Chapter: Obstetric and Gynecological Nursing : Normal Pregnancy
Antenatal Care
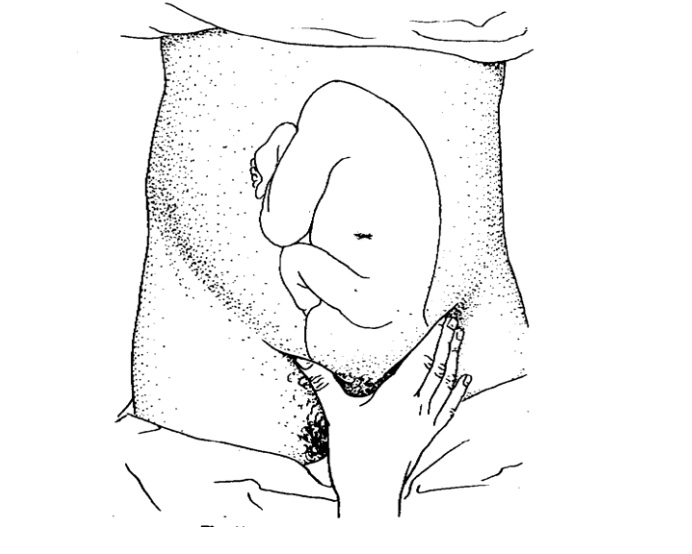
Antenatal Care
Definition: - Antenatal care is the care
given to a womanduring her pregnancy.
Objectives:
·
To promote and maintain good health of the mother and fetus during
pregnancy
·
To ensure that the pregnancy result in healthy infant and healthy
mother.
·
To detect early and treat appropriately 'high risk' conditions (Medical
or Obstetrical).
·
To prepare the woman for Labour, Lactation and the subsequent care of
the baby.
Early antenatal care is important as soon as possible after pregnancy
hasbeen confirmed (after one or two missed periods)
Defintions
Gravidity: Pregnancy
Primigravida = a woman pregnant for the first time
Multigravida = a woman who has had two or more
pregnancice
Parity- refers to delivery,
Nullipara = a woman who has not given
birth to a child birth)
Multipara a woman who has given birth to
more than onechild
Grandmultipara woman who has given birth to or
morechildren
Lie: is the relationship of the
long axis (spine) of the fetus tothe long axis of the mother’s uterus, and the
normal lie is longitudinal Abnormal are transverse, oblique and variable.
Attitude: is the relationship of the fetal
parts to one another,and the normal attitude is flexion, abnormals are
extension and deflection
Presenting part: is the part of the fetus felt
at the lower poleof the uterus and felt on abdominal examination and on vaginal
examintion.
Presentation: is the part of the fetus in the
lower pole of theuterus and the normal presentation is vertex, abnormal are
breech, face, brow and shoulder.
Position: is the relationship of the
denominator to thesix areas of the mother’s pelvis, normal position is anterior
or lateral abnormal is Malposition is Occipital posterior position.
Crowned: When the Bi-parietals pass the
ischial spinesand the head no longer recedes between contractions.
Denominator: The part of the fetus which
determines theposition. (Vertex- occipute, breach -sacrum.Face- mentum).
Engaged: when the Bi-parietal diameters
of the fetal headpasses thruogh the pelvic brim.
1. History Taking
History taking:- Is a means of assessing the health of the woman to find
out any condition which may affect child bearing.
1. Social Histiory
Name, age, address, occupation; Age less than 18 years or greater than
35 years are considerd as high risk mothers.
2. Family History
To know the genetic predisposition to certain diseases
3. Medical History
Former illnesses may have damage certain structures or organs which
could give rise to complications during pregnancy and labour.
4. Surgical History:-
• Any abdominal operations
The Obstetric History
1. Past Obstetrical History.
Record of previous pregnancies and labour
Was labour premature or postmature, spontaneous or induced, history of
instrumental deliveries, previous obstetric complications and previous babies?
2. History of the Present Pregnancy
2. Examination of the Pregnant Woman at First Visit
Objective:
·
To diagnose pregnancy
·
To identify high risk pregnancy
·
To give advice for pregnant mother
General Appearance
As she walks in, observe any deformity, stunted growth, limp etc. does
she look well or pale and tired?
Clinical Observation
Weight:-The average weight gain during
pregnancy is about12-14 kg in the first trimester a woman should gain o.4 kg
per month and in the second and third trimester she should gain 0.4 kg per
week. It is Concedred as excessive if it is more than 3 kg a month during the
second and third trimester; it is lessthan normal if it is less than 1 kg per
month during the second and third trimester. Women who are under weigth coming
in to pregnancy should gain more weigth than the average (0.5 kg per month or
week rather than 0.4 kg). And may gains lessthan average (0.3 kg). Sudden
increase in weight that suggests fliud retention or a loss of weight tht suggests
illness should be carefully evaluated at prenatal visits.
Blood pressure: - Checked and recorded at each
visit,
Physical Examination:-
Face: - Oedema, sign of anaemia
Neck - Swollen glands
Breast Examination
Asses the size, any Lumps in the breast
Nipples are they inverted or flat?
Teach the mother self - examination of the
Breast
Heart and lungs are examined as usual to exclude diseases.
Abdominal Examination
AIMS
·
To observe signs of pregnancy
·
To assess fetal size and growth
·
To assess fetal health
·
To diagnose the location of fetal parts.
·
To detect any deviation from normal.
Steps for Abdominal Examination
1.
Inspection
2.
Palpation
3.
Auscultation
Inspection (5s)
a) Shape:-
·
Note contour -is it round, oval, irregular or pendulous?
·
Longtudinal, ovoid in primigravida
·
Rround in multipara.
·
Broad in transuerse lie.
b) Size:- Should correspond with the
supposed period ofgestation
c) Skin: - The dark line of pigmentation
which is lineanigra isseen any rash?
d) Strae gravidarum
e) Scar - Any operation scar(c/s)
On Palpation:
1. Fundal height and fundal
palpation (1st Leopoled Maneuver)
1.1 Fundal Height
At about 12 to 14 weeks of pregnancy, the uterus is palpated above the
symphysis pubis as a firm globular sphere; it reaches the umbilicus at 20 to 22
weeks, the xyphoid process at 36 weeks, and then often returns to about 4 cm
below the xyphiod due to “lightening”
at 40 weeks.
Method: Measure distance of fundus with
points on abdomenand assessing the fundal height in finger breadth below the
xiphisternum or measure by centimeter.
1.2 Fundal Palpation
Purpose- To know lie and presentation.
Method: - Use 2 hands using palms of hands
palpate oneither side of the fundus. Fingers held close together, palpate the
upper pole of then uterus and feel that as it is hard or soft or irregular.
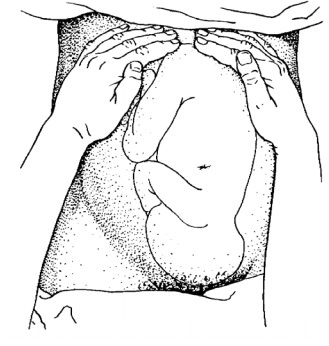
Figure:12 Fundal palpation
2. Lateral Palpation: (2nd Leopled
maneuver)
Purpose-To know lie and position
Method: - always facing the mother, fix
the hand on thecenter of the abdomen, fix the right hand and palpate with left
hand and vise versa. Note the regularity; the regular side is the back.
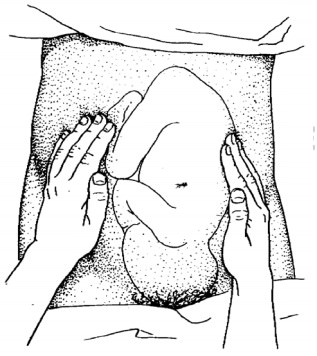
Figure ; 13 Lateral palpation
3. Deep pelvic Palpation: (3rd Leopoled Maneuver)
Purpose -To
Know Presentation & Attitude
Method: - Feel presenting part, is it hard
or soft whilepalpatingfor the presenting part feel for eminences on back side.
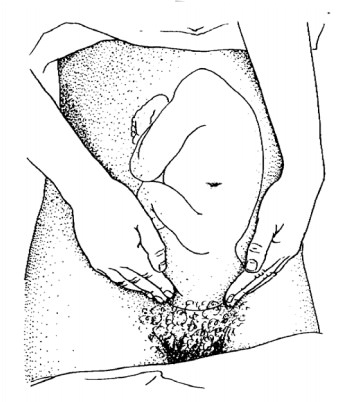
Figure 14: Deep pelvic palpation
4. Pawlick's Grip: (4th Leopard Maneuver)
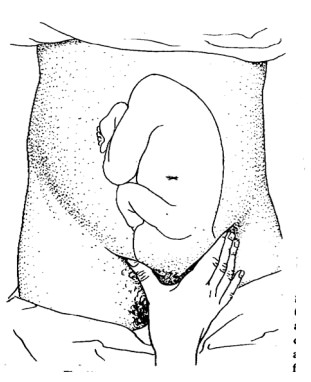
Figure 15. Pwlick’s grip
Auscultation: Check Fetal heart, rate and
rhythm, count forone minute if regular.
Method: Use Pinards stethoscope
·
hand should not touch it while listening,
·
ear must be in close from contact with stethoscope,
Pelivic assessement
·
By x-ray of the pelvis
·
Clinical (assessing sign of contracted pelvis)
·
Head fitting
Head fitting
The head is the best pelvimeter
METHOD 1: Head fitting, sitting patient,
Method
METHOD 2 : Left hand grip method Grasp
the fetal head withleft hand and push it down wards and backwards if a sense of
give is felt the head has entered and there is no over and no cephalo pelvic
disproportion.
Genito-Urinary System
·
Frequency of micturation
·
Check for abnormal discharge
Circulatory System
Varicosities: - Varicose veins may occur in
the legs, anus(hemorrhoids) and vulva. Vulval varicosities are rare and very
painful.
The Vulva
·
Vulval warts
·
Purulent irritating discharge
The Lower Limbs
Examine for bones alignment and deformities.
Check pitting oedema in the lower limbs by applying fingertip pressure
for 10 seconds over the tibial bone.
3. Laboratory test
Urine:-For Protein and glucose
Blood Tests:-V.D.R.L.
·
Rhesus and blood grouping.
·
Hemoglobin
4. Points to Be Advised On
·
The advantages of antenatal check up
·
The use of tetanus toxoid vaccine.
·
The danger of lifting heavy loads (exercise).
·
Rest at least 10 hrs at night and 2 in the afternoon, clothing shuold be
confortable
·
Breast care
·
Diet - Rich in Iron and protein
Report the following
·
Vaginal bleeding
·
Reduced fetal movements
·
Frontal or reccuring headaches
·
Sudden swelling
·
Rupture of the membranes
·
Premature onset of contractions etc.
Booking for Confinement
·
Every 2 weeks up to 36 weeks
·
Weekly 36 weeks there after.
N.B. High risk mothers eg. multiple pregnancy, suspected disproportion
etc. should attend weekly.
At subsequent Visits:-
·
Blood pressure, weight (edema)
·
Abdominal examination (all steps of abdominal examination)
·
Hematocrit test should be repeated at 28 and 36 weeks of
·
gestation Health Education
·
Listening and managing any complaint
Related Topics