Chapter: 12th Physics : Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic spectrum
Electromagnetic spectrum
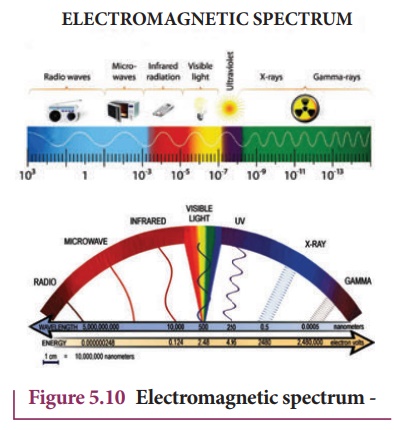
Electromagnetic spectrum
is an orderly distribution of electromagnetic waves in terms of wavelength or
frequency as shown in Figure 5.10.
Radio waves
It is produced by
oscillators in electric circuits. The wavelength range is 1 ├Ś 10-1 m
to 1 ├Ś 104 m and frequency range is 3 ├Ś 109 Hz to 3 ├Ś 104
Hz. It obeys reflection and diffraction. It is used in radio and television communication
systems and also in cellular phones to transmit voice communication in the
ultra high frequency band.
Microwaves
It is produced by
electromagnetic oscillators in electric circuits. The wavelength range is 1 ├Ś
10-3 m to 3 ├Ś 10-1 m and frequency range is 3 ├Ś 1011
Hz to 1 ├Ś 109 Hz. It obeys reflection and polarization. It is used
in radar system for aircraft navigation, speed of the vehicle, microwave oven
for cooking and very long distance wireless communication through satellites.
Infrared radiation
It is produced from hot
bodies (also known as heat waves) and also when the molecules undergo
rotational and vibrational transitions. The wavelength range is 8 ├Ś 10-7
m to 5 ├Ś 10-3 m and frequency range are 4 ├Ś 1014 Hz to 6
├Ś 1010 Hz. It provides electrical energy to satellites by means of
solar cells. It is used to produce dehydrated fruits, in green houses to keep
the plants warm, heat therapy for muscular pain or sprain, TV remote as a
signal carrier, to look through haze fog or mist and used in night vision or
infrared photography.
Visible light
It is produced by
incandescent bodies and also it is radiated by excited atoms in gases. The
wavelength range is 4 ├Ś 10-7 m to 7 ├Ś 10-7 m and
frequency range are 7 ├Ś1014 Hz to 4 ├Ś 1014 Hz. It obeys
the laws of reflection, refraction, interference, diffraction, polarization,
photo-electric effect and photographic action. It can be used to study the
structure of molecules, arrangement of electrons in external shells of atoms
and sensation of our eyes.
Ultraviolet radiation
It is produced by Sun,
arc and ionized gases. The wavelength range is 6 ├Ś 10-10 m to 4 ├Ś 10-7
m and frequency range are 5 ├Ś 1017 Hz to 7 ├Ś 1014 Hz. It
has less penetrating power. It can be absorbed by atmospheric ozone and harmful
to human body. It is used to destroy bacteria, sterilizing the surgical
instruments, burglar alarm, detect the invisible writing, finger prints and
also in the study of molecular structure.
X-rays
It is produced when
there is a sudden deceleration of high speed electrons at high-atomic number
target, and also by electronic transitions among the innermost orbits of atoms.
The wavelength range 10-13 m to 10-8 m and frequency
range are 3 ├Ś 1021 Hz to 1 ├Ś 1016 Hz. X-rays have more
penetrating power than ultraviolet radiation. X-rays are used extensively in
studying structures of inner atomic electron shells and crystal structures. It
is used in detecting fractures, diseased organs, formation of bones and stones,
observing the progress of healing bones. Further, in a finished metal product,
it is used to detect faults, cracks, flaws and holes.
Gamma rays
It is produced by
transitions of atomic nuclei and decay of certain elementary particles. They
produce chemical reactions on photographic plates, fluorescence, ionisation,
diffraction. The wavelength range is 1 ├Ś 10-14 m to 1 ├Ś 10-10
m and frequency range are 3 ├Ś 1022 Hz to 3 ├Ś 1018 Hz.
Gamma rays have high penetrating power than X-rays and ultraviolet radiations;
it has no charge but harmful to human body. Gamma rays provide information
about the structure of atomic nuclei. It is used in radio therapy for the
treatment of cancer and tumour, in food industry to kill pathogenic
microorganism.
EXAMPLE 5.4
A magnetron in a
microwave oven emits electromagnetic waves (em waves) with frequency f = 2450 MHz. What magnetic field
strength is required for electrons to move in circular paths with this
frequency?.
Solution
Frequency of the
electromagnetic waves given is f =
2450 MHz
The corresponding
angular frequency is
Žē= 2ŽĆf = 2 x 3.14 x 2450
x 106
= 15,386 x 106
Hz
= 1.54 ├Ś 1010
s-1
The magnetic field B = meŽē
/ |q|
Mass of the electron, me
= 9.22 x 10-31 kg
Charge of the electron
q =ŌłÆ1 . 60 ├Ś10ŌłÆ 19 C ŌćÆ
|q| = 1.60 ├Ś10ŌłÆ19 C
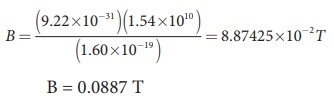
B = 0.0887 T
This magnetic field can be easily produced with a permanent magnet. So, electromagnetic waves of frequency 2450 MHz can be used for heating and cooking food because they are strongly absorbed by water molecules.
Related Topics