Chapter: 11th Geography : Chapter 4 : Lithosphere: Exogenic Processes
The River
The
River
The streams have a huge capacity to erode the rock
over which they flow. In fact, the formation of the river channel is the result
of the erosional capacity of the stream. The erosional capacity of the stream
depends on its volume of water and velocity of flow. The river performs three
types of work. They are erosion, transportation and deposition.
1. Erosion: The breaking of rocks by the river in along its course is called erosion. Erosional work of
a river is performed mechanically and chemically. River erosion is carried out
in the following ways:
·
Hydraulic action: It refers to the physical force of the moving water which breaks the rocks in its
course.
·
Corrasion ( abrasion): It refers to the breaking of rock in the bed and on the bank by fragments carried
by the stream.
·
Corrosion( solution): It refers to the dissolving process of soluble minerals by the splashing of stream
water.
·
Attrition: It refers to the eroded materials carried by the stream strike against each other.
2. Transportation: Stream carrying the fragmented materials broken by the stream is called
transportation. After erosion, the eroded materials get transported alont with
the running water. This transportation of eroded materials is carried in four
ways:
·
Traction: The heavier and larger rock fragments like gravels, pebbles etc are forced by the flow of the
river to roll along its bed. These fragments can be seen rolling, slipping,
bumping and being dragged. This process is called as traction and the load
transported in this way are called traction load.
·
Saltation: Some of the fragments of the rocks move along the bed of a stream by bouncing continuously.
This process is called as saltation.
·
Suspension: The holding up of small particles of sand, silt, and mud by the water as the stream flows
is called suspension.
·
Solution: Some parts of the rock fragments dissolve in the river water and transported. This type
of transportation is called solution transportation.
3. Deposition: When the velocity of the stream decreases, the stream deposits sand, silt and other
fragments. It is called as the deposition. When a river moves in a gentle
slope, its speed reduces and river begins to deposit its load. The river starts
depositing larger materials first and smaller and finer materials are carried
further down to the mouth of the river.
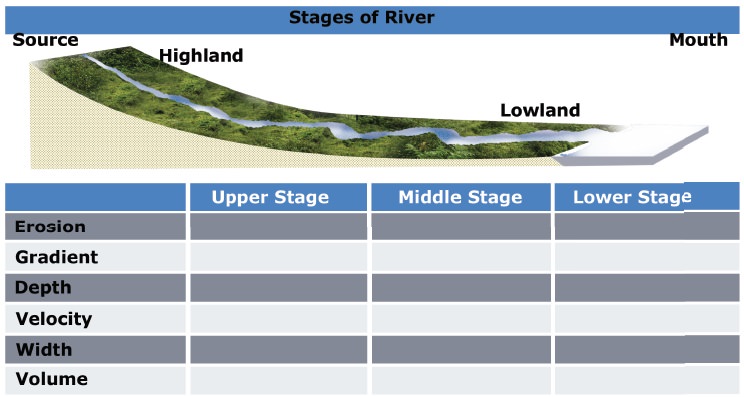
Stages of the River
The course of a river includes the upper stage, the
middle stage, and the final stage. Each stage of the river is dominated by a
kind of work. Let’s discuss the stages of a river, the main work and the
landforms made in each stage.
1. The Upper Stage
The upper stage of a river is also called the
youthful stage or mountain stage. The velocity and speed of the stream are very
high because the slope here is steep. The vertical erosion is the most dominant
work here. The valley is formed here. The place where a river starts is called
a source. In the mountain stage, the
number of small streams originates from different locations. They are called Tributaries.
The place where two rivers join is called as the confluence. The mountain which has two river systems draining on either side of the slope is termed as the water divide.
2. The Middle Stage
Middle stage is the matured stage of a river.
Vertical erosion or deepening of the valley is significantly reduced. Lateral
erosion is the dominant work. Due to the lateral erosion of this stage, the
widening of the valley occurs. The volume of the river water increases and the
slope of river is moderate. The depth of the river is deep here.
3. The Lower Stage
This is the final stage of a river where the
valleys are extremely broad and it has generally gentle slope. The valley
becomes almost flat which is called a peneplain. Most of the peneplain forms
low residual hills with steep slopes which are called as Monadnocks.
Students
activity
Look at
the diagram, read the table of content carefully and fill in the columns with
suitable words.
The main work of the river in this stage is the
deposition. The depth of the river is shallow here. When the main river splits
into many small rivers, they are called as the distributaries. The place where
the river ends is called mouth of the river. (for example: Sea coast, Lake.)
Landforms by the Erosional Work of River
The significant landforms resulting from erosion by
rivers include gorge, canyon, V-Shaped Valley, waterfall, pothole, structural
bench, river terrace, river meander, ox-bow lake, peneplain, etc.
Gorges are formed due to active down cutting of the valleys. So, a Gorge is a narrow and deep river
valley which has steep slopes.

Canyons
are extended form of gorges. Canyons represent very deep, narrow
but long valleys. The steepness of the valley sides depends on the nature of
the rocks. The Grand Canyon of the Colorado River in the state of Arizona, USA
having a length of 482.8 kilometers and depth of 2088.3 meter is the largest
canyon in the world. The Canyon of Gandikota is situated on the Pennar River in
Andhra Pradesh is known as the Grand Canyon of India.
V-Shaped
Valley The valleys made by the rivers are erosional landforms. The
valley is formed in the youthful stage of the river erosion. Due to the steep
slope and large volume of water, the river cuts its bed vertically forming
narrow and deep river valley. This is called as V-shaped valley.
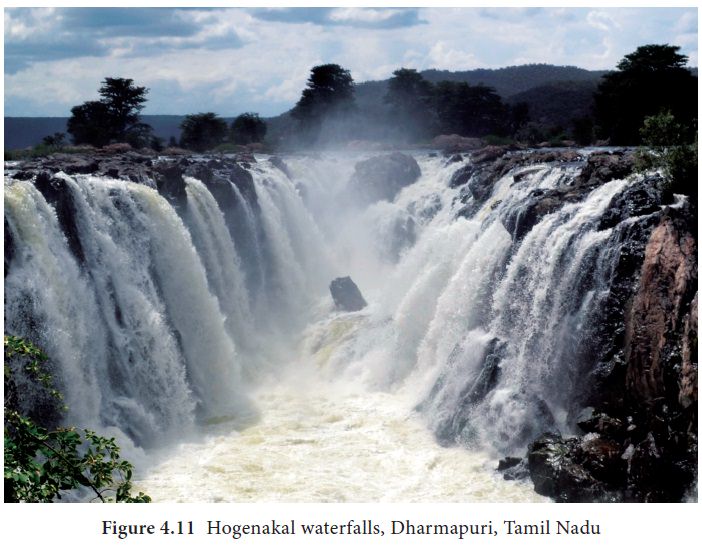
Rapids and waterfalls
Rapids are stream sections with extremely strong
currents, numerous obstacles, and steps in their streambeds. A waterfall is a vertical
drop in a streambed. Both water fall and rapids are formed by vigorous erosion.
Series of a waterfall in a river is called as Cascade.
Plunge pool
A plunge pool is a deep depression in a stream bed
at the base of a waterfall. It is created by the erosional forces of falling
water at the base of a waterfall.
Angel Falls, in Venezuela, is Earth’s highest waterfall (979 m). Hogenakal falls, Dharmapuri, Tamil Nadu some times is called as the Niagara of India.
Grooves
Long and narrow depression at the base of a
waterfall made by river runoff is called a groove. The grooves are created by
water eroding soil from a hill or mountain in a short period of time.
The swirling movement of the water falling into the
plunge pool is called eddying.
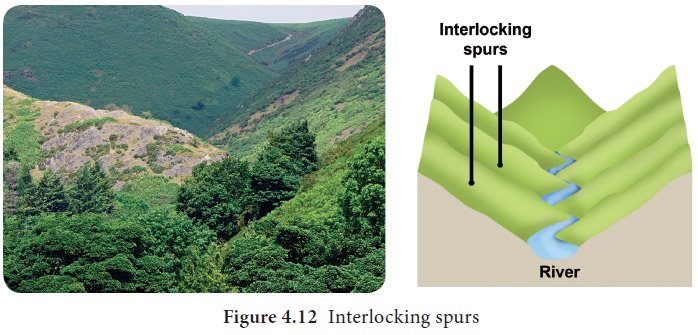
Interlocking spurs
An interlocking spur, also known as an overlapping spur, is a projecting ridge that extends alternately from the opposite sides of a V-shaped valley. A river with a winding course flows down the interlocking spur.
Pot Holes
The kettle-like small depressions in the rocky beds
of the river valleys are called potholes. They are always cylindrical in shape.
Potholes are generally formed in coarse-grained rocks such as sandstones and
granites.

River Terraces
The narrow step like flat surfaces on either side
of the valley floor are called river terraces. They represent the level of
former valley floors.
Landforms by the deposition of river
1.
Alluvial fan
Alluvial fans are often found at the foot of arid
or semiarid mountain ranges where intermittent streams flow. An alluvial fan is
a fan shaped deposit of gravel, sand and other smaller particles of sediment.
Alluvial fans are found in Kosi river, Himalayan
region, Death Valley National Park and along the sides of the Colorado River at
Grand Canyon National Park, U.S.

2. Peneplains
Peneplains represent low featureless plain having
undulating surface and remnants of convex-concave residual hills.
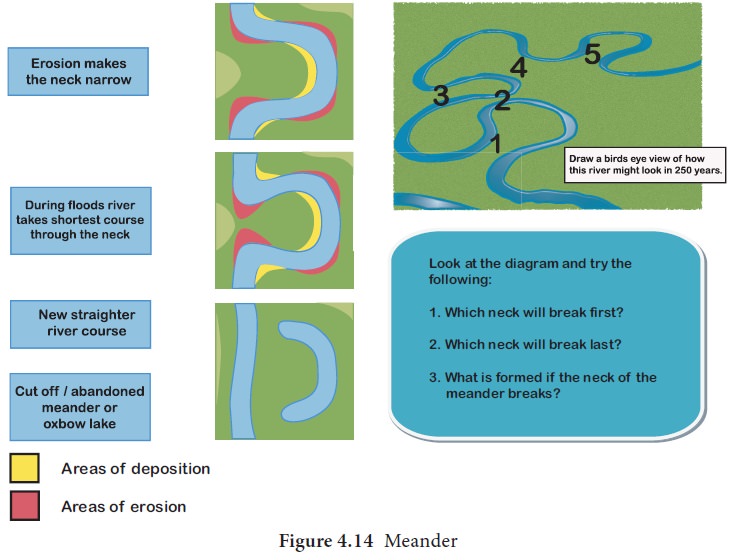
3. Meander
A meander
is a winding curve or bend in a river. Meanders
are the result of both erosional and depositional processes. They are typical
landform of the middle and lower course of a river. This is formed by vertical
erosion, lateral erosion, and deposition within the floodplain.
4. Oxbow lake
Oxbow lake is a free standing body of water formed
when the meander is cut off from the main river. This landform is so named
because it resembles horse shoe
5. Levees:
Raised bed and a bank of the river due to frequent flooding and
deposition of the sediments is called levees.
6. Flood Plain
A flood plain is a flat area of land adjacent to a
river. It stretches from the bank of its channel to the base of the enclosing
valley walls which experiences flooding during the period of high discharge.
7. Estuary
The word “estuary” is derived from the Latin word aestuarium meaning tidal inlet of the
sea, which is derived from the term aestus,
meaning tide. An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water
with one or more rivers flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open
sea.
The inflow of both sea water and fresh water
provide high levels of nutrients both in the water column and in sediment.
Hence, it makes estuaries among the most productive natural habitats in the
world. Narmada river estuary is located in Gujarat.
8.Delta
Delta is found in the old stage of a river. It is
the triangular shaped landform made up of alluvial deposition in the mouth of
the river. It is named after the fourth Greek alphabet called delta. Example,
The Ganges Bhramaputra delta is the largest delta in the world.
Types of Delta: Delta is classified into the following based on the shape and kind of the load deposited by the river.
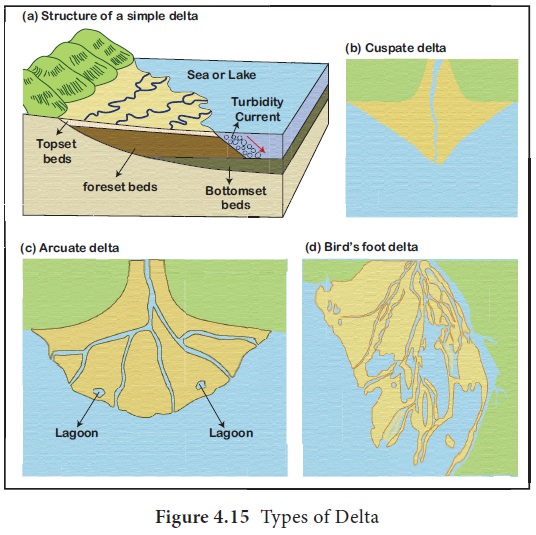
1.
Arcuate Delta: A bowed or curved delta with the convex margin facing the body of water. It is also known as fan-shaped delta. Example, River Nile Delta in
Egypt and Ganga Delta in India.
2.
Estuarine Delta : it is formed at the mouth of submerged rivers depositing down the sides of the
estuary. Example, Seine River of France.
3.
Birds foot Delta: They are formed
due to deposition of finer materials by river water. Deposited alluvial
material divides the river into smaller distributaries. Such delta is also
called as finger delta. Example, Mississippi river delta, the USA.
4.
Lacustrine Delta: It is formed when a river flows into a lake. Example, Lough Leanne river delta,
Ireland.
5.
Truncated Delta: Sea waves and ocean currents modify and even destroy deltas deposited by the river
through their erosional work. Thus, eroded and dissected deltas are called
truncated deltas.
6.
Abandoned Delta: when the river
shifts its mouth, the delta already made is left abandoned. Such a delta is
called abandoned delta. Example, Yellow river delta, China and the Western part
of Ganga delta made by Hoogly river, India.
7.
Cuspate delta is a tooth shaped delta formed when a single distributary
Related Topics