Types - Immunology - Vaccines | 12th Zoology : Chapter 8 : Immunology
Chapter: 12th Zoology : Chapter 8 : Immunology
Vaccines
Vaccines
A vaccine is a biological preparation that
provides active acquired immunity to a particular disease and resembles a
Vaccines “teach” our body how to defend itself when viruses or bacteria, invade it. Vaccines deliver only very little amounts of inactivated or weakened viruses or bacteria, or parts of them. This allows the immune system to recognize the organism without actually experiencing the disease. Some vaccines need to be given more than once (i.e., a ‘booster’ vaccination) to make sure the immune system can overcome a real infection in the future Vaccine initiates the immunization process. The vaccines are classified as first, second and third generation vaccines.
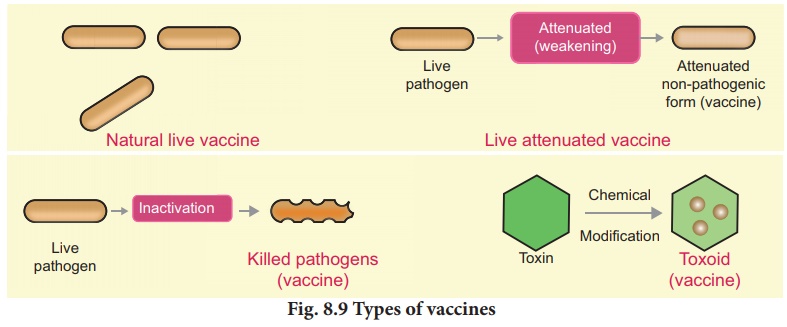
First generation vaccine is further subdivided
into live attenuated vaccine, killed vaccine and toxoids (Fig. 8.9). Live
attenuated vaccines use the weakened (attenuated), aged, less
virulent form of the virus. E.g. Measles, mumps and rubella (MMR)
vaccine and the Varicella (chickenpox) vaccine, Killed (inactivated) vaccines
are killed or inactivated by heat and other methods. E.g. Salk’s
polio vaccine. Toxoid vaccines contain a toxin or chemical secreted
by the bacteria or virus. They make us immune to the harmful effects of the
infection, instead of to the infection itself. E.g. DPT vaccine (Diphtheria,
Pertussis and Tetanus).
Second generation vaccine contains the pure
surface antigen of the pathogen. E.g.Hepatitis-B vaccine. Third generation
vaccine contains the purest and the highest potency vaccines
which are synthetic in generation. The latest revolution in vaccine is DNA
vaccine or recombinant vaccine (Refer Chapter- 10 for
details).
Related Topics