Types, Functions, Food Sources, Symptoms of deficiency - Water Soluble Vitamins | 11th Nutrition and Dietetics : Chapter 11 : Vitamins, Minerals and Water
Chapter: 11th Nutrition and Dietetics : Chapter 11 : Vitamins, Minerals and Water
Water Soluble Vitamins
Water Soluble Vitamins
Water soluble vitamins are soluble in water and so they cannot be stored in the body. Therefore, a day-to-day supply of these vitamins is essential.
The B vitamins have important metabolic roles as coenzyme partners with cell enzymes that control energy metabolism and build tissue. Eight vitamins are there in this group.
1. Vitamin B1 (Thiamine)
Thiamine acts as a catalyst in the oxidation process which prepares glucose in the body to provide energy. Vitamin B1 is a vital coenzyme which changes the three sources of energy – fats, carbohydrates and proteins into energy (glucose). So, without B1 the body cannot use the food to make energy. It is known as ‘Appetite vitamin’ and makes a person feel hungry.
Functions:
· Thiamine helps increase hunger. Thus aids normal growth.
· Thiamine controls mental andnervous fatigue, irritability and restlessness.
· Promotes growth, protects the heart muscle and stimulates brain action.
· The vitamin improves peristalsis and helps to prevent constipation.
· Improves circulation of blood and promotes a healthy skin.
Food Sources of Thiamine
Whole grain cereals, wheat, rice, oats, yeast, sunflower seeds, peanuts, Bengal gram, capsicum, turnip, beet, fish, liver, legumes, nuts, wheat germ, baked beans, whole grains enriched breads and cereals, egg etc.,

Symptoms of thiamine deficiency
· Loss of appetite, poor digestion.
· Muscular weakness and feeling tired
· Insomnia, mental depression,
· Loss of weight, leg cramps
· Digestive disorder
· Slow heart beat and
· Gastrointestinal problems
Deficiency Diseases
Thiamine deficiency causes beriberi and there are three kinds of Beriberi
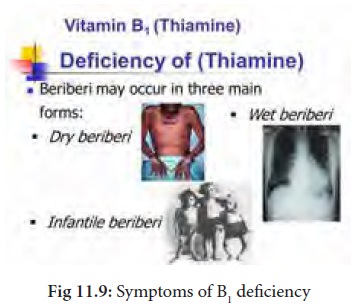
1. Dry Beriberi affects the nervous system, tingling and loss of sensation which may cause limb paralysis and degeneration of nervous tissues. There is difficulty in walking, foot and wrist drop.
2. Wet Beriberi affects the heart. There is difficulty in breathing. It enlarges the heart causing painful palpitations, disfunctioning of heart and heart attack.
3. Infantile Beri occurs mostly in infants who cry without sound. Infants has difficulty in breathing, body turn blue and may die within 24-28 hrs.
It also leads to poor functioning of gastrointestinal tract and poor appetite.
2. Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)
Riboflavin is water soluble and relatively heat stable. It is easily absorbed from the intestine and the excess is excreted through urine. It is essential for the health of skin and for normal vision.
Functions
· Riboflavin plays an important role in the health of the eyes and alleviates eye strain and is essential for proper vision and healthy sight.
· Riboflavin assists production of Red blood cells (RBC).
· It strengthens mucous lining of mouth, lips and tongue.
· It is required for normal growth and wound healing.
· Riboflavin is needed in every cell of the body. It helps cells to use
· oxygen so that the body can convert sources of energy into glucose.
Food Sources of Riboflavin:
Yeast, milk, curd, cheese, eggs, chicken, liver, pork, spinach, carrot leaves, beets, brown rice, sprouts, beans, Fruits like Apricots, papaya, custard apple. Nuts like Almond and walnut are rich sources of riboflavin. Large amounts are found in dairy products, eggs and meats. Green leafy vegetables and enriched grains are moderate sources of Riboflavin.

Symptoms of Riboflavin deficiency
· Cracks and redness at corners of mouth – Cheilosis.
· Painful, smooth, purplish red tongue - Glossitis.
· Sore throat.
· Inflamed eyes and eyelids, sensitivity to light.
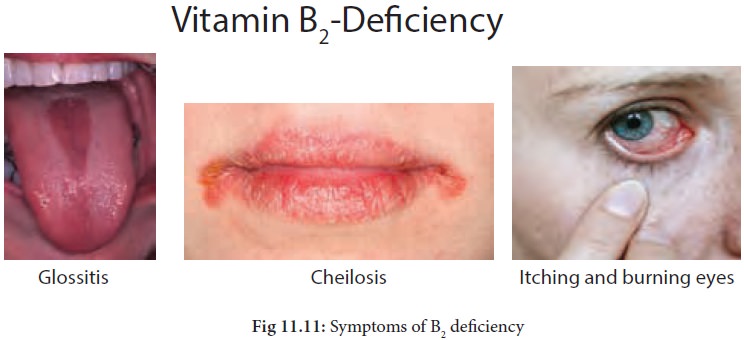
· Itching and burning eyes.
· Intolerance to bright light, dim vision, water in eyes.
· Skin rashes and
· Digestive disturbances.
3. Vitamin B3 (Niacin)
Niacin is a water soluble vitamin which is also known as vitamin PP (pellagra preventive factor) Niacin exists in two forms: nicotinic acid and nicotinamide.
Functions
· Important for proper blood circulation and healthy functioning of the nervous system.
· Promotes the health of digestive track.
· It repairs DNA.
· It regulates blood sugar levels.
· It lowers cholesterol levels.
· It is essential for normal functioning of skin and nerve system.
Food Sources of Niacin
Liver, chicken, meats, prawns, fish, legumes, cereal, mushroom, peanuts, green leafy vegetables, broccoli, dates, peas, groundnuts, almonds, sunflower seeds, avocado are rich in Niacin.

Symptoms of Niacin deficiency
· A mild deficiency of niacin may result in a coated tongue, sores in the mouth, irritability, nervousness, skin lesions, diarrhoea, forgetfulness, insomnia and headache.
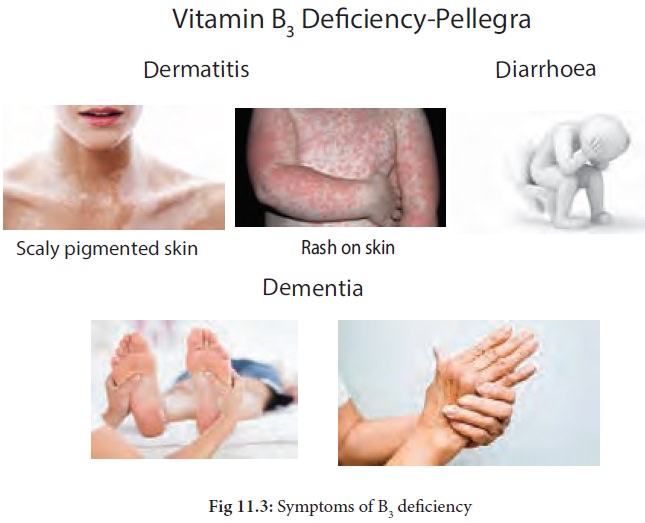
· Pellegra - Niacin deficiency leads to Pellagra-a disease of 3D’s- dermatitis, diarrhoea and dementia followed by death (if not treated).
· Dermatitis - This includes rough, scaly pigmented skin with rash on skin exposed to sunlight. Swollen mouth on skin exposed to sunlight.
· Diarrhoea - loose stools and vomiting.
· Dementia - nerve damage, numbness in limbs, tingling in hands and feet. Poor muscle coordination, disorientation and loss of memory.
4. Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine)
Pyridoxine is a colourless compound soluble in water and alcohol. It is well absorbed in the upper segment of the small intestine. It is stored in muscle but found in tissues throughout the body.
Functions
Production of red blood cells.
· It is readily absorbed from intestines.
· Improves immunity.
· Improves nervous system functions.
· Reduce muscle spasms, cramps and numbness.
· Maintains proper balance of sodium and phosphorous in the body.
Food sources of Pyridoxine: Good food sources include whole grains, legumes, bananas, potato, liver, kidney and other meats, fortified breads and cereals. Sunflower seeds, soya beans, walnuts and yeast are the richest sources of pyridoxine among plant foods.

Symptoms of Pyridoxine deficiency
· Nervousness, Insomnia, Anaemia, oedema, mental depression.
· Loss of muscle control, muscle weakness, tooth decay.
· Arm and leg cramps,
· Water retention,
· Skin lesions and skin disorder.
5. Vitamin B9 (Folic Acid)
Vitamin B9 includes both folate and folic acid and is important for several functions
in the body. It is important for women who are pregnant to consume enough folic acid.
Functions of folic acid: The different functions of folate include:
· Folic acid helps the body to convert carbohydrates into glucose, which is used to provide energy.
· Folic acid helps in building of antibodies which prevent and heal infections.
· It helps in normal functioning of the nervous system and maintains the mental and emotional health.
· It helps in production of body’s generic material - DNA and RNA.
Food sources of Folic acid: The rich sources of folate are fish, mutton, liver, egg, chicken, green leafy vegetables, pulses, Lentils, beans, asparagus, lettuce, Parsley, avocado, sunflower seeds, beets, broccoli, spinach, orange juice, tofu, fish, meat, fortified cereals, milk, cheese, eggs, oysters, crab etc.,

Symptoms of folic acid deficiency
· A recent study connected folic acid deficiency with autism.
· Loss of memory, severe and irreversible damage to nervous system and brain.
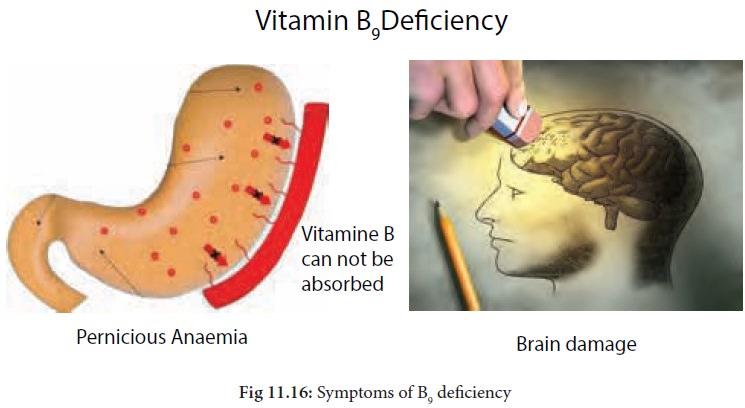
· Pernicious anaemia which is an immune system disease.
· Deficiency of folic acid causes megaloblastic anaemia.
6. Vitamin B12 (Cyanocobalamin)
The vitaminis named as cyanocobalamin because of the presence of cobalt and cyanide in its structure. It can be absorbed in the body only in the presence of intrinsic factor (IF).
Functions
· It is essential for the production and regeneration of red blood cells.
· It improves concentration, memory and balance.
· It synthesises and regulates DNA.
· It plays an important role in normal functioning of brain and nervous system.
· It also helps to absorb folic acid.
Food Sources of Cyanocobalamin
Cyanocobalamin is synthesized by bacteria and is found in foods of animal origin. Liver is the richest source of cyanocobalamin. Meat, chicken, oysters, eggs, fish, milk, curd, cheese are good sources of Vitamin B12.

Symptoms of Cyanocobalamin deficiency:
· Loss of memory
· Fatigue
· Anemia
· Severe and irreversible damage to the nervous system and brain
· Pernicious anaemia is caused due to its deficiency in the body which is an immune system disease.
7. Vitamin C
Vitamin C is also known as ascorbic acid. It is an antioxidant and water soluble vitamin. It is destroyed by light, heat and when exposed to air and metals. During cooking much of it is destroyed. Iron and copper act as catalysts and cooking in these vessels increases the loss of vitamin C. When the vegetables are cut into fine pieces more enzymes is released and it causes more loss. Vitamin C is essential in cholesterol metabolism.
Functions
· It is helpful in the formation of collagen the cementing material between cells that holds them together.
· Vitamin C builds up natural body defence and helps provide immunity to the body.
· It helps the body to absorb more iron from plant sources.
· It aids in the healing of wounds.
· It helps to keep gums healthy.
· It helps body to fight infections.
· Improves bone formation.
· It prevents the deposition of cholesterol on the walls of the arteries and prevent heart diseases.
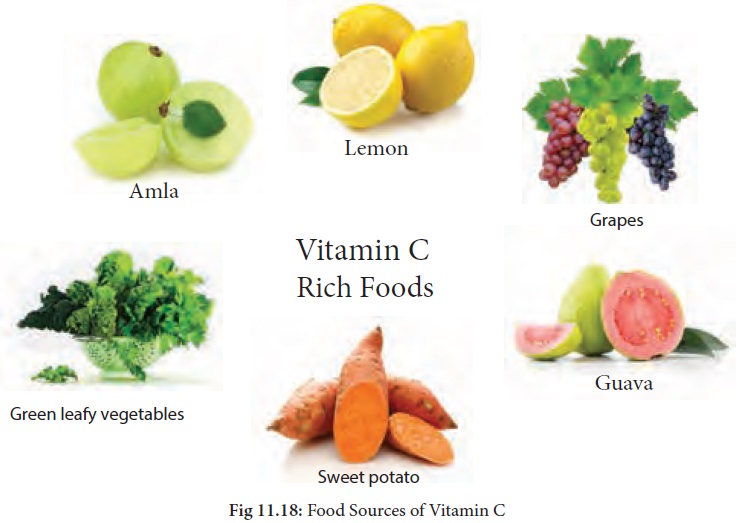
Food Sources of Vitamin C: Amla, kiwi, strawberry, raspberry, grapes, berries, guava, citrus fruits like sweet lime, lemon, oranges, green leafy vegetables, spinach, hot chillies, turnip greens, broccoli, red bell pepper, tomato juice, raw tomato, sweet potato etc.,
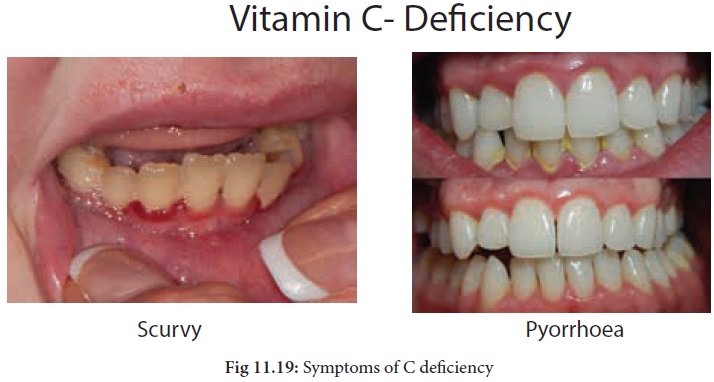
Symptoms of Vitamin C deficiency
· Gums swell and bleed and become purple and spongy. This is known as pyorrhoea. Foul smell emits from the mouth.
· Deficiency can lead to scurvy in which a slight injury produces excessive bleeding and large hemorrhages are seen under the skin.
· There is tenderness, swelling and pain in the limbs.
· Reduced immunity causes simple infections like common cold, flu- viral, etc.,
· Irritability, aneamia, poor wound healing and Diarrhoea.
· Gastrointestinal discomfort.
· Weight loss, fatigue and joint pain.
Related Topics