Chapter: Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology: The Reproductive Systems
Fallopian Tubes
FALLOPIAN TUBES
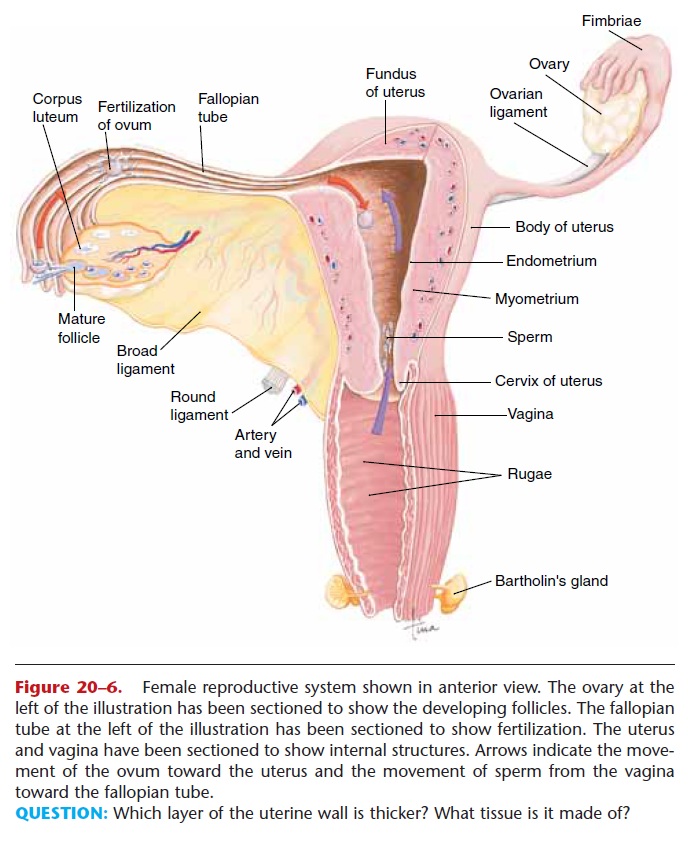
There are two fallopian tubes (also called uterine tubes or oviducts); each is about 4 inches (10 cm) long.
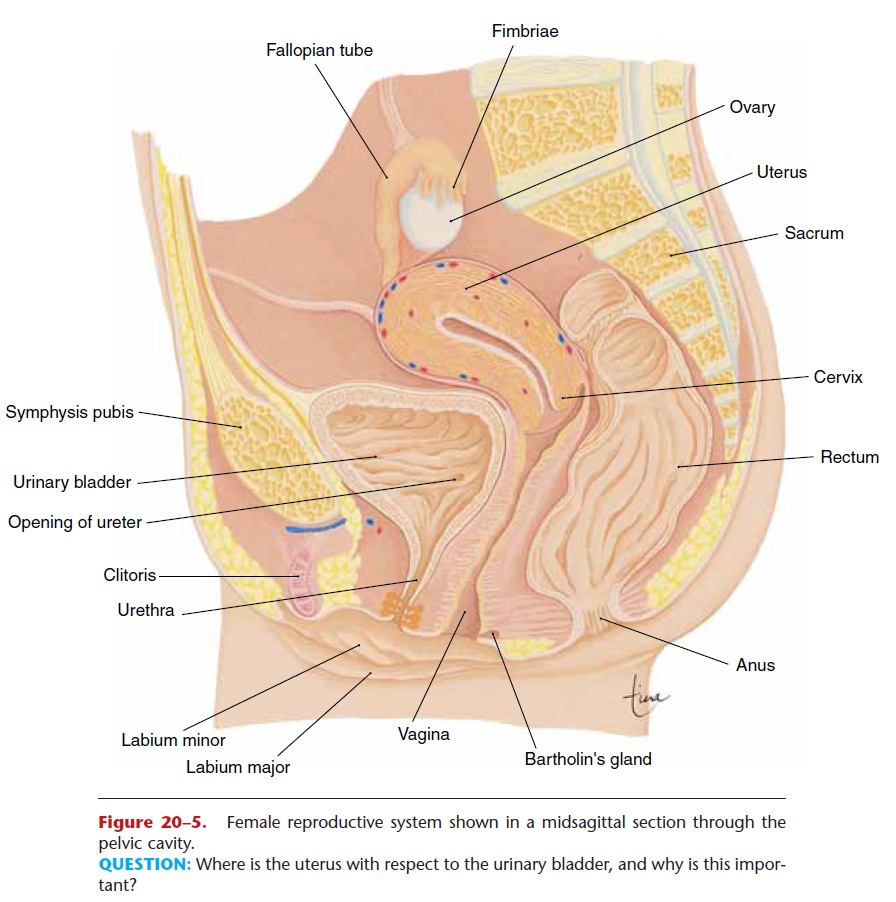
The lateral end of a fallopian tube encloses an ovary, and the medial end opens into the uterus. The end of the tube that encloses the ovary has fimbriae, fringe-like projections that create currents in the fluid sur-rounding the ovary to pull the ovum into the fallopian tube.
Because the ovum has no means of self-locomotion (as do sperm), the structure of the fallopian tube ensures that the ovum will be kept moving toward the uterus. The smooth muscle layer of the tube contracts in peristaltic waves that help propel the ovum (or zygote, as you will see in a moment). The lining (mucosa) is extensively folded and is made of ciliated epithelial tissue. The sweeping action of the cilia also moves the ovum toward the uterus.
Fertilization usually takes place in the fallopian tube. If not fertilized, an ovum dies within 24 to 48 hours and disintegrates, either in the tube or the uterus. If fertilized, the ovum becomes a zygote and is swept into the uterus; this takes about 4 to 5 days.
Sometimes the zygote will not reach the uterus but will still continue to develop. This is called an ectopic pregnancy; ectopic means “in an abnormal site.” The developing embryo may become implanted in the fal-lopian tube, the ovary itself, or even elsewhere in the abdominal cavity. An ectopic pregnancy usually does not progress very long, because these other sites are not specialized to provide a placenta or to expand to accommodate the growth of a fetus, as the uterus is. The spontaneous termination of an ectopic pregnancy is usually the result of bleeding in the mother, and sur-gery may be necessary to prevent maternal death from circulatory shock. Occasionally an ectopic pregnancy does go to full term and produces a healthy baby; such an event is a credit to the adaptability of the human body and to the advances of medical science.
Related Topics