Introduction - Electromagnetic Waves | 12th Physics : Electromagnetic Waves
Chapter: 12th Physics : Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic Waves
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
INTRODUCTION
We see the world around
us through light. Light from the Sun is one of the sources of energy without
which we human beings cannot survive in this planet. Light plays crucial role
in understanding the structure and properties of various things from atom to
universe. Without light, even our eyes cannot see objects. What is light?. This
puzzle made many physicists sleepless until middle of 19th century. Earlier,
many scientists thought that optics and electromagnetism are two different
branches of physics. But from the work of James Clerk Maxwell, who actually
enlightened the concept of light from his theoretical prediction is that light
is an electromagnetic wave which moves with the speed equal to 3 Ă— 108 m/s (in
free space or vacuum). Later, it was confirmed that light is just only small
portion of electromagnetic spectrum, which ranges from gamma rays to radio
waves.

In the unit 4, we
studied that time varying magnetic field produces an electric field (Faraday’s
law of electromagnetic induction). Maxwell strongly believed that nature must
possess symmetry and he asked the following question, “when the time varying
magnetic field produces an electric field, why not the time varying electric
field produce a magnetic field?”
Later he proved that
indeed it exists, which is often known as Maxwell’s law of induction. In 1888,
H. Hertz experimentally verified Maxwell’s predication and hence, this
understanding resulted in new technological invention, especially in wireless
communication, LASER (Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation)
technology, RADAR (Radio Detection And Ranging),
etc.
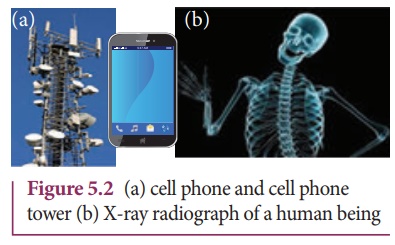
In today's digital
world, cell phones (Figure 5.2 (a)) have greater influence in our day to day
life. It is a faster and more effective mode of transferring information from
one place to another. It works on the basis that light is an electromagnetic
wave. In hospitals, the location of bone fracture can be detected using X-rays
as shown in Figure 5.2 (b), which is also an electromagnetic wave. For cooking
microwave oven is used. The microwave is also an electromagnetic wave. There
are plenty of applications of electromagnetic waves in engineering, medical
(example LASER surgery, etc), defence (example, RADAR signals) and also in
fundamental scientific research. In this unit, basics of electromagnetic waves
are covered.
Related Topics