Chapter: Environmental Science and Engineering
Structure and Function of Forest Ecosystem(Terrestrial Ecosystem)
FOREST ECOSYSTEM (TERRESTRIAL ECOSYSTEM)
Introduction
v A forest
is an area with a high density of trees.
v World’s
total land area is 13,076 million hectares - (Source: FAO; 1989)
v Of which
total forests account for about 31% of the world’s land area.
v In India,
the forest cover is roughly 19% of the total land area.
v The
forest ecosystems are of great concern from the environmental point of view.
v It
provides numerous environmental services like;
Ø Nutrient
cycling,
Ø Maintaining
biodiversity
Ø Providing
wildlife habitat
Ø Affecting
rainfall patterns
Ø Regulating
stream flow
Ø Storing
water
Ø Reducing
flooding
Ø Preventing
soil erosion
Ø Reclaiming
degraded land & many more….
v Apart
from environmental values, forest ecosystems have some traditional values as
well.
v Examples
are:
Ø Fire Wood
& Timber.
Ø Fruits.
Ø Gums.
Ø Herbs
& drugs.
Structure and Function of Forest Ecosystem
I. Biotic components
v The
various biotic components, representatives from the three functional groups, of
a forest ecosystem are:
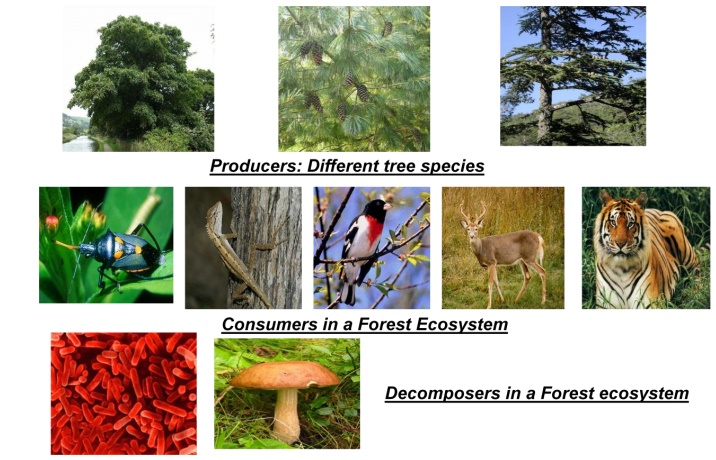
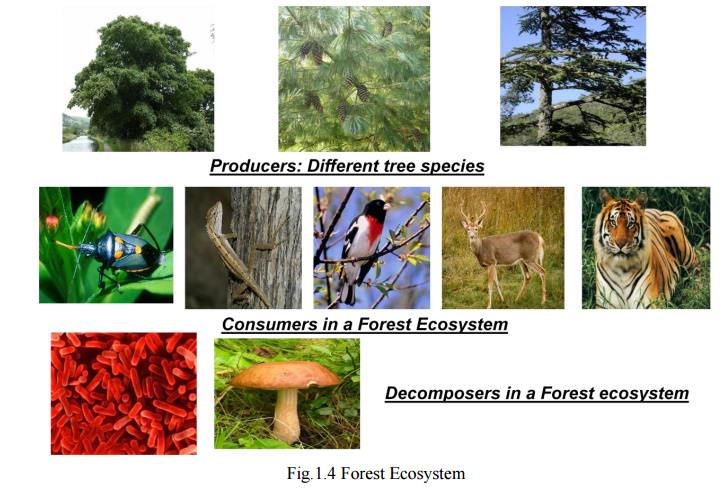
1) Producer Organisms
v In a
forest, the producers are mainly trees.
v Trees are
of different kinds depending upon the type of forest developed in that climate.
v Apart
from trees, climbers, epiphytes, shrubs and ground vegetation.
v Dominant
species of trees in major types of forest ecosystems are:
v Tectona
grandis, Acer, Betula, Picea, Pine, Cedrus.
2) Consumers
v In a
forest, consumers are of three main types;
a) Primary Consumers
v These are
Herbivores which feed directly on producers.
Eg:
v Ants,
Beetles, Bugs, spiders etc. feeding on tree leaves.
v Larger
animals such as Elephants, Deer, giraffe etc. grazing on shoots and/or fruits
of trees.
b) Secondary Consumers
v These are carnivores and feed on primary
consumers.
Eg:
Birds, Lizards, Frogs, Snakes and Foxes.
c) Tertiary Consumers
v These are
secondary carnivores and feed on secondary consumers
v These
include top carnivores like Lion, Tiger.
3) Decomposers
v These
include wide variety of saprotrophic micro- organism like;
v Bacteria
(Bacillus Sp., Clostridium sp., pseudomonas.
v Fungi
(Aspergillus sp., Ganoderma sp., Fusarium.
v Actinomycetes
(Streptomyces).
v They
attract the dead or decayed bodies of organisms & thus decomposition takes
place.
v Therefore,
nutrients are released for reuse.
II. Abiotic components
v These
include basic inorganic & organic compounds present in the soil &
atmosphere.
v In
addition dead organic debris is also found littered in forests.
Related Topics