Chapter: Digital Electronics : Synchronous and Asynchronous Sequential Circuits
Mealy and Moore Models
MEALY AND MOORE MODELS
The most general model of a sequential circuit has inputs, outputs and internal states. It is common to distinguish between two models of sequential circuits:
· Mealy model – The output is a function of both the present state and input.
· Moore model – The output is a function of the present state only.
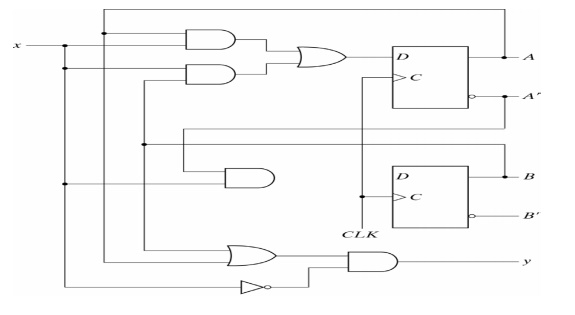
An example of a Mealy model is:
An example of a Moore model is:
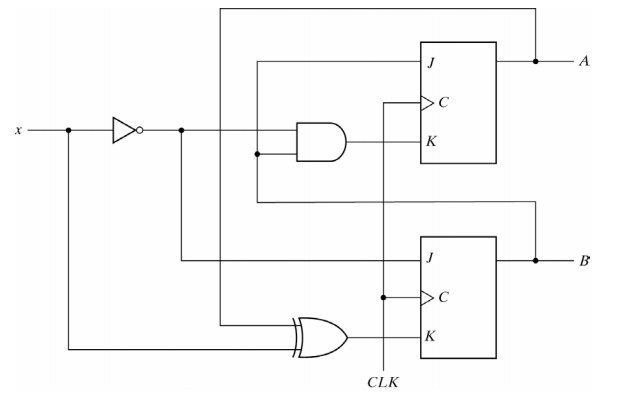
In a Moore model, the outputs of the sequential circuit are synchronized with the clock because they depend on only flip-flop outputs that are synchronized with the clock
In a Mealy model, the outputs may change if the inputs change during the clock cycle. To achieve synchronization, the inputs must be synchronized with the clock and the outputs must be sampled only during the clock edge.
Related Topics