Chapter: 12th Physics : Electromagnetic Waves
Sources of electromagnetic Waves
Sources of electromagnetic Waves
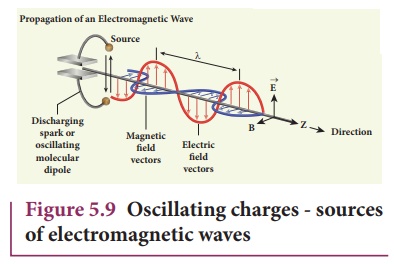
Any stationary source charge
produces only electric field (refer Unit 1). When the charge moves with uniform
velocity, it produces steady current which gives rise to magnetic field (not
time dependent, only space dependent) around the conductor in which charge
flows. If the charged particle accelerates, in addition to electric field it
also produces magnetic field. Both electric and magnetic fields are time
varying fields. Since the electromagnetic waves are transverse waves, the
direction of propagation of electromagnetic waves is perpendicular to the plane
containing electric and magnetic field vectors.
Any oscillatory motion
is also an accelerating motion, so, when the charge oscillates (oscillating
molecular dipole) about their mean position as shown in Figure 5.9, it produces
electromagnetic waves.
Suppose the
electromagnetic field in free space propagates along z direction, and if
the electric field vector points along y axis then the magnetic field vector
will be mutually perpendicular to both electric field and the propagation
vector direction, which means
E y = E sin( k z ŌłÆŽēt)
B x = B sin( k z ŌłÆŽēt)
where, Eo and
Bo are amplitude of oscillating electric and magnetic field, k is a
wave number, Žē is the angular frequency of the wave and k^ (unit vector,
here it is called k propagation vector) denotes the direction of propagation of
electromagnetic wave.
Note that both electric
field and magnetic field oscillate with a frequency (frequency of
electromagnetic wave) which is equal to the frequency of the source (here,
oscillating charge is the source for the production of electromagnetic waves).
In free space or in vacuum, the ratio between Eo and Bo
is equal to the speed of electromagnetic wave, which is equal to speed of light
c.
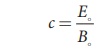
In any medium, the ratio
of Eo and Bo is equal to the speed of electromagnetic
wave in that medium, mathematically, it can be written as
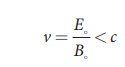
Further, the energy of
electromagnetic waves comes from the energy of the oscillating charge.
EXAMPLE 5.3
Compute the speed of the
electromagnetic wave in a medium if the amplitude of electric and magnetic
fields are 3 ├Ś 104 N C-1 and 2 ├Ś 10-4 T,
respectively.
Solution
The amplitude of the
electric field, Eo = 3 ├Ś 104 N C-1
The amplitude of the
magnetic field, Bo = 2 ├Ś 10-4 T. Therefore, speed of the
electromagnetic wave in a medium is
= 3 ├Ś104 / 2
├Ś10ŌłÆ4 = 1.5├Ś108 msŌłÆ1
Related Topics