Names, Functions, Food Sources, Symptoms of deficiency - Nutrition Minerals | 11th Nutrition and Dietetics : Chapter 11 : Vitamins, Minerals and Water
Chapter: 11th Nutrition and Dietetics : Chapter 11 : Vitamins, Minerals and Water
Nutrition Minerals
Minerals
The body contains
about 24 minerals, all of which must be provided by the diet. These are
required by the body in very minute amounts and are often referred to as trace
elements. The main important ones are iron, iodine, calcium, zinc and sodium.
1. Iron
Iron was first
recognized as a constituent of the body by Lernery in 1713. It is now known
that all the iron in the body exists
Overall the body contains 2.5g to 4.0g of iron. Most of the
iron in the body is found in the blood, but some is present in every cell bound
to iron containing enzymes. Iron is present in Haemoglobin which contains
ferrous iron. It is essential for carrying oxygen to different tissues.
Functions
·
Iron is an important mineral needed for the formation of
haemoglobin which is responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to
different cells and tissues of the body in the form of oxyhaemoglobin. Thus
iron helps in the oxidation process.
·
It acts as co-factors of enzymes and other proteins.
·
It is required for the formation of red blood cells.
Food Sources of iron:
Haeme iron from animal
foods is better absorbed than nonhaeme iron present in plant sources. Liver is
the best source of iron. Iron is also absorbed well from red meat like lamb.
Nonhaeme iron is present in cereals, millets, pulses and green leafy
vegetables. Of the cereal grains, wheat and millets like bajra and ragi are
very good source of iron. Inclusion in our daily diet about 50g of green leafy
vegetables which are rich in iron can meet a fair proportion of iron needs.

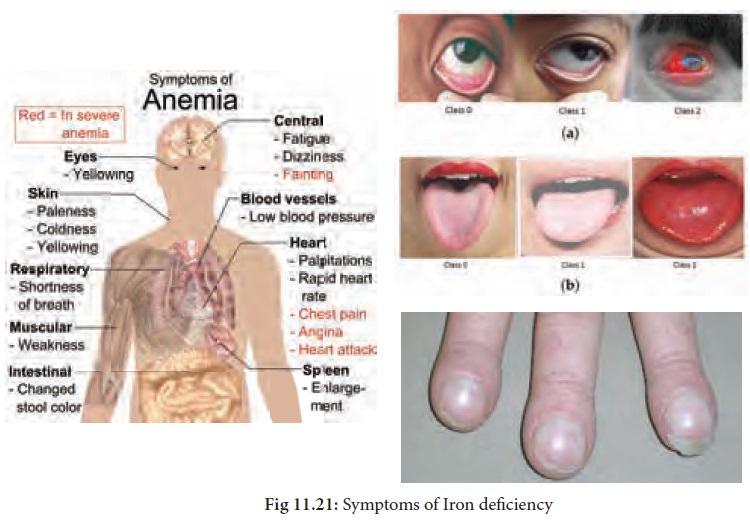
Symptoms of Iron deficiency:
Iron deficiency leads
to Anaemia which has the following symptoms:
·
Eyes, tongue and nails become pale.
·
Person feels extremely
tired
and fatigued.
·
Decreased physical activity
and breathlessness on
exertion.
·
Tingling sensation in fingers and toes.
·
Nails become brittle and become concave and appear like a spoon.
·
Loss of appetite and giddiness.
·
Poor coordination of body functions.
2. Iodine
The significance of
Iodine as an essential trace element lies in its role in thyroxine production.
Iodine is a constituent of thyroxine, the active principle of the thyroid
gland. The thyroid gland plays an important role in energy metabolism and in
the growth of the body.
Functions
·
It is essential for the production of thyroid hormone called
thyroxin which is secreted by the thyroid gland.
·
Thyroxin controls the basic metabolic rate in the body as it
controls the metabolism of all nutrients.
·
Thyroxin regulates the rate of oxidation within the cells.
·
It stimulates the physical and mental growth.
·
It regulates the functioning of nerve and muscle tissue.
Food Sources of Iodine:
Iodine is present only
in small amounts in common foods, the quantity of iodine present depending on
the iodine content of the soil. Iodised salt, sea salt, vegetables grown at sea
shore, garlic, onion, cheese and sea fish are good sources of iodine.

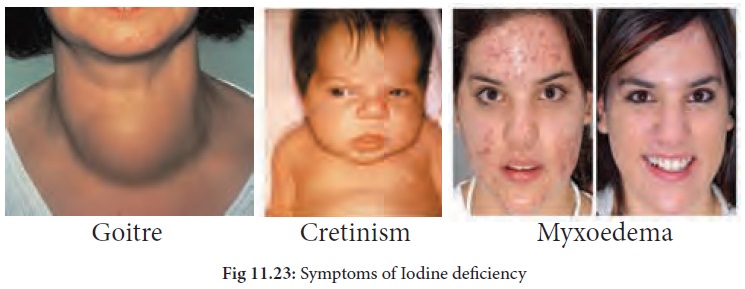
Symptoms of Iodine deficiency:
·
Wide variety of physical and neurological disorders
associated with iodine deficiency are called “Iodine Deficiency Disorders -
IDD”.
·
Goitre: It is characterized by swelling of thyroid gland.
· Cretinism: Person is deaf and has a shuffiing gait, retarded mental and physical growth, thus shorter in stature (dwarf).
·
Myxoedema: Face of patient becomes expressionless.
3. Calcium
Calcium is the major
element in the body and an adult man of 60 kg has nearly one kilogram of
calcium. Almost 99% of this calcium is found in the hard tissues of the body,
namely the bones and teeth. Vitamin D is essential for the absorption of calcium.
In vitamin D deficiency, calcium absorption is impaired.
Functions
· It is essential for the formation of bones and teeth.
·
It is essential for clotting of blood.
·
It regulates the
permeability
of capillary walls.
·
It is essential for the contraction of heart and muscle.
·
It regulates the excitability of nerve fibres and nerve centres.
·
It acts as an activator for the enzymes present in the gastric
juice.
·
It plays an
important
role
in maintenance of
health.
·
Required for proper foetal growth.
·
It speeds up all healing process.
·
It is essential for proper utilization of phosphorus and
vitamins A, C and D
Food Sources of calcium:
The richest source of
calcium among animal foods is milk and among vegetables it is green leafy
vegetables. Among green leafy vegetables, amaranth, fenugreek and drumstick
leaves are particularly rich in calcium. Ragi is the main source of calcium.
Sesame seeds with husk and small dried fish are also good source of calcium.

Symptoms of Calcium deficiency:
·
Bone mass is reduced when calcium deposit is less.
·
Rickets in children, Osteomalacia in adults, Osteoporosis in old
age occurs.
·
Decreased rate of growth rate.
·
Very often fractures occur due to brittle bones.
4. Zinc
Zinc is an essential
trace element which plays an important role in many enzymes of our body. Our
body contains 2-3 grams of zinc. It has been found to be present in the hormone
insulin. It plays an essential role in the formation of DNA and RNA. It aids in
the healing of burns and wounds.
Functions:
·
It plays a vital role in growth and cell division especially
during pregnancy and prevents congenital abnormalities and premature delivery.
·
It plays an
important
role
in maintaining
fertility in males.
·
It provides immunity to our body.
·
It helps in healing cuts, wounds, acne and rashes.
·
It is important for healthy vision and prevents night blindness
and cataracts.
Food Sources of Zinc:
Seafoods, meat, eggs
are good sources of Zinc. Milk and milk products, whole cereals, pumpkin seeds,
cashewnuts, spinach, legumes contain considerable amounts.

Symptoms of Zinc deficiency:
·
Stunted growth.
·
Loss of appetite.
·
Dry and rough skin.
·
Dull brittle hair.
·
Brittle nails with white spots.
·
Loss of memory.
·
Reduced sense of taste and smell.
·
Delayed healing of wounds.
·
Frequent infections and acne.
· Diarrhoea and pneumonia can be fatal.
5. Sodium
Sodium is a plentiful
mineral in the body. It is essential in the recommended quantity for the body.
The average adult contains approximately 100g of sodium. Sodium is easily
absorbed in the small intestine. Sodium is lost in sweat during exercise or in
hot environments. Sodium and chloride compound is table salt.
Functions:
·
Sodium is the most abundant cation in the extracellular fluid of
the body.
·
Itactswithotherelectrolytes,especially potassium, in the
intracellular fluid to regulate the osmotic pressure and maintain proper water
balance within the body.
·
It is the major factor in maintaining the acid-base equilibrium,
in transmitting nerve impulses and in relaxing muscles.
·
It maintains normal mineral content of extra and intra cellular
fluid.
Food Sources of Sodium:
Vegetables like dry
lotus stems and green leafy vegetables, dried fruits, roots like beetroot,
carrot and radish are rich in sodium. Animal foods like milk, egg white, fish
and meat contain substantial amount of sodium.

Symptoms of Sodium deficiency:
·
Deficiency of sodium is caused by excessive sweating, prolonged
use of diuretics, chronic diarrhoea.
· Deficiency may lead to nausea, muscular weakness, heat exhaustion and mental apathy. Oversupply of sodium is a more common problem because of overuse of dietary sodium chloride or common salt.
·
Too much sodium may lead to water retention, high blood pressure
and even stomach ulcers.
Related Topics