Chapter: 11th Political Science : Chapter 7 : Political Thought
Aristotle (384 - 322 BCE) - Political Thought
Aristotle (384 - 322 BCE)
Learning Objectives
·
To understand the
Political thought of Aristotle.
·
This will help to
compare thinkers on similar concept
·
To gain knowledge
about
Aristotle ideas on Ideal State, Citizenship, normal and perverted
forms of constitution and Monarchy, forms of government and democracy

Life and Times
William Ebenstien says” In the One history of
political philosophy no has surpassed Aristotle in encyclopaedic interest
and accomplishment”.
Aristotle was
Plato’s student at his ‘Academy’. After Plato’s death, Aristotle
found his own school called ‘The Lyceum’ in 335 BCE. It is here that Alexander
studied under Aristotle. The teaching and research program included every
branch of knowledge. Aristotle was born in Stagira in 384
BCE. Unlike Plato, Aristotle came from an upper middle
class family. His father Nicomachus was the personal physician to king Amyntas
of Macedon.
‘Aristotle’ whose name means ‘the
best purpose’ stood true to his name when he proposed the ‘Best Practicable
State’ as opposed to Plato’s ‘Ideal State’. According to Aristotle,
“the State exists for an end and this end is the supreme good of man in both
moral and intellectual life”.
Aristotle’s Works
He wrote many books on subjects ranging from Greek
literature to Zoology. But his most famous work is called ‘Politics’ from which
modern Political Science has grown. Thus he is called as the ‘father of
Political Science’. Though the exact date of its publication is not known, it
is a voluminous work consisting of 8 books and having more than 1000 pages.
Unlike Plato’s agreement with his teacher Socrates,
Aristotle
did not agree on many things his teacher Plato had to say.
Aristotle’s Thought
Almost all his political ideas are known through
his book ‘Politics’.
State as a Natural Institution
According to him authority of the State is moral
and the State is natural. Since the family could not satisfy the ever
increasing needs of the people, they had to come out of their limited circle
and thought of creating the State. The families combined together to make the
State and made it a perfect association. Aristotle believes that the State is
an individual writ large because the individual can think of perfection only in
a State.
Functions of the State
According to Aristotle the foremost function of
the State is to promote good life and create essential conditions for mental,
moral and physical development of the people. The State should also function in
such a way that good habits of individuals are converted into good actions and
promote good, happy and honourable life.
Theory of Citizenship
Aristotle did not
believe that mere residence or enjoyment of legal rights or birth should confer
the right of citizenship on a person. He said, “It is the function which entitles
a person to become citizen”. A person should participate in the popular
assembly which was vested with the authority of exercising sovereign powers. A
citizen should be able to partake in decision making process of the government.
Classification of States
He classifies States on quantitative as well as
qualitative basis:
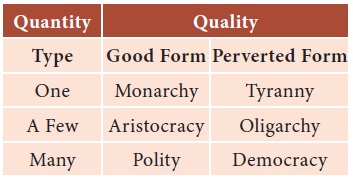
According to Aristotle, if sovereignty resides in
one person it is Monarchy. It degenerates into Tyranny. Thus the people wrest
the State from the tyrant and give it to a few rulers and thus Aristocracy
comes into being. Then it perverts into Oligarchy, people again revolt and
transfer power to many rulers by which the State becomes a Polity. When this
degenerates, it becomes a Democracy because these rulers no longer have sight
of the common good for which the State came into being. This again gives rise
to Monarchy.
Views on Slavery
According to Aristotle , the slave is the first
of the animate property of a Master, i.e., the slave is first among all living
property of the household of which the master is the head. He says those who
are not virtuous are slaves. The slave is an instrument of action and not that
of production because as soon as he starts performing productive functions, he
loses his character as a slave and becomes virtuous.
Views on Family
Aristotle believes
that the family is a natural institution and in fact it existed prior to the
State. It is natural as individuals become members from their very birth. It is
the starting point of moral life and the nucleus of the State.
Views on Property
Aristotle supported
the possession of private property which is essential for good and normal
life. However, he prescribed limits to private property. He also objected to
the abolition of private property.
Aristotle an Liesure
The reason Aristotle says the citizens of a
State must have property as well as slaves is because the citizens must have
leisure, so that the citizen may spend useful time in thinking and deliberating
on furthering the good life of all though the State.
Views on Revolution
Aristotle is of the
opinion that revolutions occur firstly due to constitutional changes.
This change could be large or small. For e.g.:
change from Monarchy to Tyranny could set off a revolution by the people.
Secondly he says revolutions could occur due to loss of purpose of the State
though there may not be any change in the State’s constitution.
Aristotle’s Six Forms of
Government
Thus, Aristotle is still considered one of
the greatest thinkers in politics, psychology and ethics. His intellectual
range was vast covering most of the sciences and many of the arts. His works
have laid the foundation of centuries of philosophy. Even after the
intellectual revolution of the Renaissance, the Reformation and the
Enlightenment, Aristotelian concepts remain embedded in world philosophy.
Therefore, he is undoubtedly one of the most influential philosophers of all
time.
ACTIVITY
Divide the class
into Plato’s
group and Aristotle’s group and debate in support of each philosopher’s
theories.
List out the
various other works of Aristotle.
Find out the name
of the school of philosophy established by Aristotle.
Compare modern citizenship with Aristotle’s
ideas of citizenship.
ACTIVITY
DO YOU AGREE?
Tyranny, oligarchy and democracy form
of governments the rulers seek their own personal profit. Do you agree?
Discuss.
Related Topics