Components, Types of acquired immunity - Immunology - Acquired immunity | 12th Zoology : Chapter 8 : Immunology
Chapter: 12th Zoology : Chapter 8 : Immunology
Acquired immunity
Acquired immunity
The immunity that an individual acquires after birth is known as acquired immunity. It is the body's resistance to a specific pathogen.
The unique features of acquired immunity are antigenic specificity, diversity, recognition of self and non-self and immunological memory.
Components of acquired immunity
Acquired immunity has two components – cell mediated immunity (CMI) and antibody mediated immunity or humoral immunity.
1. Cell mediated immunity
When pathogens are destroyed by cells without producing antibodies, then it is known as cell mediated immune response or cell mediated immunity. This is brought about by T cells, macrophages and natural killer cells.
 2. Antibody mediated immunity or humoral immunity
2. Antibody mediated immunity or humoral immunity
When pathogens are destroyed by the production of antibodies, then it is known as antibody mediated or humoral immunity. This is brought about by B cells with the help of antigen presenting cells and T helper cells. Antibody production is the characteristic feature of vertebrates only.
Types of acquired immunity
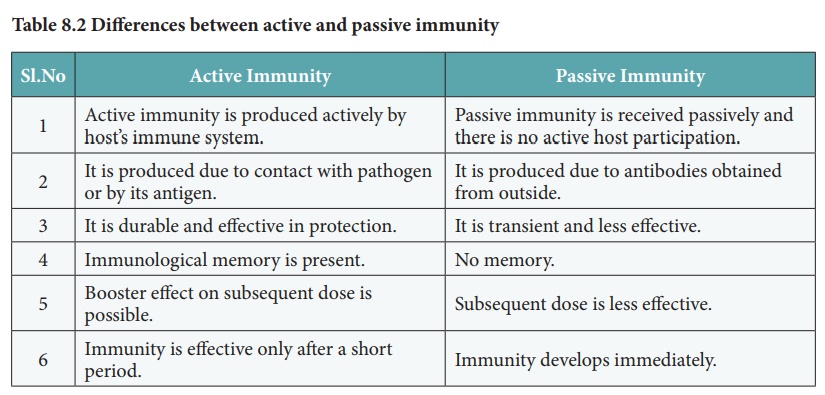
Acquired immunity may be active immunity or passive immunity (Table 8.2).
The immunological resistance developed by the organisms through the production of antibodies in their body is called active immunity. Active immunity is acquired through the use of a person’s immune responses, which lead to the development of memory cells. Active immunity results from an infection or an immunization.
Passive immunity does not require the body to produce antibodies to antigens. The antibodies are introduced from outside into the organism. Thus, passive immunity is acquired without the activation of a person’s immune response, and therefore there is no memory.
Active Immunity
1. Active immunity is produced actively by host’s immune system.
2. It is produced due to contact with pathogen or by its antigen.
3. It is durable and effective in protection.
4. Immunological memory is present.
5. Booster effect on subsequent dose is possible.
6. Immunity is effective only after a short period.
Passive Immunity
1. Passive immunity is received passively and there is no active host participation.
2. It is produced due to antibodies obtained from outside.
3. It is transient and less effective.
4. No memory.
5. Subsequent dose is less effective.
6. Immunity develops immediately.
Related Topics