Chapter: Electrical machines : Synchronous Generator
Armature Reaction Reactance - Synchronous Generators
Armature Reaction Reactance
Armature
reaction refers to the influence of the armature flux on the field flux in the
air gap when the stator windings are connected across a load.
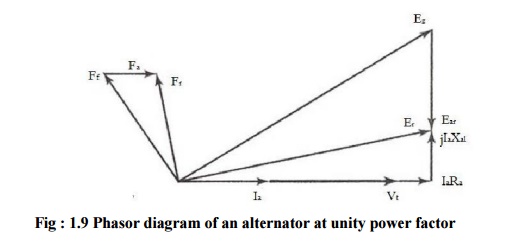
If Ff
is the field mmf in the generator under no load, then the generated voltage Eg
must lag Ff by 90o. Per phase armature current Ia
produces armature mmf Fa which is in phase with Ia . The
effective mmf is Fr.
The
armature mmf Fa will induced an emf Ear in the armature
winding. Ear is called the armature reaction emf. This emf will lag
its mmf by 90o. Hence the resultant armature voltage is the vector
sum of the no-load voltage Eg and armature reaction emf Ear
.
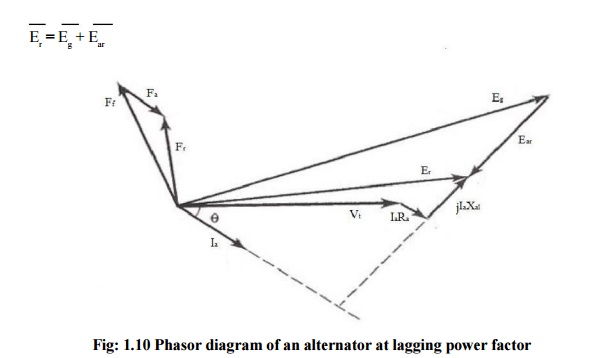
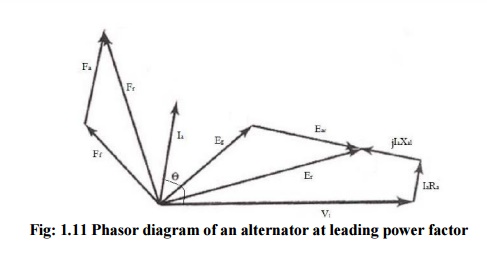
From the
observations of the phasor diagrams for lagging and leading power factors, that
the resultant mmf Fr is smaller or larger depending on the power
factor. As a result the terminal voltage Vt is larger or smaller
than the no-load induced emf when the power factor is leading or lagging.
Since the
armature reaction emf Ear lags the armature mmf Fa or Ia
by 90o, so it can be expressed as
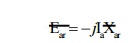
Where Xar
is called armature reaction reactance.
Related Topics