Applications of Operational Amplifier - Log Amplifier using Operational Amplifier | Linear Integrated Circuits : Applications of Operational Amplifier
Chapter: Linear Integrated Circuits : Applications of Operational Amplifier
Log Amplifier using Operational Amplifier
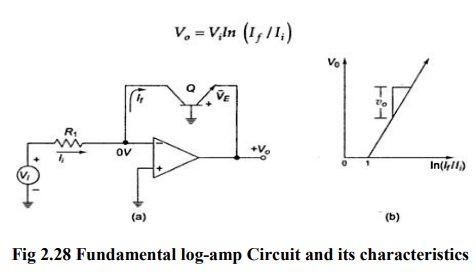
There
are several applications of log and antilog amplifiers.
Antilog
computation may require functions such as ln x, log x or sin hx.
Uses:
Direct
dB display on a digital Voltmeter and Spectrum analyzer.
Log-amp
can also be used to compress the dynamic range of a signal.
A
grounded base transistor is placed in the feedback path. Since the collector is
placed in the feedback path. Since the collector is held at virtual ground and
the base is also grounded, the transistor‘s= voltage[-current−1] relationship
becomes that of a diode and is given by,
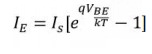
and
since Ic =IE for a grounded base transistor IC = Is e kT
Is-emitter
saturation current ≈10-13A
k=Boltzmann‘s
constant
T=absolute
temperature (inºK)
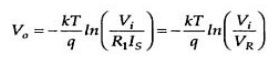
where
Vref =R1Is
The
output voltage is thus proportional to the logarithm of input voltage.
Although
the circuit gives natural log (ln), one can find log10, by proper scaling
Log10X=0.4343
ln X
The
circuit has one problem.
The
emitter saturation current Is varies from transistor to transistor and with
temperature. Thus a stable reference voltage V ref cannot be obtained. This is
eliminated by the circuit given below
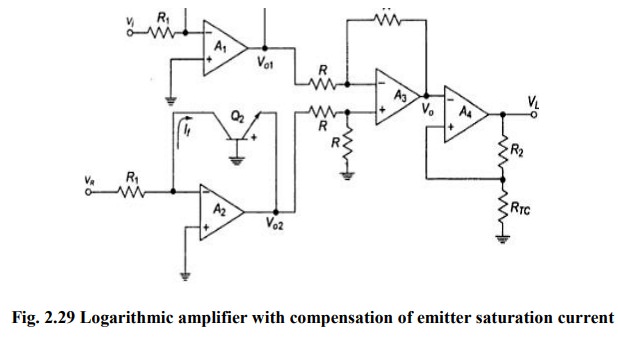
The
input is applied to one log-amp, while a reference voltage is applied to one
log-amp, while a reference voltage is applied to another log-amp. The two
transistors are integrated close together in the same silicon wafer. This
provides a close match of saturation currents and ensures good thermal
tracking.
Assume IS1=IS2=IS
Thus
the reference level is now set with a single external voltage source. Its
dependence on device and temperature has been removed. The voltage Vo is still
dependent upon temperature and is directly proportional to T. This is
compensated by the last op-amp stage A4 which provides a non-inverting gain of
(1+R2/RTC). Temperature compensated output voltage VL
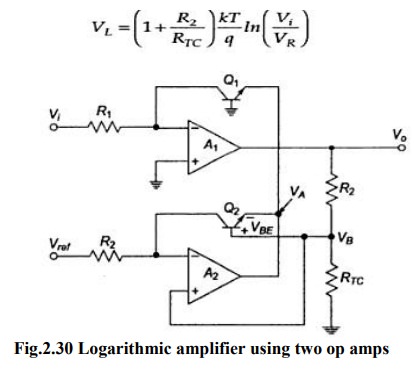
Where
RTC is a temperature-sensitive resistance with a positive
coefficient of temperature (sensor) so that the slope of the equation becomes
constant as the temperature changes.
Related Topics