Chapter: Basic Concept of Biotechnology : Animal Biotechnology
Methods of genetic manipulation in animals
Methods of genetic manipulation in
animals:
A
transgenic animal is one that carries a foreign gene that has been deliberately
inserted into its genome. The foreign gene is constructed using recombinant DNA
methodology. Two methods of producing transgenic animals are widely used: (1)
transforming embryonic stem cells (ES cells) growing in tissue culture with the
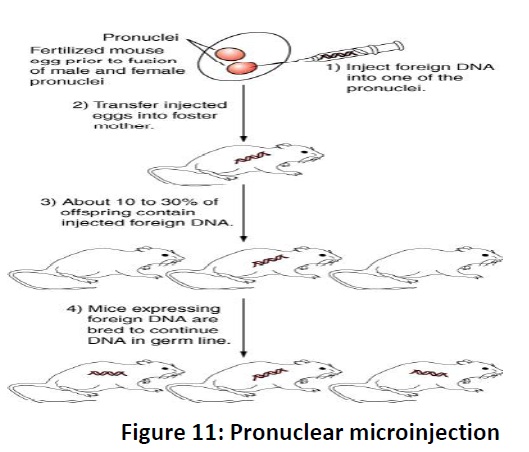
desired DNA and (2) injecting the desired gene into the pronucleus of a
fertilized egg. (3) Desirab Retrovirus-mediated transgenesis. (4) Pronuclear
microinjection (Fig. 11). (5) Sperm-mediated transfer.
Genes
from one species are transferred to other animals or species to improve the
productivity of livestock. Faster growth rates, leaner growth patterns, more
resistance to disease, increased milk production, more efficient metabolism,
and transferring antimicrobial genes to farm animals are some of the goals of
transgenic animal researchers. These include laboratory culture of large
numbers of viable embryos for nonsurgical transfer to surrogate mothers,
development of methods for sexing sperm and embryos, cloning embryos by nuclear
transplantation and gene transfer to create livestock with superior performance
traits. In all cases material progress will depend upon a deeper understanding
of the underlying physiological and developmental control mechanisms and public
confidence that due regard is being paid to animal welfare, and to social and
environmental implications. Genetic improvement of livestock depends on access
to genetic variation and effective methods for exploiting this variation.
Genetic diversity constitutes a buffer against changes in the environment and
is a key in selection and breeding for adaptability and production on a range
of environments.
In
developed countries, breeding programmes are based upon performance recording
and this has led to substantial improvements in animal production. Developing
countries have distinct disadvantages for setting up successful breeding
programmes: infrastructure needed for performance testing is normally lacking
because herd sizes are normally small and variability between farms, farming
systems and seasons are large; reproductive efficiency is low, due mainly to
poor nutrition, especially in cattle; and communal grazing precludes
implementation of systematic breeding and animal health programmes.
Related Topics