Chapter: Civil : Railway Airport Harbour Engineering : Railway Engineering : Sleepers
Types of concrete sleepers
Types
of concrete sleepers
The various types of concrete
sleepers (prestressed, pre-tension, post-tension, and two-block) being
manufactured by Indian Railways have been described in Table 7.6.
Table
7.6 Different
types of concrete sleepers being manufactured by Indian Railways
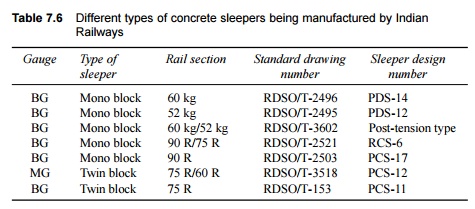
Mono-block prestressed concrete sleepers
with pandrol clips
The
mono-block prestressed concrete sleeper (Fig. 7.11), which is similar to the
German B-58 type of sleeper, has an overall length of 2750 mm and a weight of
270 kg approximately. The sleeper has a trapezoidal cross section with a width
of 154 mm at the top and 250 mm at the bottom and a height of 210 mm at the
rail seat. A cant of 1 in 20 is provided on the top surface of the sleeper for
a distance of 175 mm on either side of the centre line of the rail to cover the
area of rail fittings. The sleeper is prestressed with 18 high tensile steel
(HTS) strands of 3 × 3 mm diameter and 12 6-mm-diameter mild steel links. The
initial prestressing of the steel is 100 kg/cm2. The 28-day crushing
strength of the concrete is normally not less than 525 kg/cm2.
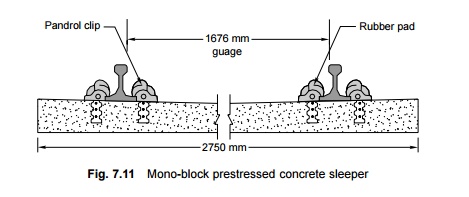
The rail
rests on a grooved 130 × 130 mm rubber pad, with the grooves lying parallel to
the axis of the rail. The fastenings provided for the 52-kg rail are Pandrol
clips, which are held in malleable cast iron inserts as shown in Fig. 7.12.
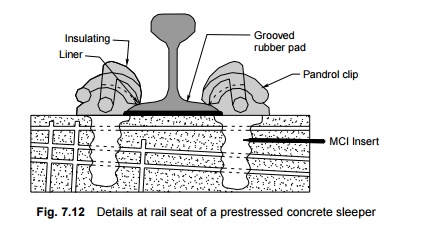
PCS-12 and PCS-14
PCS-12 is
the latest type of prestressed concrete (PRC) sleeper for use on BG routes with
52-kg rails and elastic rail clips. For use with 60-kg rails and elastic rail
clips, the PCS-14 sleeper has been standardized on Indian Railways.
The important dimensions of both
of these types of sleepers are shown in Fig. 7.13 and listed as follows.
l Length =
2750 mm
l Weight =
267 kg
l Reinforcement:
Eighteen 3 × 3 mm diameter strands
l Concrete
is to be of controlled quality with a minimum 28-day crushing strength of 525
kg/cm2
l Each
strand to be tensioned with an initial tensile force of 2730 kg
Mono-block post-tension type of concrete
sleepers for BG
The first factory in India for
the manufacture of post-tension type of mono-block concrete sleepers was set up
by Northern Railways at Allahabad in collaboration with M/s Dyckerhoff and
Widmann (D&W) of West Germany. The factory, which started production in
1981, has a planned capacity of manufacturing 300,000 concrete sleepers per
year. The salient feature of post-tension type of concrete sleepers are the
following.
Size of sleeper
l Length =
2750 mm
l Width at
centre = 160 mm (top)
200 mm
(bottom)
l Depth at
centre = 180 mm
l Weight =
295 kg
Design features
l Initial
prestressing force = 37 t
l Final
prestressing force = 31 t
l Minimum
concrete strength in 28 days = 550 kg/cm2
l Minimum
strength of concrete at the time of applying prestress = 450 kg/
cm2
The use of concrete sleepers
using the post-tension method has not been successful on Indian Railways and
its manufacture has since been stopped.
Mono-block PRC sleepers for MG (PCS-17)
A design
for mono-block PRC sleepers (PCS-17) has recently been standardized for MG. The
sleeper has a trapezoidal cross section similar to that of a BG sleeper. The
concrete should have a 28-day compressive strength of 525 kg/cm2.
The salient features of this sleeper are the following (Fig. 7.14).
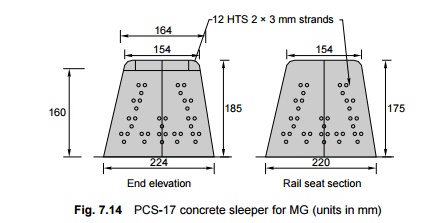
l Length =
2000 mm
l Weight =
158.5 kg
Reinforcement:
Twelve 3 × 3 mm diameter strand of HTS wire tensioned to initial force of 2730
kg
PRC sleepers can be used for 90 R
rails with elastic rail clips and glass filled nylon liners (GFN 66) and on
sole plates.
Two-block RCC sleeper for BG yards
A design for a two-block RCC
sleeper for BG yards has been standardized by RDSO as per drawing number
RDSO/T-2521 for extensive trials on Indian Railways. There is a general
scarcity of wooden and CST-9 sleepers for use in BG yards and the new RCC
sleepers will ease the situation in a big way. Some of the salient features of
this sleeper are as follows.
l Considering
low speeds in yard lines and less impact effect, the rail seat design load has
been taken only as 10 t without any lateral thrust.
l
Size at rail seat (top width × bottom width ×
depth) = 22 cm × 30 cm × 17 cm
l Overall
length of the sleeper = 247.5 cm
l Weight of
the sleeper = 170 kg
l Main
reinforcement in each block
n At top: Five 8-mm-diameter steel bars
n At bottom: Two 8-mm-diameter steel bars
l The
fastenings used are steel clips and a spring washer with screw fitted to
a
polythene dowel.
Two-block concrete sleeper for MG yards
Two-block concrete sleepers for
use in MG yards have recently been developed. The sleeper consists of two
cement concrete blocks, each weighting about 36 kg and consisting of an MS
reinforcement of about 7 kg. The two RCC sleeper blocks are connected by an
angle tie bar of 55 × 50 × 6 mm section and 1.5 m length. The rail is fixed to
the sleeper block either by a clip and bolt arrangement or by polythene dowels
and rail screws. A pad is provided below the rail seat to provide cushioning.
Mono-block versus two-block concrete
sleepers
There are relative advantages and
disadvantages of mono-block and two-block concrete sleepers. Some of these are
enumerated below.
(a) Mono-block
sleepers give better longitudinal and lateral stability to the track compared
to two-block concrete sleepers.
(b) The
mono-block concrete sleeper, being a monolithic concrete mass, is likely to
have a longer working life compared to the two-block concrete sleeper connected
with a tie bar. In the latter case, a tie bar is weak and has a comparatively
shorter life due to corrosion, etc.
(c) The
mono-block concrete sleeper requires heavy capital expenditure for its
manufacture, being a prestressed reinforced concrete unit, compared to the
two-block sleeper, which is an ordinary reinforced concrete sleeper.
(d) In a
mono-block prestressed concrete sleeper, a crack that develops because of
overstressing is likely to close down upon return to normal condition, whereas
in a two-block sleeper, such a crack will continue to remain open.
(e) Mono-block
sleepers are likely to become centre-bound unlike two-block sleepers.
(f) During
derailments and rough handling the tie bars of two-block sleeper get deformed,
thereby affecting the gauge.
(g) In a
two-block sleeper, the two blocks are not likely to rest on the ballast in a
way that each rail is properly inclined to the vertical, a feature which could
affect the alignment and gauge of the track.
Related Topics