Distribution of water in the body, Sources, Functions, Requirements, Dehydration - Water | 11th Nutrition and Dietetics : Chapter 11 : Vitamins, Minerals and Water
Chapter: 11th Nutrition and Dietetics : Chapter 11 : Vitamins, Minerals and Water
Water
WATER
Water is vital for
human existence. Water is the largest component of the human body,
making up to 60 to 70 percent of the total body’s weight. This percentage of water in
human being is required to be maintained by water as a foodstuff. Infants have greater
percentage of water than adults. Old age declines the water percentage of the
body. Water is second only to oxygen in its vital importance to the body. One
can live without food for a longer time than one does without water. Water is
colourless, calorie less componud of hydrogen and oxygen that virtually every
cell in the body needs to survive.
Substances dissolve in water as ions with positive and negative charge. They are called electrolytes. The common electrolytes in our body are sodium, potassium and chloride. Because of this, water can dissolve most substances and in doing so, it enables minerals and other chemicals to undergo biological reactions in the body.
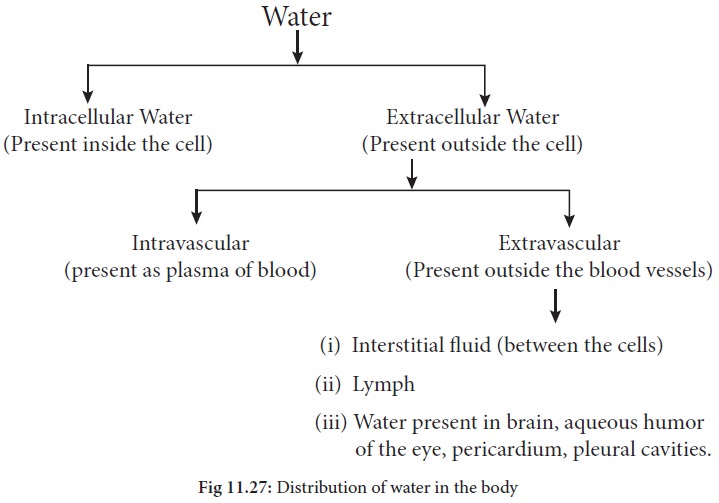
Distribution of water in the body:
Total body water
content is mainly determined by total amount of salt in the body. Salt and
water concentration in the
body is controlled by
the kidneys.
Water in the body – Intracellular and Extracellular fluid
Water flows in and out
of the body cells through cell membranes.
Intracellular fluids:
Fluid contained within
a cell represents about two thirds of all body fluids.
Extracellular fluids:
Fluid present outside
the cells, it includes intravascular and interstitial fluids; represents about
one-third of all body fluid.
Extracellular fluids
are further divided into interstitial fluid, water between cells and
intravascular fluid water in the blood stream and lymph. Interstitial fluid
forms a transport link between tissue cells and the blood.
Sources of water
The body has three
sources of water. Besides drinking water, the following are the sources of
water.
1. The water contained in
food, eg. Fruits and vegetables contain 80-90 percent water. Milk contain 80-88
percent. Meat contains 40-75 percent, Flour, cracks and bread contain 5-35
percent of water.
2. In addition to water,
ingested fluids such as ghee (milk-based preparation). Soups and
beverages also supply essential minerals and vitamins.
3. Metabolic water is
formed by the metabolism of food in the body. It may amount to about 450ml per
day.
Functions of Water
Major functions of water :
·
Carrier of Food Nutrients: Every nutrient in soluble form in water is
carried from intestines to tissues through blood.
·
Constituent of Liquid: Water is the major constituent of all liquids
of body as blood, urine, sweat, lymph.
·
Regulate body temperature: Water helps to regulate and control body
temperature. Heat is produced when food is burnt for energy. Water is
evaporated through respiration and sweat and body temperature is maintained
normal. Body’s heat is lost through the skin, lungs, urine and faeces.
·
Safety/Security of Delicate Organs: Water is around lungs,
heart, brain which protects them from outer injury. Thus provide security to
these organs and thereby to human being.
·
Water as lubricant: Water acts as lubricant in joints. Water
around

Requirements
Requirement of water
varies with climate, dietary constituents, activities and surface area of the
body. As a rule a person should take enough water to excrete about 1200 –1500
ml of urine per day. In tropics because of greater water loss through
perspiration increased water intake is required to maintain urine volume.
Normal intake of water ranges between 8 – 10 glasses per day.
Water is lost through
feces, urine, lungs (expiration) skin (invisible perspiration and visible
perspiration) amounting to about 2-3 liters per day. During infections and
fever, the liquid intake should be increased as losses are higher. A moderate
amount of water taken with or preceding a meal is an aid to digestion.
Dehydration
Dehydration results in
extreme deficiency of water and fluids. Symptoms of dehydration are fatigue,
headache, sullenness and in extreme cases, collapse.
The steps in the
progression of dehydration are as follows.
·
Thirst
·
Decreasing blood volume, impaired physical performance.
·
Increased effort for physical work, nausea.
·
Failure to regulate excess temperature.

·
Muscle spasms.
·
Failing renal function, less or no urine formed.
Excessive loss of water takes place due to vomiting, diarrohea, haemorrhage, excessive perspiration, exudating, burns, uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, fever and hot weather. It can be fatal and causes death in several children which can be easily avoided by proper fluid intake or oral rehydration therapy.
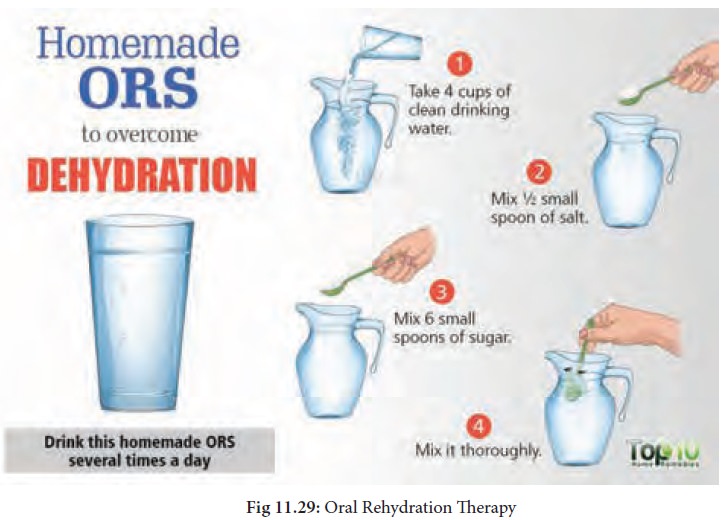
ORT: (Oral Rehydration Therapy)
Oral
rehydration therapy is
a method of treating dehydration by making the patient drink solution which can
be prepared by dissolving salt and sugar in
boiled and cooled water.
Water Intoxication
Water intoxication
results due to excess intake of water. This results in an increase in the
volume of intracellular fluid. This condition can lead to headache, nausea,
vomiting, muscle twitching and convulsions. It can even be fatal.
Related Topics