Chapter: Microprocessor and Microcontroller
8051 Instructions
8051 Instructions
8051 has
about 111 instructions. These can be grouped into the following categories
1. Arithmetic
Instructions
2. Logical
Instructions
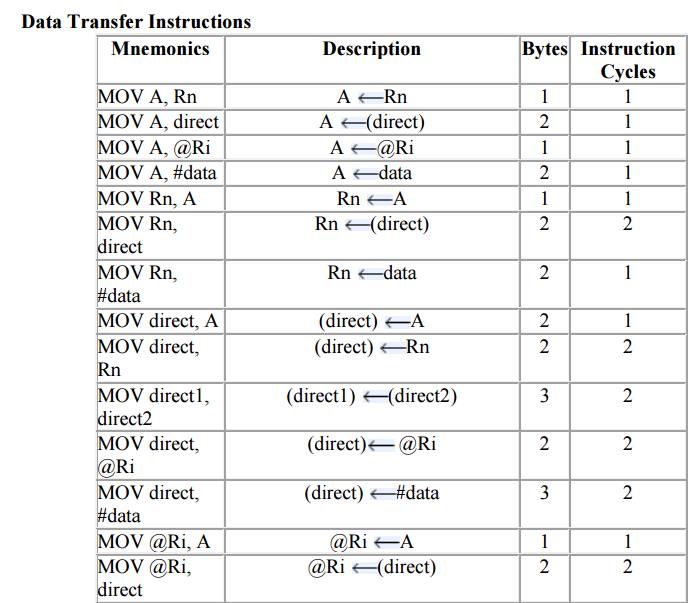
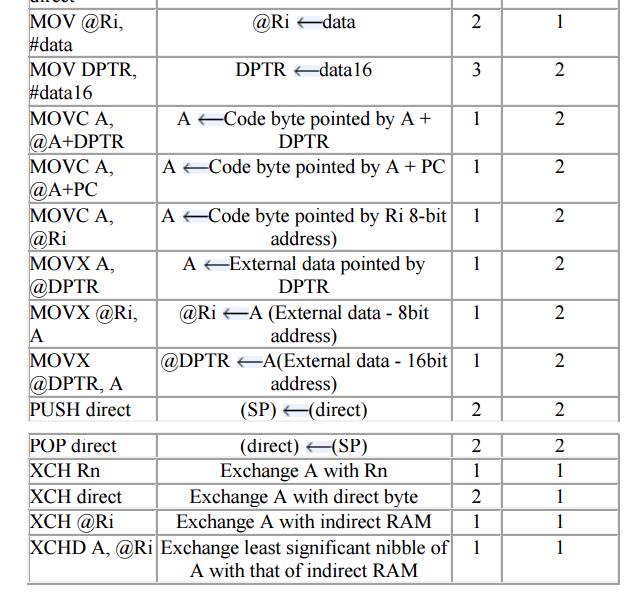
3. Data Transfer
instructions
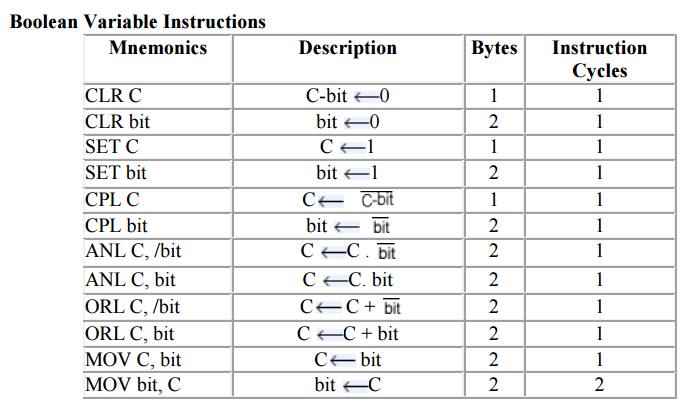
4. Boolean
Variable Instructions
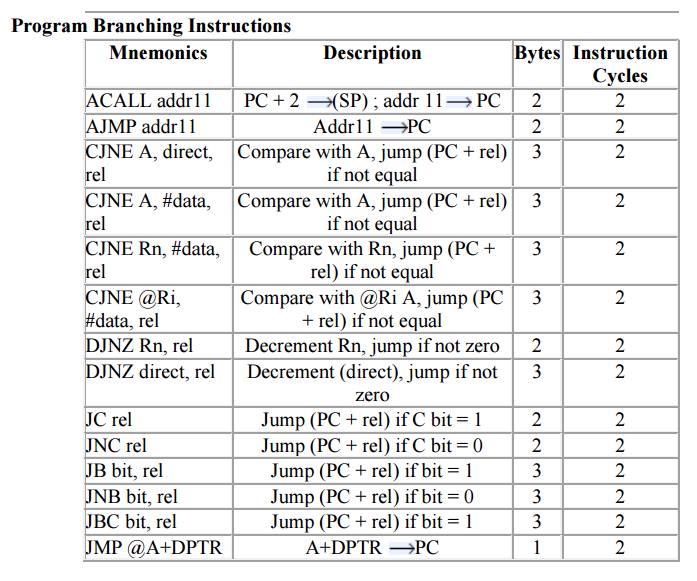
5. Program
Branching Instructions
The
following nomenclatures for register, data, address and variables are used
while write instructions.
A: Accumulator
B: "B"
register
C: Carry bit
Rn:
Register R0 - R7 of the currently selected register bank
Direct:
8-bit internal direct address for data. The data could be in lower 128bytes of
RAM (00 - 7FH) or it could be in the special function register (80 - FFH).
@Ri:
8-bit external or internal RAM address available in register R0 or R1. This is
used for indirect addressing mode.
#data8:
Immediate 8-bit data available in the instruction.
#data16:
Immediate 16-bit data available in the instruction.
Addr11:
11-bit destination address for short absolute jump. Used by instructions AJMP
& ACALL. Jump range is 2 kbyte (one page).
Addr16:
16-bit destination address for long call or long jump.
Rel: 2's
complement 8-bit offset (one - byte) used for short jump (SJMP) and all
conditional jumps.
bit:
Directly addressed bit in internal RAM or SFR
Arithmetic Instructions
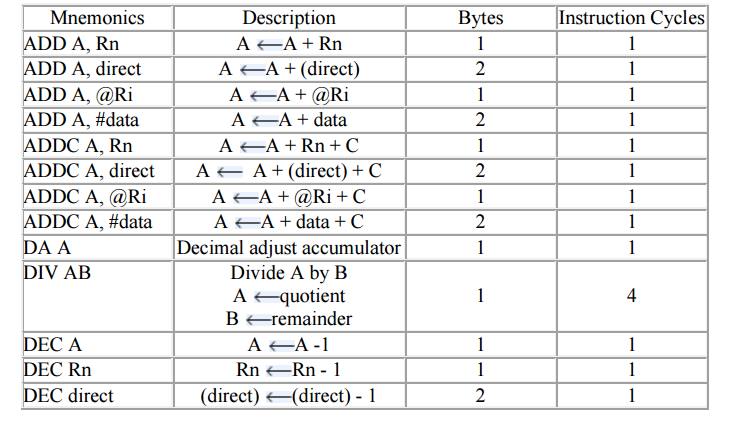
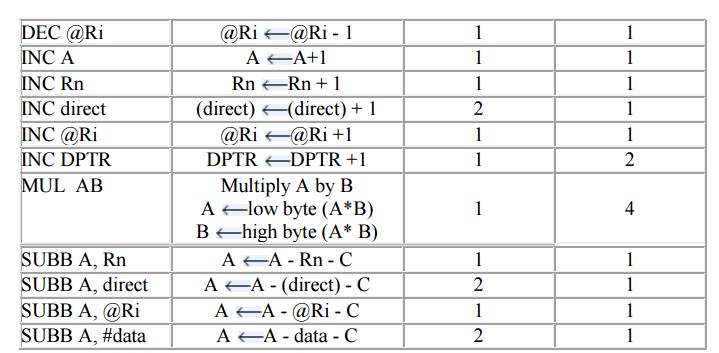
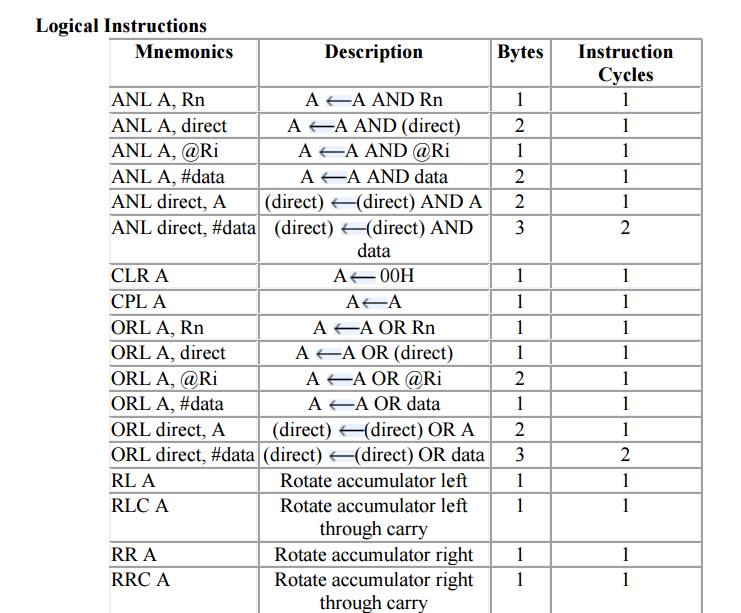
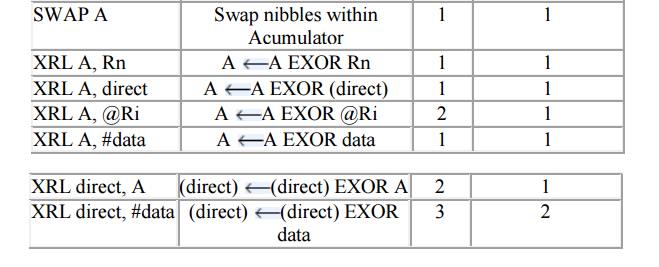
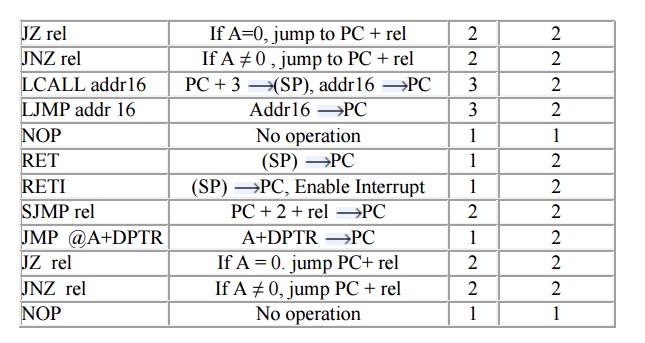
Example
programs
Character
transmission using a time delay
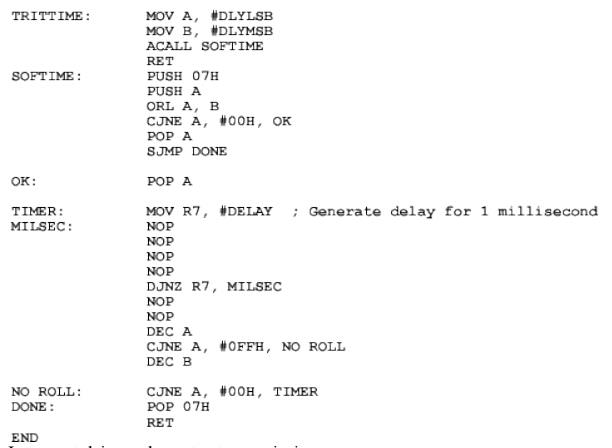
A program
shown below takes the character in 'A' register, transmits it, delays for
transmission time, and returns to the calling program. Timer-1 is used to set
the baud rate, which is 1200 baud in this program
The delay
for one character transmission (in Mode 1 i.e.10 bits) is 10/2400 = 0.00833
seconds
Or, 8.33
milliseconds
Hence
software delay of 10ms is used.
Timer-1
generates a baud rate close to 1200. Using a 12MHz crystal, the reload value is
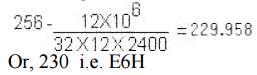
This
gives rise to an actual baud rate of 1202.
SMOD is
programmed to be 0.
Assembly
language Program is as follows

; Code to
wait for the transmission to complete
The
subroutine TRMITTIME generates a delay of about 10ms. With a clock of 12MHz,
one instruction cycle time is
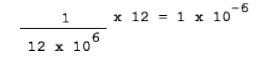
The loop
"MILSEC" generates a delay of about 1 x 10-3 sec. This gets executed
10 times for a total delay of 10 x 10-3 sec or 10ms
Interrupt
driven character transmission
In 8051,
when a character is transmitted, SBUF register becomes empty and this generates
a serial port interrupt (TI). TI and RI both point to the vector location 0023H
in the program memory. An interrupt service routine can be written at 0023H to
send the next character.
A program
is written here to transmit a character say 'A' continuously based on
interrupt. The microcontroller uses a clock of 12MHz with a baud rate of 1202.
The program is executed following a hardware reset.
Assembly
language program is as follows.

Interrupt
driven data reception
When a
character is received, if receive mode is enabled, RI flag is set. This leads
to the interruption of the main program and the processor goes to the interrupt
vector location, i.e.
0023H for
serial port. The interrupt service routine at 0023H gets executed to read the
character so that the next character can be received. The following program
receives a character on interrupt basis and outputs the character to port-1,
possibly for a display. The crystal frequency is12MHz and baud rate is set at
1202 baud.
Assembly
language program is as follows

Related Topics