Chapter: 11th Geography : Chapter 4 : Lithosphere: Exogenic Processes
Waves (Coast)
Waves
(Coast)
Horizontal movement of sea water caused by the
wind, rotation of the earth, etc., are called waves.
How do Waves Erode?
Waves carry out the erosive work in the following
ways.
1.
Abrasion: The waves striking against the coast with eroded materials is called abrasion. Abrasion is
also called as the corrasion.
2.
Hydraulic action: The waves force water and air into the cracks in the rock. The parcel of air can be
compressed by the surging water and the waves retreat, air expands explosively,
weakening the joints and cracks and causing the rock to break. This is called
the Hydraulic action.
3.
Corrosion: The action of dissolving soluble rocks by waves is termed as the corrosion or solution.
4.
Attrition: Eroded materials like boulders and rocks knock together to wear out into smaller
particles. This is called attrition.
Terms related to coast
Sea shore
is the zone of land between high tide and low tide
Shore
line is boundary between land and water.
Backshore
is the beach zone starting from the limit of frequent storm waves
to the cliff base.
Foreshore
is the portion of the beach subject to wave action during
non-storm conditions.
Offshore
is the shallow zone of the continental shelf
Coastline
is the boundary where the land meets the sea
Swash is the waves washing up the beach.
Landforms by the Erosion of Waves
Erosional landforms dominate rocky coasts but are
also found in association with predominantly depositional landforms.
Sea
cliff is steep rocky coast rising almost vertically above seawater is
called sea cliff.
Wave
Cut Platform: Rock cut flat surfaces in front of a cliff are
called wave-cut platform. They are slightly concave upward. It is also formed
when blowhole is collapsed.

A sea
cave is a hollow excavated by waves in a zone of weakness on a cliff. The
cave depth is greater than the entrance width.
Sea caves usually form at points of geological
weakness, such as bedding planes, joints, and faults. A 90 meter long sea cave
is found in the Loliem beach in Canacona in Goa. The world’s most extensive
cave is 1.5 km long Matainaka cave in New Zealand.

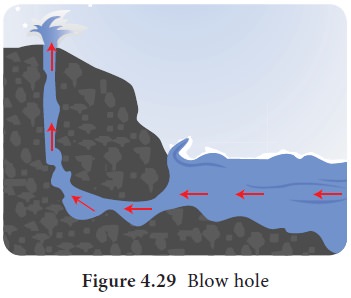
A
blowhole may form in the roof of a sea cave by the hydraulic and
pneumatic action of waves, with fountains of spray emerging from the top. If
blowholes become enlarged, they may collapse.
Arch is formed when the sea cave is cut right through by wave action. The arch is termed as sea tunnel
if it is comparatively longer.
The
stack is a steep and often vertical column of rock in the sea near a
coast, formed by wave erosion.
It is formed when the natural arch is collapsed. It
is also called chimney rock, needles, columns, pillars, skerries, etc,
Stump is the worn out stack.
Transportation Work of Waves
The eroded materials are transported by the waves
in different ways. The materials involved in the transportation by sea waves include
silt, sand, gravel, cobble, pebble and boulder.
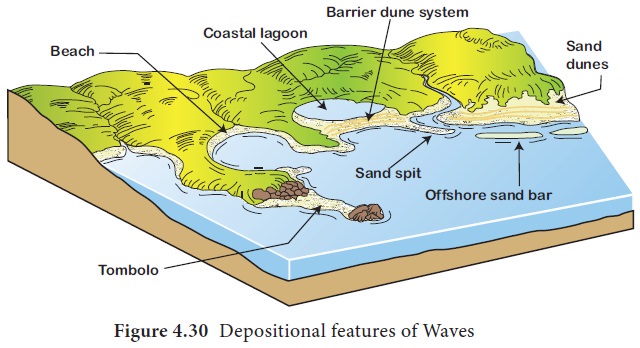
Landforms by the deposition of waves
Depositional landforms developed by the sea waves
include the beach, bar, lagoon, spit, tombolo, barrier island, etc. Let us see
one by one in detail.
1.
Beach is an
elongated stretch of sands, pebbles,
gravels, etc deposited along the coast. It can be a sandy beach or pebble
beach. Praia da Cassino beach in Brazil is the world’s longest beach stretching
for 200 km from the Rio Grande to the border with Uruguay. Marina beach,
Chennai is the second longest beach in the world.
2.
The Bar is a stretch of sand deposition off the shoreline. The larger form of a bar is called barrier.
3. The Lagoon is enclosed seawater between the bar and the coast. For example, Pulicat lake, located in the Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh is a lagoon.
4.
Spit is a
long, narrow ridge of sand or pebble
with one end connected to the coast and the other end running into the sea. For
example, Rameshwaram, Tamil Nadu.
5.
A Tombolo is a bar connecting an island with the coast.
Related Topics