Geography - Mass Wasting and Types of Mass Wasting | 11th Geography : Chapter 4 : Lithosphere: Exogenic Processes
Chapter: 11th Geography : Chapter 4 : Lithosphere: Exogenic Processes
Mass Wasting and Types of Mass Wasting
Mass wasting
Mass wasting is the movement of a large mass of
rock, soil and debris downward by the pull of gravity. It is also called a mass
movement or slope movement. It may happen suddenly or slowly. Generally, mass
wasting is classified by the type of material involved (mud, soil, and rock)
and type of motion (fall-free-falling
pieces, slide-material moves along
the rock slope and flow–material
mixed with water).
Types of Mass Wasting
Following are the types of mass wasting:
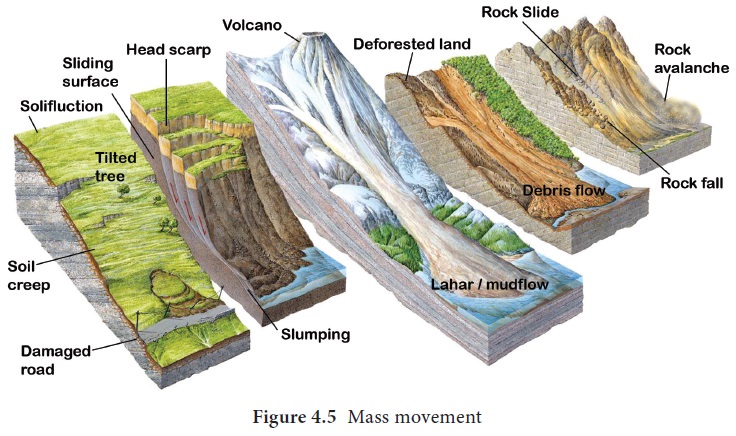
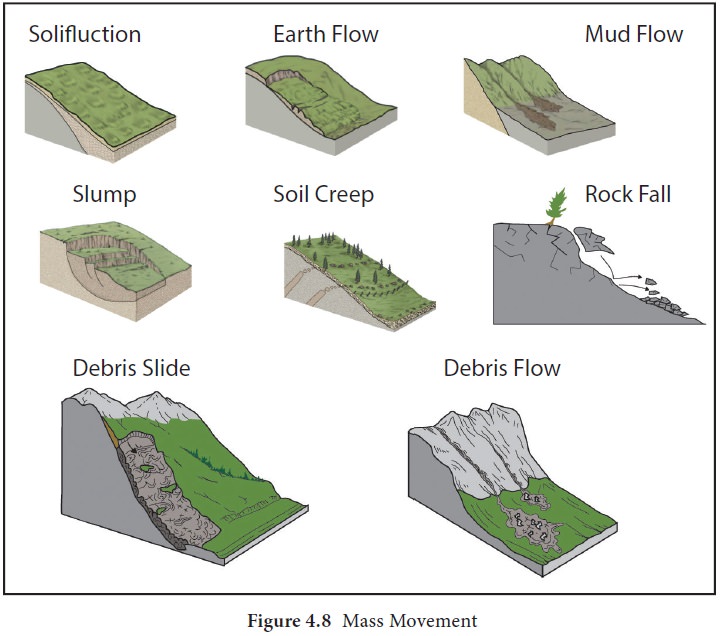
Rock falls
Rock falls occur when pieces of rock break from a cliff. Frost wedging may also eventually loosen large blocks causing them to fall. The accumulation of rock debris at the base of a steep slope is called talus.

Rockslides
Rockslides usually follow a zone of weakness.
Presence of water increases slippage. Collisions down the slope generally break
the rock mass into rubble that eventually results in rockslides.
Landslides
Landslides occur when a large piece of rock breaks
off and slides down hill. It is often initiated by earthquakes and very heavy
rain.
Slump
Great mass of bed rock moves downward by rotational
slip from a high cliff is known as slump. Most common reason for slumping is
erosion at the base of the slope which reduces the support for overlying
sediments.
Debris Slide
Debris slide is more extensive and occurs on a
larger scale than slump but there is a little amount of water. The materials
involved in debris slide are a mixture of soils and rock fragments.
Debris flows
Debris flow is defined as mass wasting event in
which turbulence occurs throughout the mass. Debris flow includes earth flows,
mudflows, and debris avalanches. Debris flow occurs when the rock or soil mass
loses coherency when lots of water is involved. Debris becomes mixed up
completely and flows as liquid mud. It often carries large boulders which can
be very destructive. When earth material moves down a hillside as a fluid-like
mass, it is called an earth flow.
These flows typically occur in humid areas on steep slopes with thick,
clay-rich soil that becomes saturated with water during storms.

A mudflow
Mudflow is a liquid mass of soil, rock debris and
water that moves quickly down a well defined channel. They occur most often in
mountainous semiarid environments. A mudflow originating on a volcanic slope is
called a lahar.
Debris avalanche
The deadliest type of debris flow is the debris avalanche. It is a rapidly churning mass of rock debris, soil, water, and air that moves down steep
slopes. The trapped air may increase the speed of an avalanche by acting as a
cushion between the debris and the underlying surface
Creep
Creep is a slow and gradual movement of soil
downhill. Its velocity is typically less than a centimetre per year. Freezing
and thawing contribute the soil creep by progressively moving soil particles
down the hill. Creep is manifested at the surface by things like tilted utility
poles, fences and trees Vegetation helps reduce the rate of soil creep.
Related Topics