Chapter: Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology: The Reproductive Systems
Vagina - Anatomy and Physiology
VAGINA
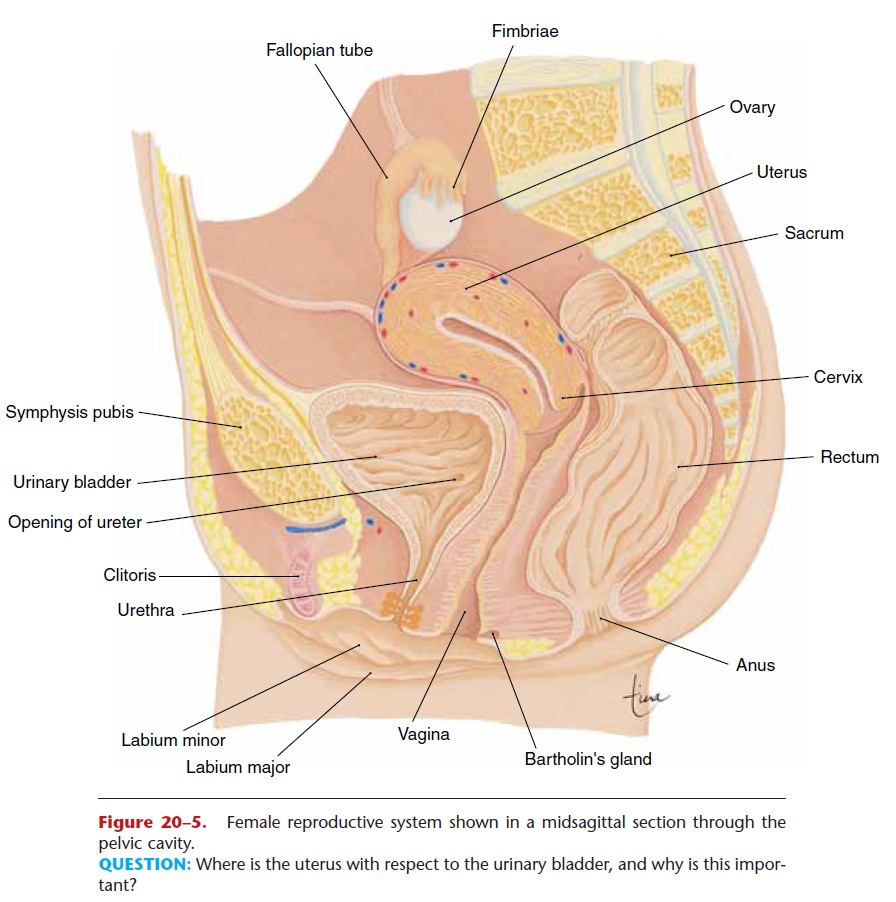
The vagina is a muscular tube about 4 inches (10 cm) long that extends from the cervix to the vaginal orifice in the perineum (pelvic floor). It is posterior to the urethra and anterior to the rectum (see Fig. 20–5). The vaginal opening is usually partially covered by a thin membrane called the hymen, which is ruptured by the first sexual intercourse or by the use of tampons during the menstrual period.
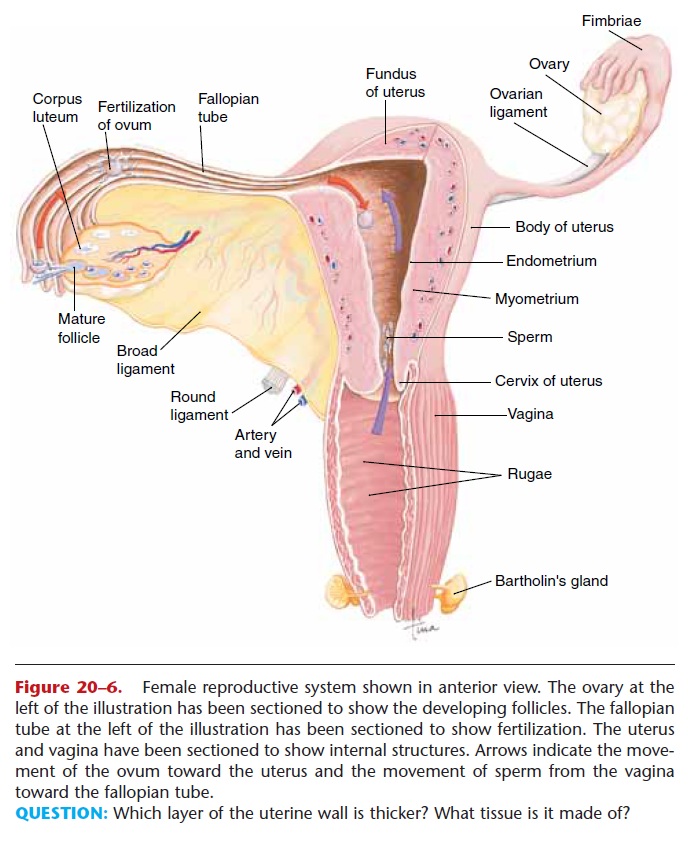
The functions of the vagina are to receive sperm from the penis during sexual intercourse, to provide the exit for menstrual blood flow, and to become the birth canal at the end of pregnancy.
The vaginal mucosa after puberty is stratified squamous epithelium, which is relatively resistant to pathogens. The normal flora (bacteria) of the vagina creates an acidic pH that helps inhibit the growth of pathogens.
Related Topics