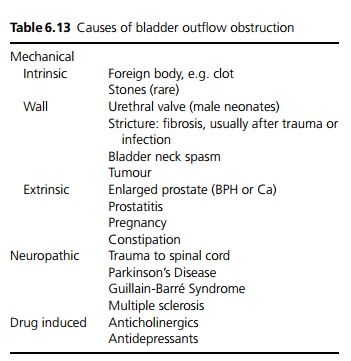
The causes of bladder outflow obstruction are shown in Table 6.13.
Pathophysiology
A reduction of >70% in the urethral lumen or vesicourethral junction (VUJ) causes obstruction, leading to reduced flow, increased voiding pressure and compensatory bladder hypertrophy. Over time, the bladder distends, then the ureters (causing hydroureters) and finally the renal pelvises. Often there may be an underlying chronic obstruction for example an enlarged prostate. Another factor may then cause acute urinary retention, e.g. constipation, bed rest (e.g. after surgery).
Clinical features
The symptoms depend on the speed of onset and degree of obstruction.
· Acute obstruction (acute urinary retention) causes severe discomfort, due to a wish to void urine, without the ability to do so. The bladder is tender, palpably enlarged. There is complete anuria, although there may be small amounts of urine voided due to overflow incontinence.
· Chronic obstruction causes three features: hesitancy, poor urinary stream (<10 mL/second) and terminal dribbling. Frequency and nocturia are not symptoms of obstruction. The symptoms usually develop over years, and if left untreated patients may present with renal failure. However, polyuria and/or nocturia may be symptoms of the loss of concentrating ability of the tubules, which can occur in long-standing obstruction.
Macroscopy
Dilation above the obstruction. Bladder trabeculation.
Complications
As a result of chronic obstruction, the bladder dilates and fails to empty fully, defined as >50 mL residual urine (normally 5–10 mL in young, fit person). Renal failure can be caused by both acute and chronic obstruction. Chronic urinary retention leads to:
· Reduced functional bladder capacity and therefore increased frequency.
· Recurrent UTI’s.
· Stone formation can be caused by urinary stasis, UTI’s predispose to stone formation, and also stones may predispose to infection.
Management
Relief of the obstruction is usually by insertion of a urinary catheter, followed by treatment of the underlying cause.
Related Topics